Description
Description
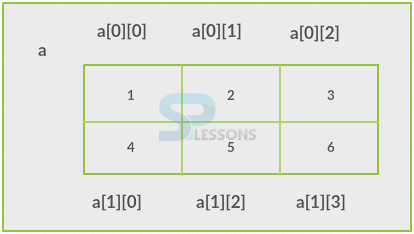
Array is nothing but collection of similar data types and it can be also known as static data structure why because the size of an array will be given at the time of its declaration. Array starts from zero. The following are the advantages of an arrays.
- Code Optimization: By using array one can reduce the length of the code then memory will be saved, one can perform input and output operations easily.
- Random access: Retrieving the data from any index position is easy.
 Example
Example
Arrays are another type of data structure supported in R. arrays are also homogeneous data structures just like vectors and matrixes. Means and array can only contain similar type of items. However, while vectors are one dimensional and matrixes are two dimensional, arrays on the other hand can be n-dimensional also. The following is an example that creates an array by using 3 x 3 matrices.
[c]# Create two vectors of different lengths.
vector1 <- c(5,9,3)
vector2 <- c(10,11,12,13,14,15)
# Take these vectors as input to the array.
result <- array(c(vector1,vector2),dim = c(3,3,2))
print(result)[/c]
In the above example, two vectors are created, vectors are also commonly known as
Atomic vectors. Atomic vectors are homogeneous data structures. Means in atomic vector, each element should be an object of same class only. So, a character vector, will have all elements of character type, while a numeric vector will have all elements of numeric type. An array() is the function to create the array type. Now compile the code then result will be as follows.
[c]
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 5 10 13
[2,] 9 11 14
[3,] 3 12 15
, , 2
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 5 10 13
[2,] 9 11 14
[3,] 3 12 15
[/c]
The big advantage of an array is that the size of an array is not increased at run time. The user can give names to the rows and columns as follows.
[c]# Create two vectors of different lengths.
vector1 <- c(5,9,3)
vector2 <- c(10,11,12,13,14,15)
column.names <- c("COL1","COL2","COL3")
row.names <- c("ROW1","ROW2","ROW3")
matrix.names <- c("Matrix1","Matrix2")
# Take these vectors as input to the array.
result <- array(c(vector1,vector2),dim = c(3,3,2),dimnames = list(row.names,column.names,
matrix.names))
print(result)[/c]
Matrixes are similar to data frames as matrix also have two dimensional arrangement, just like a spreadsheet. However, unlike data frames, matrixes are homogeneous data structures. Means, a matrix can contain items of similar type only. Typically, generally use matrixes to store and process numeric data. The result will be as follows.
[c]
, , Matrix1
COL1 COL2 COL3
ROW1 5 10 13
ROW2 9 11 14
ROW3 3 12 15
, , Matrix2
COL1 COL2 COL3
ROW1 5 10 13
ROW2 9 11 14
ROW3 3 12 15
[/c]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The
array()is the function to create an array type. - The limitation of array is, it is of homogeneous type and every element is referred through index only and elements are not stored in the structured format and array size is restricted.
- Array is stored in continuous memory location.But once the size is declared, it cannot be changed.