Introduction
Introduction
This chapter demonstrates about the Ruby Branching which is one type of flow control in pure procedural language and following are the concepts covered in this chapter.
- Branching
- if-else statement
 Description
Description
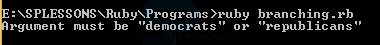
Ruby Branching is a one type of flow control procedural language which implements an array called democrats and the other is the republicans the code below demonstrates the branching.
[ruby]
democrats = ["Carter", "Clinton"]
republicans = ["Ford", "Reagan", "Bush1", "Bush2"]
party = ARGV[0]
if party == nil
print "Argument must be \"democrats\" or \"republicans\"\n"
elsif party == "democrats"
democrats.each { |i| print i, " "}
print "\n"
elsif party == "republicans"
republicans.each { |i| print i, " "}
print "\n"
else
print "All presidents since 1976 were either Democrats or Republicans\n"
end
[/ruby]
Result
By running the above code in command prompt, the output can be obtained as shown in the image below.
 Description
Description
Ruby Branching have some conditional structures which are similar to modern languages in which if expression is utilised for the conditional statement and values should be nil or false and true or everything. The code is executed if the conditional is true other wise else clause is executed. here is the Syntax of the if-else statement as shown below.
[ruby]
if conditional [then]
code...
[elsif conditional [then]
code...]...
[else
code...]
end
[/ruby]
The code below demonstrates the if-else statement as shown.
[ruby]
x=1
if x > 2
puts "x is greater than 2"
elsif x <= 2 and x!=0
puts "x is 1"
else
puts "I can't guess the number"
end
[/ruby]
Result
By running the above code in command prompt, the output can be obtained as shown in the image below.
Ruby Branching if statement executes the if statement when if conditional is true other wise executes the else, the code below demonstrates the execute the if statement as shown.
[ruby]
$debug=1
print "debug\n" if $debug
[/ruby]
Result
By running the above code in command prompt, the output can be obtained as shown in the image below.
Ruby case statement
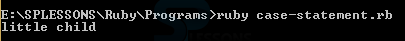
Ruby Branching case statement is used to compare the specified expression by using the === operator and which executes the snippet of the clause if it matches in specified expression when clause is evaluated as the left operand and when clause is not matched then else clause will executes the code below demonstrates the Ruby case statement as shown below.
[ruby]
$age = 5
case $age
when 0 .. 2
puts "baby"
when 3 .. 6
puts "little child"
when 7 .. 12
puts "child"
when 13 .. 18
puts "youth"
else
puts "adult"
end
[/ruby]
Result
By running the above code in command prompt, the output can be obtained as shown in the image below.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Branching is an one type flow control procedural language.
- if will be execute only if condition is true.
- conditional structure common to all modern languages.