Description
Description
Observer Pattern is a Behavioral Pattern used when one to many relationship exists between the objects. If the object is changed then all its dependencies will be changed automatically. Observer pattern is present in java.util package and contains object called subject. Subject contains a set of all objects known as observers.
 Advantages
Advantages
- Data can be sent between many objects.
- Adding and removing of observers can be done.
- Subject will remain the same.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
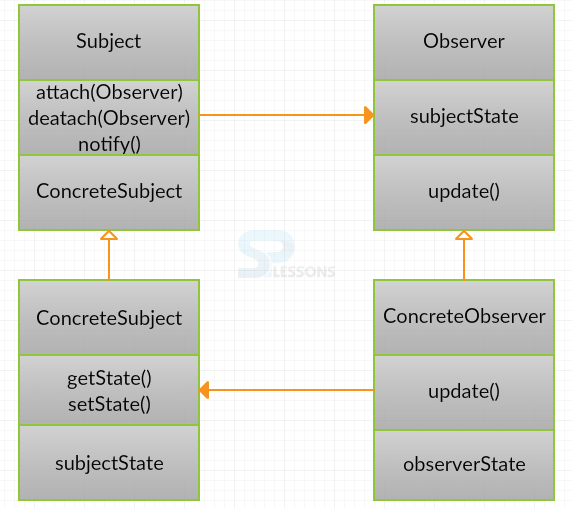
- Subject: Interface or conceptual class characterizes the operations for joining and de-connecting eyewitnesses to the customer. In the GOF book, this class/interface is known as Subject.
- ConcreteObserver: Concrete Observable class will keep up the condition of the item and when an adjustment in the state happens it advises the joined Observers.
- Observer: Interface or conceptual class characterizes the operations to be utilized to tell this item.
- ConcreteSubject : Concrete class is used for storing the solid observer executions.
 Examples
Examples
[java]
public interface WeatherSub
{
public void addObserver(WeatherObserver weatherObserver);
public void removeObserver(WeatherObserver weatherObserver);
public void doNotify();
}
public interface WeatherObserver
{
public void doUpdate(int temperature);
}
public class WStation implements WeatherSub// all interface methods are overrided
{
Set<WeatherObserver> weatherObservers;
int temperature;
public WStation(int temperature)
{
weatherObservers = new HashSet<WeatherObserver>();
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public void addObserver(WeatherObserver weatherObserver)//overrides the interface method
{
weatherObservers.add(weatherObserver);
}
public void removeObserver(WeatherObserver weatherObserver)//overrides the interface method
{
weatherObservers.remove(weatherObserver);
}
public void doNotify()//overrides the interface method
{
Iterator<WeatherObserver> it = weatherObservers.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
WeatherObserver weatherObserver = it.next();
weatherObserver.doUpdate(temperature);
}
}
public void setTemperature(int newTemperature)
{
System.out.println("\nWeather station setting temperature to " + newTemperature);
temperature = newTemperature;
doNotify();
}
}
public class WCustomer1 implements WeatherObserver //all interface methods must be overrided
{
public void doUpdate(int temperature)//overrides the interface method
{
System.out.println("Wcustomer 1 just found out the temperature is:" + temperature);
}
}
public class WeatherCustomer2 implements WeatherObserver// all the interface methods must be overrided
{
public void doUpdate(int temperature)//overrides the interface method
{
System.out.println("Wcustomer 2 just found out the temperature is:" + temperature);
}
}
public class Observer
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
WStation weatherStation = new WStation(33);//object is created and parameter is passed
WCustomer1 wc1 = new WCustomer1();
WCustomer2 wc2 = new WCustomer2();
weatherStation.addObserver(wc1);
weatherStation.addObserver(wc2);
weatherStation.setTemperature(32);
weatherStation.removeObserver(wc1);
weatherStation.setTemperature(40);
}
}
[/java]
Created an interface for Observer called WeatherObserver. WStation implements WeatherSub.
WeatherSub is a subject class and WCustomer1 is an observer that implements the WObserver.WCustomer2 implements the observer similar to WCustomer1. Observer class demonstrates the observer pattern.
 Output
Output
[java]
Weather station setting temperature to 32
Wcustomer 2 just found out the temperature is:32
Wcustomer 1 just found out the temperature is:32
Weather station setting temperature to 40
Wcustomer 2 just found out the temperature is:40
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Observer Pattern can be used with the mediator pattern.
- Observer Pattern is used in Java Message Service(JMS).
- Observer Pattern is used in MVC(Model View Control)frameworks.