Introduction
Introduction
Strength of materials, also called Mechanics of Materials, is a subject which deals with the behavior of solid objects subject to stresses and strains. The study of the strength of materials primarily refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members, such as beams, columns, and shafts. The various properties of a material including yield strength, ultimate strength, Young's modulus, and Poisson's ratio; along with the mechanical element's macroscopic properties (geometric properties), such as its length, width, thickness, boundary constraints and abrupt changes in geometry such as holes are considered when methods are employed to predict the response of a structure under loading and its susceptibility to various failure modes.
 Quiz
Quiz
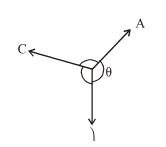
Q1. Which of the following expressions represents Lami's theorem, if A, B, C are three are in equilibrium and as shown in figure.
- A. [latex]\frac{A}{cos} = \frac{B}{cos} = \frac{C}{cos\theta}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{A}{{sin}^{2}} = \frac{B}{{sin}^{2}} = \frac{C}{{cos\theta}^{2}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{A}{{cos}^{2}} = \frac{B}{{cos}^{2}} = \frac{C}{{cos\theta}^{2}}[/latex]
D. None of the those
Answer: B
- A. Least
B. Maximum
C. Negative
D. Positive
Answer: A
- A. increases
B. decreases
C. remains constant
D. None of these
Answer: B
- A. Malleability
B. brittlen ess
C. Ductility
D. Elasticity
Answer: C
- A. Ductility
B. Malleability
C. Hardness
D. Resilience
Answer: B
- A. Hardness
B. Resilience
C. Plasticity
D. Toughness
Answer: D
- A. Hardness
B. Toughness
C. Elasticity
D. None of these
Answer: A
- A. [latex] {U}_{v} = \frac{1}{2} E {(Strain)}^{2}[/latex]
B. [latex] {U}_{v} = \frac{1}{2} E {(Strain)}[/latex]
C. [latex] {U}_{v} = \frac{1}{2} E {(Stress)}^{2}[/latex]
D. [latex] {U}_{v} = \frac{1}{2} E {(Strain)}^{2}[/latex]
Answer: A
- A. simply supported beam
B. continuous beam
C. cantilever beam
D. overhanging beam
Answer: C
- A. continuous beam
B. fixed beam
C. cantilever beam
D. None of these
Answer: B
Q11. A beam whose both ends are supported is known as
- A. simply supported beam
B. fixed beam
C. overhanging beam
D. continuous beam
Answer: A
- A. [latex]\frac{1}{P}_{E} = \frac {1}{P}_{R}+\frac {1}{P}_{C}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{1}{P}_{C} = \frac {1}{P}_{E}+\frac {1}{P}_{R}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{1}{P}_{R} = \frac {1}{P}_{E}+\frac {1}{P}_{C}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{1}{P}_{R} = \frac {1}{P}_{E}+\frac {1}{P}_{C}[/latex]
Answer: D
- A. sy = s1 + s2
B. sy = s1 – s2
C. 22y12s =s +s
D. 22y12s = s -s
Answer: B
- A. [latex]F_{x}=0[/latex]
B. [latex]F_{y}=0[/latex]
C. [latex]F_{x}=0[/latex],[latex]F_{y}=0[/latex], M=0
D. None of those
Answer: A
- A. Rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the impressed force and takes place in the direction of force acting
B. Rate of change of momentum is inversely proportional to impressed force and takes place in the direction to opposite of force acting
C. To every action there is always in equal and opposite reaction
D. None of these
Answer: A
- A. Plastic limit
B. yield point
C. elastic limit of proportionality
D. None of these
Answer: C
- A. [latex]\frac{{T}_{r}}{J} = \frac {G}{L} = \frac{{\sqrt{}}_{max}}{R}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{J}{{T}_{r}} = \frac {G}{J} = \frac{R}{{\sqrt{}}_{max}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{{T}_{r}}{L} = \frac {G}{J} = \frac{{\sqrt{}}_{max}}{R}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{{T}_{r}}{{\sqrt{}}_{max}} = \frac {G}{L} = \frac{J}{R}[/latex]
Answer: A
- A. Hardness
B. Resilience
C. Ductility
D. Toughness
Answer: D
- A. Longitudinal strain/Lateral starin
B. Laterral Strain/Longitudinal Strain
C. Stress/Strain
D. Strain/Stress
Answer: A
- A. Compression stress in a direction 45to the axis
B. Shear stress in a direction 45 to the axis
C. Tensile stress in a direction 45 to the axis
D. None of the these
Answer: C
Q21. The force whose line of action lie on the same plane and also must at a point is known as
- A. Co - planar non concurrent force
B. Co - planar concurrent force
C. Non - Coplanar concurrent force
D. Non - Coplanar Non concurrent forces
Answer: B
- A. 0.21-0.22
B. 0.23-0.27
C. 0.37-0.43
D. 0.57-0.63
Answer: B
- A. L/L
B. L.L
C. L/L
D. 2L/L
Answer: C
- A. Parbola
B. Ellipse
C. Circle
D. Hyperbola
Answer: A
- A. Rankins
B. Tresca
C. Mohr
D. ST. Venant
Answer: D
- A. Rankins
B. Tresca
C. Mohr
D. ST. Venant
Answer: B
- A. =>w > =>R
B. =>w R
C. =>w
D. =>R
Answer: A
- A. Creep
B. fayigue
C. Stiffiness
D. Endurance
Answer: B
- A. Whose lengh changes during deforamtion
B. whose lengh does not change during deforamtion
C. which lies at top most layer
D. None of those
Answer: B
- A. It has two support at ends only
B. is has less than two Supports
C. It has more than two supports
D. None of these
Answer: A
Q31. Stiffiness is measured in which of the following
- A. Modulus of elasticity
B. Toughness
C. Density
D. Ultimate Strengh
Answer: A
- A. Malleabillity
B. Creep
C. Hardness
D. Ductility
Answer: B
- A. Material of Specimen
B. Area of cross section
C. Magnitude of load
D. None of those
Answer: C
- A. [latex]I_{w}[/latex]=[latex]I_{u}[/latex]
B. [latex]I_{w}[/latex][latex]I_{u}[/latex]
C. W
D. None of those
Answer: B
- A. Cantilever beam
B. Simple supported beam
C. overhanging beam
D. None of Those
Answer: C
- A. 1/2 Original Value
B. 1/8 Original Value
C. 1/4 Original Value
D. 1/16 Original Value
Answer: C
- A. Instaneous Cross - Sectional area
B. Average Cross - Sectional area
C. Original Cross - Sectional area
D. Final cross - Sectional area
Answer: A
- A. N/[latex]mm^{2}[/latex]
B. N/[latex]m^{2}[/latex]
C. Kg/[latex]m^{2}[/latex]
D. None of those
Answer: B
- A. [latex]\frac{T}{c}[/latex]+1
B. [latex]\frac{T}{c}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{c}{T}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{T}{c}[/latex]=1
Answer: D
- A. No forces are acting of the body
B. All the internal forces acting on the body
C. All the internal and external forces acting on the body
D. None of these
Answer: C
Q41. During tensile testing for cast iron specimen, the stress-strain curve shows
- A. No yield point
B. upper yield point only
C. lower yield point only
D. Both upper and lower yield points
Answer: A
- A. Hardness
B. Ductility
C. Toughness
D. Brittleness
Answer: C
- A. Pa
B. KPa
C. GPa
D. None of these
Answer: D
- A. Energy
B. Mass
C. Angle
D. Force
Answer: D
- A. breaking stress to working stress
B. ultimate stress to working stress
C. elastic limit to working stress
D. breaking stress to ultimate stress
Answer: B
- A. Direction
B. Magnitude
C. Line of action
D. All of the above
Answer: D
- A. N-M
B. N/[latex]M^{2}[/latex]
C. N/[latex]M^{4}[/latex]
D. [latex]M^{2}[/latex]
Answer: A
- A. Force
B. Acceleration
C. Impulse
D. displacement
Answer: A
- A. less
B. more
C. equal
D. double
Answer: B
- A. kinetic friction
B. Limiting friction
C. Frictional force
D. coefficient of friction
Answer: C