Description
Description
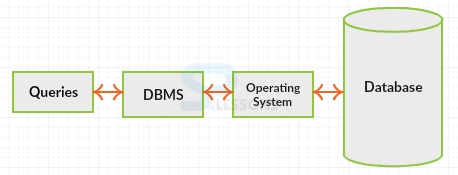
Databases are huge gathering of logical related information which can be created, accessed, managed, and updated. The data may be in any form like text and numbers.
Many types of data stores are present, such as files on the file system, where data reading and writing will be very slow. So in the present generation, Relational Database Administration framework is being utilized to store and oversee colossal measure of information. All relational database management systems like MySQL, MS Access, Oracle, Sybase, Postgre and SQL Server use SQL as standard database language.
 Description
Description
A typical utilize case for Lucene is playing out a full-content pursuit on at least one database tables. In spite of the fact that MySQL accompanies a full-content hunt usefulness, it rapidly separates for everything except the least complex sort of inquiries and when there is a requirement for field boosting, altering importance positioning. Following is the normal structure of the SQL database.
The full form of RDBMS is Relational DataBase Management System. The RDBMS is a database programming that can perform the accompanying operations.
A query is an inquiry into the database utilizing the SELECT articulation. A question is utilized to concentrate information from the database in a decipherable configuration as per the client's demand. For example, in the event that you have a worker table, you may issue a SQL proclamation that profits the representative who is paid the most.
A subquery is a nested query where the result of one query can be used in another query via relational operator or aggregation functions. And a subquery must be enclosed with in parentheses and contain only one column in the select clause if used in where clause.
An orderby clause is not allowed in a subquery. And this can be nested within other subqueries. Subquries are used in where, having, from and in select clauses. The syntax for MySQL SubQueries is as follows:
[java]Select <column_name1>,<column_name2> from <table_name> where <column_name2> <condition> (select <column_name2> from <table_name> where condition);[/java]
By viewing the below example, the concept of MySQL Subqueries can be easily understood.
[c]mysql> select * from employee21;
+--------+-------+-------+--------+-----------+
| emp_id | ename | sal | deptno | job |
+--------+-------+-------+--------+-----------+
| 1001 | mike | 12000 | 10 | manager |
| 1002 | rambo | 13000 | 20 | scalesman |
| 1003 | kate | 14000 | 10 | manager |
| 1003 | jeo | 14000 | 20 | manager |
| 1003 | finn | 14000 | 30 | manager |
+--------+-------+-------+--------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select emp_id,ename,sal from employee21 where sal >(select sal from employee21 where ename='rambo');
+--------+-------+-------+
| emp_id | ename | sal |
+--------+-------+-------+
| 1003 | kate | 14000 |
| 1003 | jeo | 14000 |
| 1003 | finn | 14000 |
+--------+-------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.08 sec)[/c]
Here in the above example, a query within another query is used, such as empid, ename and salary are selected from employee table and another select statement is performed on salary where ename is equal to rambo with some condition. So it executes employee salary greater than rambo salary.
The syntax for SQL Index is as follows.
- Enables one to create a database with tables, sections and lists.
- Assured the Referential Integrity among the rows of different tables in the current database.
- Consequently updates the indexes.
- Read an SQL query and joins data from different database tables.
CREATE [ UNIQUE ] [ CLUSTERED | NONCLUSTERED ] INDEX index_name
ON table_name ( column1 [ASC | DESC ], … column_n [ ASC | DESC ] )
[ INCLUDE ( column1, … column_n ) ]
[ WHERE condition ]
[ WITH ( PAD_INDEX = { ON | OFF }
| FILLFACTOR = fillfactor
| SORT_IN_TEMPDB = { ON | OFF }
| IGNORE_DUP_KEY = { ON | OFF }
| STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = { ON | OFF }
| STATISTICS_INCREMENTAL = { ON | OFF }
| DROP_EXISTING = { ON | OFF }
| ONLINE = { ON | OFF }
| ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = { ON | OFF }
| ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = { ON | OFF }
| MAXDOP = max_degree
| DATA_COMPRESSION = { NONE | PAGE | ROW }
[ ON PARTITIONS ( { number | range } ]
[ ON partition_scheme ( column )
| ON filegroup
| ON default_filegroup ]
[ FILESTREAM_ON { filegroup | partition_scheme };
Indicates that the combination of values in the indexed columns must be unique.
Demonstrates that the consistent request decides the physical request of the columns in the table.
Demonstrates that the sensible request does not decide the physical request of the columns in the table.
The name of the list to make.
The name of the table or view on which the list is to be made. column1, … column_n: The sections to base the file. ASC | DESC: The sort request for each of the segments. Incorporate ( column1, … column_n ) The segments that are not key segments to add to the leaf level of the nonclustered list.
The condition to determine which rows to include in the index.
Indicates that the index will be created on the specified filegroup.
Indicates the default filegroup.
 Description
Description
A typical utilize case for Lucene is playing out a full-content hunt on at least one database tables. Despite the fact that MySQL accompanies a full-content inquiry usefulness, it rapidly separates for everything except the least difficult sort of inquiries and when there is a requirement for field boosting, modifying importance positioning, and so forth.
[c]String sql = "select id, firstname, lastname, phone, email from person";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next()) {
Document doc = new Document();
doc.add(new Field("id", rs,getString("id"), Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.UN_TOKENIZED));
doc.add(new Field("firstname", rs,getString("firstname"), Field.Store.YES, Field.Index.TOKENIZED));
// ... repeat for each column in result set
writer.addDocument(doc);
}[/c]
With regards to showing indexed lists to the client, user have 2 decisions:
- Since the table has as of now been straightened into Lucene, simply utilize the Fields in the Document. Since Lucene is additionally quick, this takes stack off your database and is something worth being thankful for.
- On the off chance that client need to show extra information in your output page, just gather the "id"s from the Hits, then bring the information from the table and fabricate the page from the resultset.
 Key Points
Key Points
- SQL Index – Provide efficiently to retrieving the data and records from the database.
- SQL Drop Table will drop a column from the table and drop table will drop the entire table.
- SQL is authorized under GNU(General Public Licence). It is a multi-client, multi threaded database administrator framework.