Description
Description
A graph database is a database that uses graph structure to represent and store data. And a graph database is very strong in storing and retrieving highly related data and even though there are many relationships within a data, a graph database will remain very prominent during data retrieval, even with millions of nodes.
The graph database product that encounter very flexible and cannot be used for a fixed schema or a node. That means one can add or delete and property of nodes without affecting already stored nodes. Because of that, a graph database responds well in an agile environment where course change of a product are very common. All graph databases support one or more query language to retrieve and store data. Graph database also implement the property great model. Earlier that a graph model contains nodes and relationships.
In a graph database, nodes and relationships can also contain some of the properties, such as:
- The node represent a name property with a certain value.
- Another node represent another property.
- The relationship contains a property with a start date.
- Both the nodes will be represented by a relationships.
- The relationship contains the property graph model that is named between two nodes.
 Description
Description
Due to the popularity of relational database for storing data in the traditional relational is all various. It doesn't depend on the types of the application that must fit into the relational database. The reality is that even though relational database is not a one-size-fits-all solution. For certain kind of applications, the relational database is great, but relational database are not very good with highly related data and that is where a graph database approaches. The bottom line is consider the type of database for every application while composing.
If the application works with highly related data, consider it as a graph database. Also graph database tends to have a schema less approach and the structure of the nodes in the relationships is not fixed and it is easy to add a property to newer nodes and leave the older properties. This gives the same flexibility with most of the document databases, but not with the relational databases and the human brain is more compatible with graphs then it is with a relational schema and it creates to analyse a data structure and also easier to write queries. These patterns are then matches by the database. These patterns are much like the patterns the brains uses to fetch the data or retrieve memories.
 Description
Description
The most important difference between a relational database and a graph database are:
| Graph Database | Relational Database |
|---|---|
| Graph database store data as node. | Relational database uses tables to store data |
| Graph database uses nodes with entities | Relational database uses schemas with nullables |
| Graph database uses relations as the first class | Relational database uses relations with foreign keys |
| Graph database relates to data fetching with a pattern | Relational database uses related data fetched with joins |
 Description
Description
The most important difference between a graph database and document database are:
| Graph Database | Document Database |
|---|---|
| Graph database stores data in nodes | Document database stores data in a document |
| Graph database doesn't contain any schema | Document database doesn't contain schema |
| Graph database perform relation has the first class citizens | Document database contains the relations with foreign keys or embedded |
| Graph database contain related data fetched with a patterns | Document database related to data fetched with joins or embedded |
 Description
Description
The below example illustrates the graph theory.
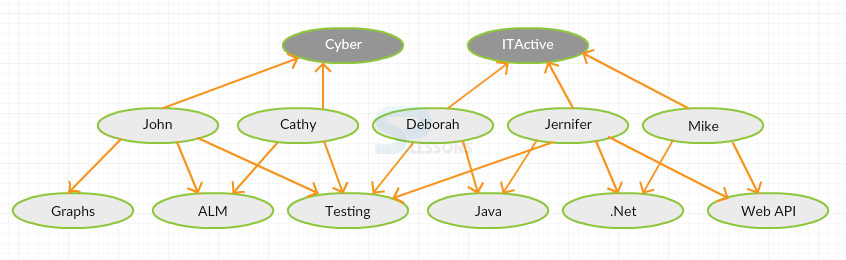
In social graph database there are 3-different kinds of entities. The top layer are companies. On the midde are people and there on the bottom layer are interests. The red relationships has a name
Work_For. The black ones have the names Skilled_At. The company that has these graphs is interesting in matching people with particular skills. An interesting query would would be one that follows a questions and that relationships contain properties that score in the Skill_AT.
The top layer consists of nodes representing rights. These are bundled in the second layer, which are the security groups. The relationships within the groups and the rights are called Contains. People are on the third layer and can be in one or more groups by the relationship Has_Groups. Which are also connected to individual right by the right grounded or are denied relationship.
Here is a product along an on the ground map which is atypical example of a graph. Stations are nodes with connections in between which are relationships. But relationships could contain a travel time. With a query it is possible to calculate the shortest route one station to other or determine a route based on other criteria.  Key Points
Key Points
- Graph Database - Uses graph structure to represent and store data.
- Use of graph database - Gives the same flexibility with most of the document database.