Introduction
Introduction
In software development, performance is the key issue. To create more number of new instances for a class, Object Pool Pattern are used.
 Description
Description
Object Pool Pattern are used to store the thread pools in a web container of server and source pools are used to process the request data. Objects in the pool should undergo the life cycle process.
- Creation
- Validation
- Destruction
 Advantages
Advantages
- Using existing objects instead of creating new objects.
- Increases the performance and boosts the speed of an application.
- Object pool pattern is used when the rate of initializing a instance of the class is high.
- Different classes can use the same object.
- The connection management, sharing a resource, and reuse can be done easily.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
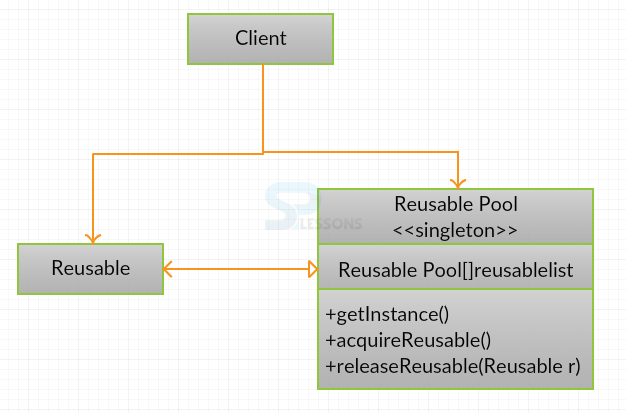
Reusable: Instances of class in this role will collaborate with other objects for a limited period, then they are no longer required to collaborate.
Client: Instances of class in this role will use Reusable objects.
ReusablePool: Instances of class in this role manage Reusable objects that are to be used by Client objects.
 Examples
Examples
[java]
public abstract class ObjectPoolDesign
{
private long expirationTime;
private Hashtable<T, Long> locked, unlocked;
public ObjectPool()
{
expirationTime = 3000;
locked = new Hashtable<T, Long>();
unlocked = new Hashtable<T, Long>();
}
protected abstract T create();
public abstract boolean validate(T o);
public abstract void expire(T o);
public synchronized T checkOut()
{
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
T t;
if (unlocked.size() > 0)
{
Enumeration<T> e = unlocked.keys();
while (e.hasMoreElements())
{
t = e.nextElement();
if ((now - unlocked.get(t)) > expirationTime)
{
unlocked.remove(t);
expire(t);
t = null;
} else
{
if (validate(t))
{
unlocked.remove(t);
locked.put(t, now);
return (t);
} else {
unlocked.remove(t);
expire(t);
t = null;
}
}
}
}
t = create();
locked.put(t, now);
return (t);
}
public synchronized void checkIn(T t)
{
locked.remove(t);
unlocked.put(t, System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
public class JDBCConnectionPool extends ObjectPool<Connection>
{
private String dsn, usr, pwd;
public JDBCConnectionPool(String driver, String dsn, String usr, String pwd)
{
super();
try//exception may occur
{
Class.forName(driver).newInstance();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.dsn = dsn;
this.usr = usr;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
protected Connection create()
{
try//exception may occur
{
return (DriverManager.getConnection(dsn, usr, pwd));
}
catch (SQLException e)//handles the exception
{
e.printStackTrace();
return (null);
}
}
public void expire(Connection o)
{
try
{
((Connection) o).close();
}
catch (SQLException e)//handles the exception
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public boolean validate(Connection o) // return type is boolean
{
try//exception may occur
{
return (!((Connection) o).isClosed());
}
catch (SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
return (false);
}
}
}[/java]
Created an objectpoolDesign class with private array of Objects inside.
Created acquare and release methods in the ObjectPoolDesign class.
Make sure that your ObjectPool is Singleton.
The JDBCConnectionPool will require the application to specify the database driver, DSN, username, and password upon instantiation (via the constructor).
 Key Points
Key Points
- Object Pool Pattern can be implemented as singleton.
- Clients can access the resources, and objects as new objects them