Description
Description
Array is nothing but collection of similar data types and it can be also known as static data structure why because the size of an array will be given at the time of its declaration. Array starts from zero. The following are the advantages of an array.
- Code Optimization:By using array one can reduce the length of the code then memory will be saved, one can perform input and output operations easily.
- Random access:Retrieving the data from any index position is easy.
 Description
Description
The following is the way of declaring an array.
[c]type
array-identifier = array[index-type] of element-type;
[/c]
In the above syntax,
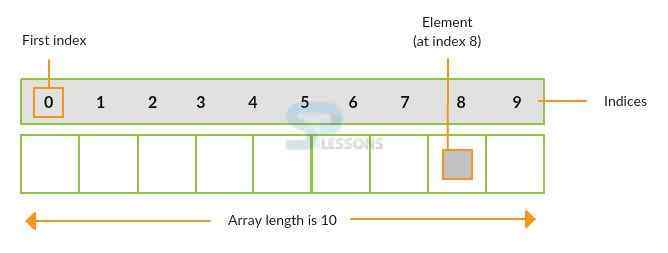
array-identifier is used to indicate array name, the index-type type may be anything except real, the element-type stores type of an array. The following is an image which describes array.
 Description
Description
The following are the types of arrays.
The following is an example for the one dimensional array.
[c]program exArrays;
var
n: array [1..5] of integer;
i, j: integer;
begin
(* initialize elements of array n to 0 *)
for i := 1 to 5 do
n[ i ] := i + 100; (* set element at location i to i + 100 *)
(* output each array element's value *)
for j:= 1 to 5 do
writeln('Element[', j, '] = ', n[j] );
end.
[/c]
In the above example,
- One dimensional array
- Multi dimensional array
- Dynamic array
- Packed array
n is an array of 10 integers, now compile the code result will be as follows.
[c]Element[1] = 101
Element[2] = 102
Element[3] = 103
Element[4] = 104
Element[5] = 105[/c]
The following is the syntax for the two dimensional array,
[c]type
array-identifier = array [index-type1, index-type2, ...] of element-type;
var
a1, a2, ... : array-identifier;[/c]
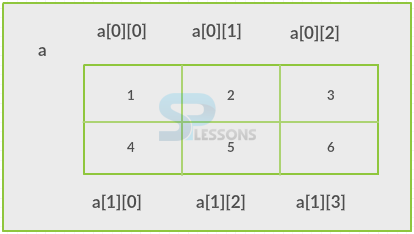
The following is an image to understand two dimensional array. For Eg: int a[2][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6};
The following is an example.
[c]var
a: array [0..3, 0..3] of integer;
i,j : integer;
begin
for i:=0 to 3 do
for j:=0 to 3 do
a[i,j]:= i * j;
for i:=0 to 3 do
begin
for j:=0 to 3 do
write(a[i,j]:2,' ');
writeln;
end;
end.[/c]
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[c]
0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3
0 2 4 6
0 3 6 9
[/c]
While working with dynamic array, the initial length is zero. The original length will be set with the function called SetLength. The following is the syntax to declare the dynamic array.
[c]type
darray = array of integer;
var
a: darray;[/c]
The following is an example.
[c]var
a: array of array of integer;
i, j : integer;
begin
setlength(a,5,5);
for i:=0 to 4 do
for j:=0 to 4 do
a[i,j]:= i * j;
for i:=0 to 4 do
begin
for j:= 0 to 4 do
write(a[i,j]:2,' ');
writeln;
end;
end.[/c]
Output: The following is the result.
[c]
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 4
0 2 4 6 8
0 3 6 9 12
0 4 8 12 16
[/c]
The pascal language permits the array information to store in packed mode, the packed array is the keyword to declare packed array. The following is the syntax for the packed array.
[c]type
pArray: packed array[index-type1, index-type2, ...] of element-type;
var
a: pArray;[/c]
The following is an example.
[c]var
a: packed array [0..3, 0..3] of integer;
i, j : integer;
begin
for i:=0 to 3 do
for j:=0 to 3 do
a[i,j]:= i * j;
for i:=0 to 3 do
begin
for j:=0 to 3 do
write(a[i,j]:2,' ');
writeln;
end;
end.[/c]
Output: Now the result will be as follows.
[c]
0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3
0 2 4 6
0 3 6 9 [/c]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The packed arrays are bit packed arrays.
- The
SetLengthis the function to set the original length of an array. - Two dimensional arrays consists of rows and columns in which values are given sequentially.