Introduction
Introduction
This chapter explains about Less Guards and Less CSS Guards.
 Description
Description
The expressions can be matched using Guards. Following are the two types of Guards in Less.
- Mixin Guards
- CSS Guards
 Description
Description
Mixin Guards are the conditional statements of Less. Mixins can be used in conjunction with guards for constructing a conditional block.
The conditional execution has been opted in Less through guarded mixins instead of
if/else statements in the mode of @media query features.  Example
Example
Below snippet code demonstrates the main scheme.
[c]
.mixin (@a) when (lightness(@a) >= 50%) {
background-color: black;
}
.mixin (@a) when (lightness(@a) < 50%) {
background-color: white;
}
.mixin (@a) {
color: @a;
}
[/c]
Here, the keyword
when introduces a guard sequence and runs the below code.
[c]
.class1 { .mixin(#fff) }
.class2 { .mixin(#444) }
[/c]
By compiling the above code, it automatically generates the following code.
[c].class1 {
background-color: black;
color: #fff;
}
.class2 {
background-color: white;
color: #444;
}
[/c]
 Types
Types
The following are the different types of Less mixin guards.
 Description
Description
The comparison operators used in guards are.
>>===<<
true is used additionally as such any value other than the keyword true is false.
[c].truth (@a) when (@a) {…..}
.truth (@a) when (@a = true) {…..}
[/c]
[c].class{
.truth(60); // will not match any of the above definitions.
}
[/c]
 Description
Description
The logical operators can be used in guards, and syntax is based on CSS media queries.
The keyword
and is used to combine the guards.
[c].mixin (@a) when (isnumber (@a)) and (@a > 0) {…..}[/c]
The operator or is used to emulate and are separated by comma (,).
[c].mixin (@a) when (@a > 30), (@a < -30) {......}[/c]
The keyword not is used to negate conditions.
[c].mixin (@b) when not (@b >0) {……}[/c]
 Description
Description
is function is used to match mixins based on value type.
[c].mixin (@a; @b: 0) when (isnumber (@b)) {…..}
.mixin (@a; @b: white) when (iscolor(@b)) {…..}[/c]
Following are the type checking functions.iscolorisnumberisstringiskeywordisurl
ispixelispercentageisemisunit
 Description
Description
A mixin match depends on other mixing matches. By using the
default function, one can create a conditional mixins, that are similar to else or default statements.
[c].mixin (@a) when (@a >0) {…..}
.mixin (@a) when (default()) {…..} // matches only if first mixin does not, i.e. when @a <=0[/c]
 Example
Example
Below example explains the use of Less Mixin guards.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
 Step 1
Step 1
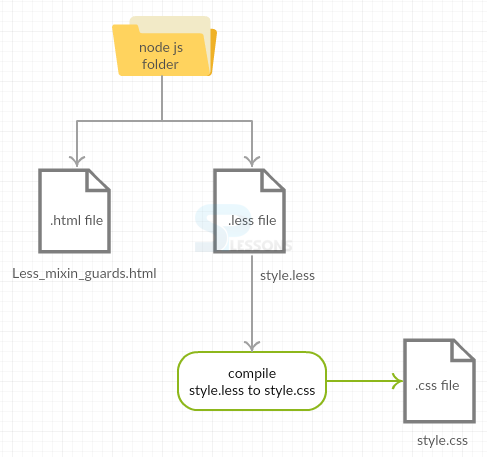
Create a simple HTML file in the Nodejs folder as shown below.
Less_mixins_guards.html
[c]<html>
<head>
<title>Mixin Guards</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
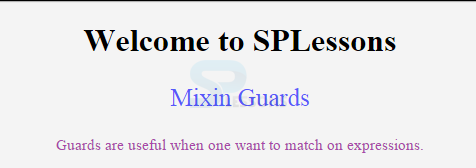
<h1>Welcome to SPLessons</h1>
<p class="class1">Mixin Guards</p>
<p class="class2">Guards are useful when one want to match on expressions.</p>
</body>
</html>
[/c]
 Step 2
Step 2
Create LESS file in the same Nodejs folder as shown below.
style.less
[c].mixin (@a) when (lightness(@a) >= 50%) {
font-size: 25px;
}
.mixin (@a) when (lightness(@a) < 50%) {
font-size: 15px;
}
.mixin (@a) {
color: @a;
}
.class1 {
.mixin(#5858FA)
}
.class2 {
.mixin(#A4A)
}
body {
text-align: center;
background: rgb(244, 244, 244);
font-family: 'Lato';
}
[/c]
 Step 3
Step 3
Compile the above less file in command prompt using the following command.
[c]lessc style.less style.css[/c]
 Step 4
Step 4
By compiling the above less file, it automatically generates the following CSS code.
style.css
[c].class1 {
font-size: 25px;
color: #5858fa;
}
.class2 {
font-size: 15px;
color: #aa44aa;
}
body {
text-align: center;
background: #f4f4f4;
font-family: 'Lato';
}
[/c]
 Result
Result
 Description
Description
The simple values or number of arguments are matched using Guards. The guards are applied to css selectors for declaring the mixins and for calling it immediately.
The below snippet code demonstrates the main scheme of using CSS Guards.
[c]
.my-optional-style() when (@my-option = true) {
button {
color: black;
}
}
.my-optional-style();[/c]
Now, directly apply guard to a style.
[c]button when (@my-option = true) {
color: black;
}[/c]
Use
if type statement along with & operator to group multiple guards as shown below.
[c]& when (@my-option = true) {
button {
color: black;
}
a {
color: red;
}
}
[/c]
 Example
Example
Below example explains the use of CSS Guards in Less.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
 Step 1
Step 1
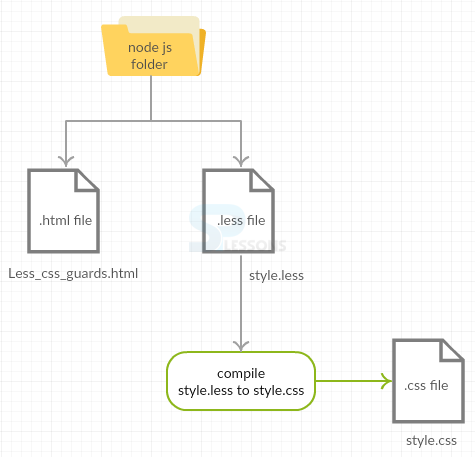
Create a simple HTML file in the Nodejs folder as shown below.
Less_css_guards.html
[c]<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="cont">
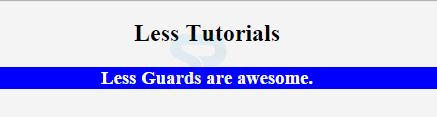
<h2>Less Tutorials</h2>
</div>
<div class="style">
<h3>Less Guards are awesome.</h3>
</div>
</body>
</html>
[/c]
 Step 2
Step 2
Create a LESS file in the same Nodejs folder as shown below.
style.less
[c]@usedScope: global;
.mixin() {
@usedScope: mixin;
.cont when (@usedScope=global) {
background-color: red;
color: black;
}
.style when (@usedScope=mixin) {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
}
@usedScope: mixin;
}
.mixin();
body {
text-align: center;
background: rgb(244, 244, 244);
font-family: 'Lato';
}
[/c]
 Step 3
Step 3
Compile the above less file in command prompt using the command
[c]lessc style.less style.css[/c]
 Step 4
Step 4
By compiling the above code it automatically generates the following CSS code.
style.css
[c].style {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
}
body {
text-align: center;
background: #f4f4f4;
font-family: 'Lato';
}
[/c]
 Result
Result
 Key Points
Key Points
- Less guards are mandatory for constructing a conditional block in less.
- Less guards can be declared and called immediately with the help of CSS guards in less.
 Programming
Tips
Programming
Tips
- Make sure that both the HTML and LESS files are created in the same node js folder.
- Check all the required changes in the coding before running the application.