Description
Description
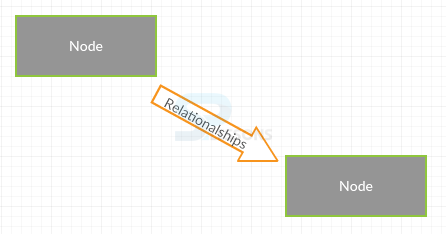
A Graph consists of nodes, which are connected by directional relationships. A node represents an entity. An entity is typically in a section of something in the real world, like a customer, order and person.
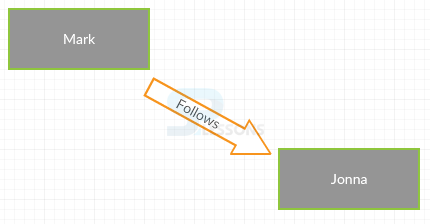
For example, imagine a graph that illustrates a social media users. Mark and jonna are the nodes in the graph illustrating the social media clients and the relational ships between the two as characterize below.
The compilation of nodes and relational s together is called a graph. And an also extend the graph with other types of nodes and relationships.Here jonna has a writes relationship to a tweet which results into which relationship that are nor reciprocated at this time, so graph is extendable with ease and graphs supports the way the system works.
 Description
Description
The below example illustrates the graph theory.
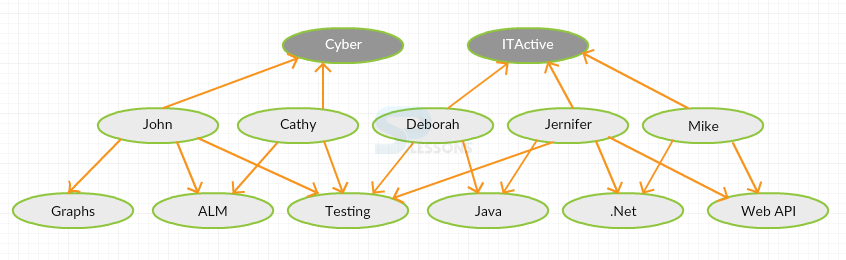
In social graph database there are 3-different kinds of entities. The top layer are companies. On the midde are people and there on the bottom layer are interests. The red relationships has a name
Work_For. The black ones have the names Skilled_At. The company that has these graphs is interesting in matching people with particular skills. An interesting query would would be one that follows a questions and that relationships contain properties that score in the Skill_AT.
The first layer consists of nodes representing rights. These are bundled in the second layer, which are the security groups. The relationships within the groups and the rights are called Contains. People are on the third layer and can be in one or more groups by the relationship Has_Groups. Which are also connected to individual right by the right grounded or are denied relationship.
Here is a product along an on the ground map which is atypical example of a graph. Stations are nodes with connections in between which are relationships. But relationships could contain a travel time. With a query it is possible to calculate the shortest route one station to other or determine a route based on other criteria.  Key Points
Key Points
- Basis of Graph Theory - Consists of nodes which are connected by directional relationships.