Description
Description
Working directory is a very common and important concept if user have worked in any of the language environment. In the context of the data import and export the working directory is the default location for the file for which it can be read by the R. And it is also the default location of the file where it will be exported. Here user can import all type of files.
 Description
Description
CSV stands for
comma separated value files, are one of the most common file formats for storing data. So if user have opened a CSV file in a Notepad application, then user will find values are separated by comma. So user may have header information in the file, and then in each row values will be stored and are separated by comma.
Each row in the file represents one data instance, while each column represents a feature or attribute. User can also open the CSV file in a spreadsheet application such as Excel where values will be arranged in different cells of the spreadsheet. To import CSV files in R user can use the read.csv function. When user open the CSV file with notepad where data will be separated with comma as follows.
[c]
No,Chaptername
1,Introduction
2,Datatype
3,Variables
4,Arrays
5,Packages
[/c]
In the above scenario user has taken index file for the R programming, the following is the code to choose the csv file.
[c]
help("read.csv")
?read.csv
splessons<-read.table(file.choose(), header=T, sep=" , ")
[/c]
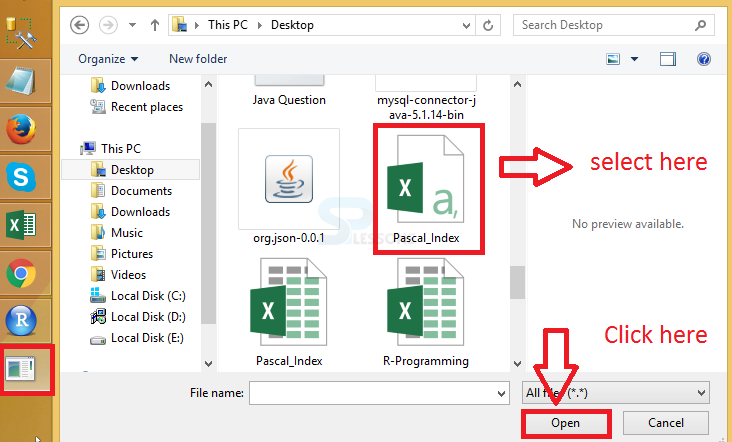
After writing the above code run the code the following file folder will be opened.
When user select the CSV file then automatically data will be displayed as follows.
[c]
No, Chaptername
1 1 Introduction
2 2 Datatype
3 3 Variables
4 4 Arrays
5 5 Packages
[/c]
 Description
Description
Excel files are also very popular, to store data. In R, there are several add on packages, to import Excel files in R. Here user need to install
XLConnect package.
The following is the code for the Excel to import.
[c]
setwd(file.path("E:"))
file<-file.path("R-Programming.xlsx")
install.packages("XLConnect")
library(XLConnect)
my.data<-readWorksheetFromFile(file,sheet=1,startRow=2)
str(my.data)
[/c]
This package will work on all major operating systems such as Windows, Mac and Linux provided you have a Java installed on machine. This package can be used to read both xls as well as xlsx file. So if this package is not installed on your machine, then user can install this package using install.packages function. And once the package is installed, user can first load the package using the library function. When the above code is run following is the result will be displayed.
[c]
'data.frame': 14 obs. of 4 variables:
$ R.Tutorial : chr "R Install Rstudio" "R Basic Example" "R Data Structures" "R Variables And Operators" ...
$ R.Tutorial.1: chr "R Install Rstudio" "R Basic Example" "R Data Structures" "R Variables And Operators" ...
$ R.Tutorial.2: chr "R-Install Rstudio" "R-Basic Example" "R - Data Structures" "R-Variables And Operators" ...
$ X1 : num 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ...
[/c]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The xlsx is the package needs to be installed while working with excel.
- The
install.packagesfunction is used to install package. - An user can import all the files such as table, text etc.