Description
Description
SPlesson tutorial is going to show that how JSON works with one of the open source language JAVA. Before going to learn this chapter first learn the java basics, JSON will have library called json.simple that needs to be added to the project. As earlier discussed JSON will have bundle of classes such as
JSONValue, JSONObject, JSONArray, JSONString, JSONNumber. Following is an environment set up for JAVA. The following are some API's of Java JSON.
- JSON.org
- GSON
- Jackson
- Boon
 Introduction
Introduction
JAVA which is a combination of JDK and JRE.
 Step-1
Step-1
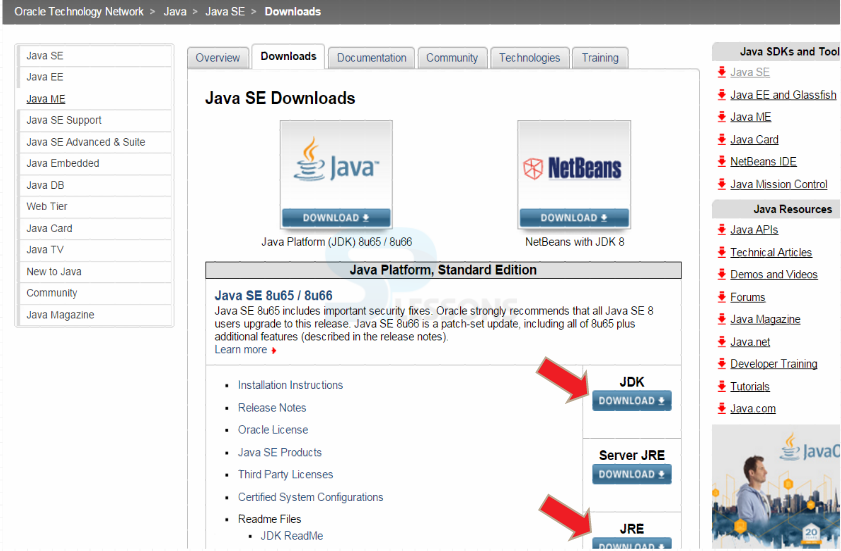
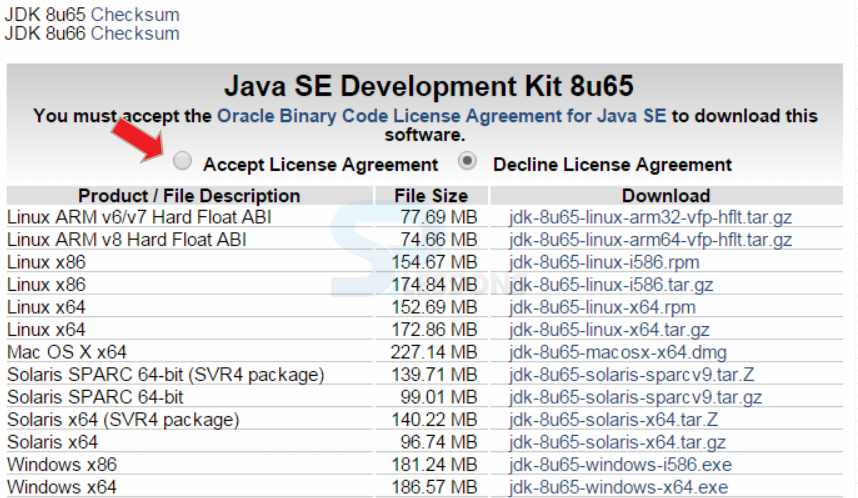
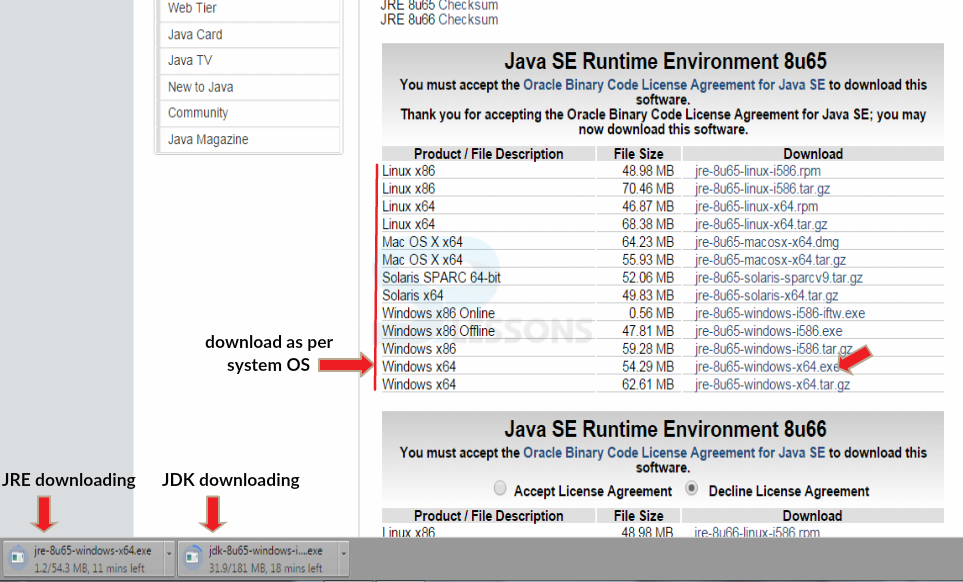
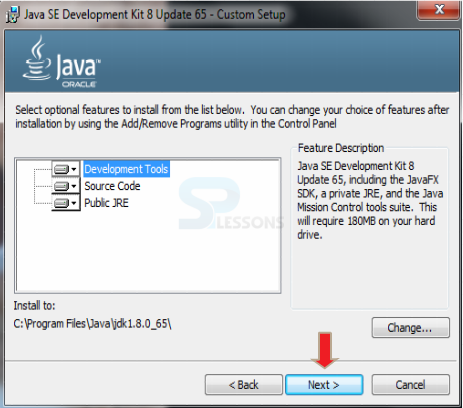
Initially, download JAVA by clicking the url -> JAVA URL
 Step-4
Step-4
 Step-5
Step-5
 Step-6
Step-6
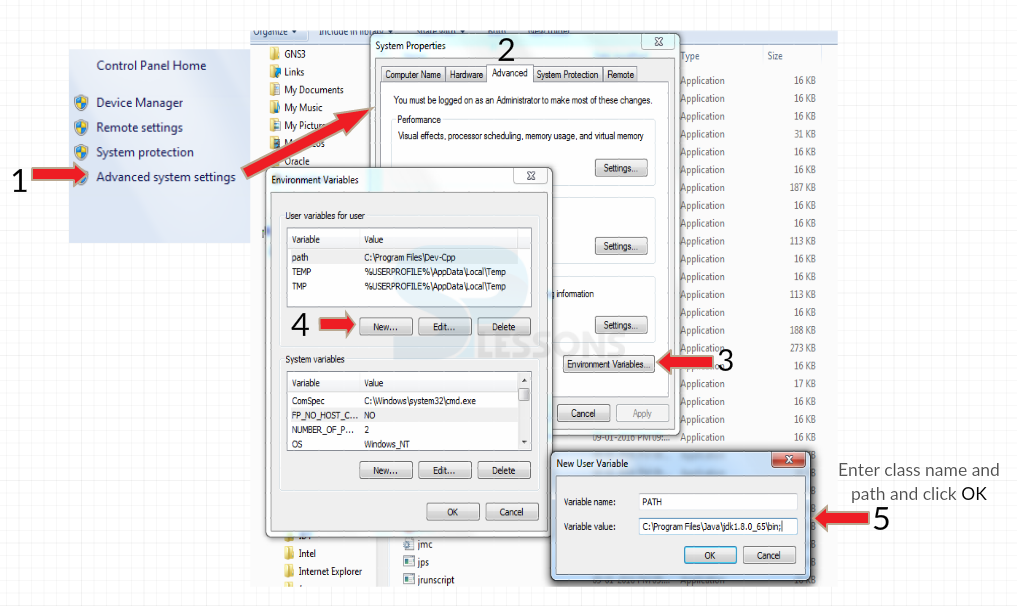
Java is now installed and one need to set the classpath.To set the path,go to
My Computer->Advanced system settings->Environment Variables->New
Follow the below figure which shows step-by-step procedure.
Name the variable as "PATH"
Variable value as "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_65\bin" (destination folder of java)
 Step-7
Step-7
To develop any Java program, any of the text editor is needed.Any text editor like Notepad,Eclipse,NetBeans etc can be used.Eclipse IDE can be downloaded from Eclipse Link
 Introduction
Introduction
This chapter Eclipse Installation for Java Development demonstrates in detail about downloading and installing Eclipse for Java. There are many ways and steps to get Eclipse up and running and would be better if there was a single comprehensive installer. Following are the concepts covered.
- Downloading Eclipse
- Installing Eclipse
- Workspace - Launching Eclipse
 Description
Description
Before downloading the Eclipse, pick up the target platform Linux/Mac/ Windows and make sure that the machine has a Java run time environment already installed, use either a 32-bit or a 64-bit versions of Eclipse and must have a JRE/JDK source that matches i.e.
Select the Preferred Eclipse version.
- 32 bit JRE needs the 32 bit version of Eclipse
- 64 bit JRE needs the 64 bit version of Eclipse
- Java
- C++
- Others
- Make your own
- For Java, Download JDK for the selected platform
 Description
Description
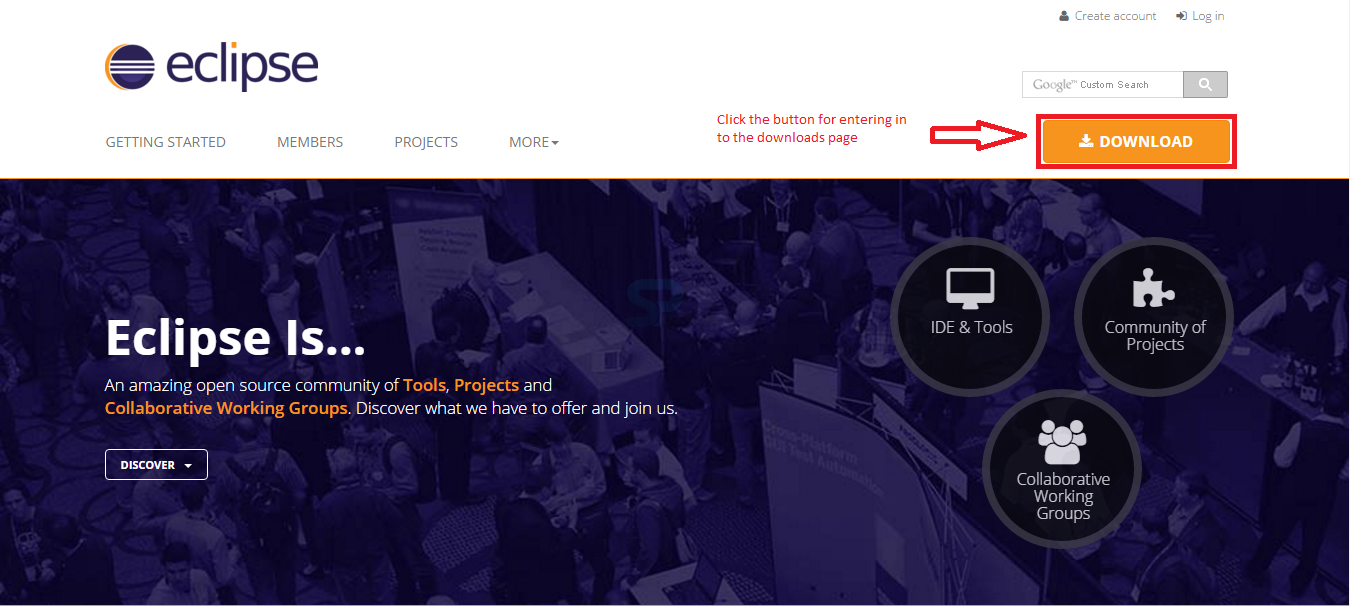
In order to use the Eclipse for Java Development download the Eclipse from the official website link given below.
http://www.eclipse.org/
By clicking the link, a page appears with a download link for Eclipse as below, now click the Download button on the page in order to download the Eclipse for Java development.
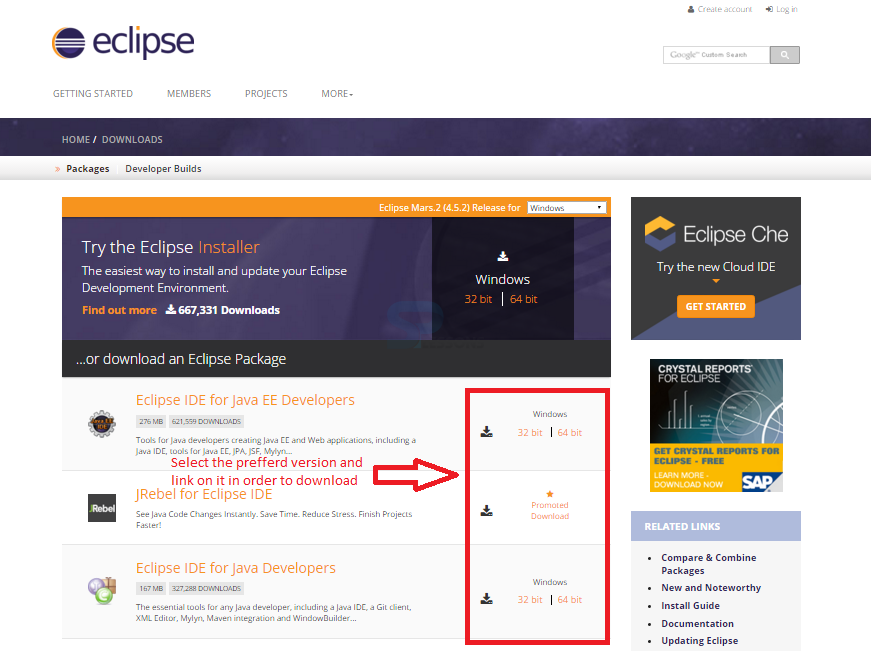
A page appears providing a list of Eclipse versions by clicking the download link button, select the preferred version and download the Eclipse by clicking on it as shown in the image below.
It shows drop down box in the right corner of the download page to set the operating system on which eclipse is to be installed.choose from the drop down box Windows, Linux, and Mac. Eclipse is packaged as a zip file, so extract the zip file into preferred drive.
 Description
Description
If the directory has a fairly long path when the user unzip the downloaded files under Windows can get errors about path names being too long. In order to avoid such errors make sure that the default download directory is fairly deep on the hard drive that and first move this up fairly high on the hard drive before unzipping, and thereafter no errors about path names being exceeded.
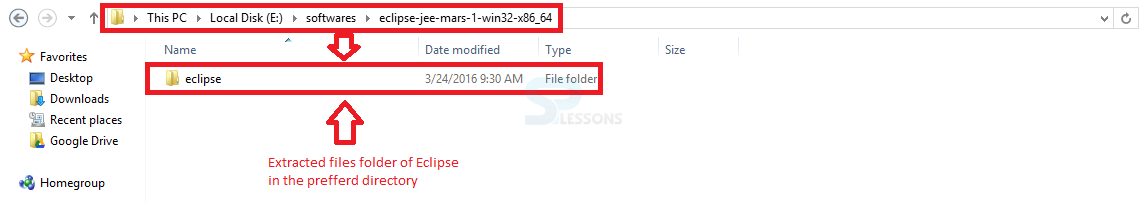
In order to install Eclipse, required a tool which can extract the contents of a zip file. The tools like PeaZip, IZArc, 7-zip etc. Now, Right click on the downloaded Zip file and extract all the files to the preferred directory to be installed by clicking Extract. The image below display the Eclipse files folder extracted to the particular directory given.
 Description
Description
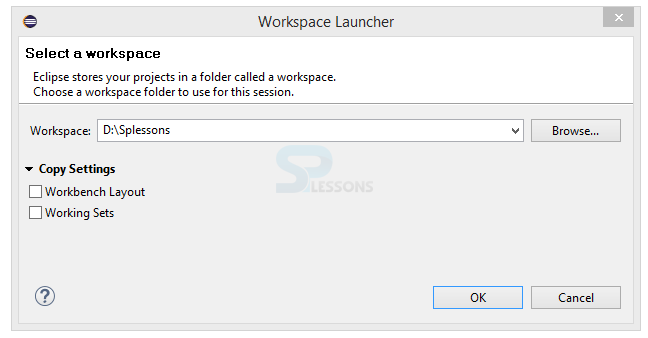
Immediately after lunching Eclipse, a window appears asking the drive to store the Workspace. A workspace is a collection of projects that are to be work with when launching Eclipse. A project can take any number of forms from a desktop executable, a library, a set of web pages, and more. If the client used to working with a product like Visual Studio, a workspace can be a little bit of an adjustment. Not all projects in a workspace have to be related and can take any approach that are like to creating a workspace.
The user can create a single workspace and create every programming project under that workspace. Eclipse is actually geared towards this approach. It has some additional tools like working sets, but working sets allow for convenient grouping to make it easy to work with a subset of the projects and can also create any number of workspaces. The workspace can be set to default or changed to new folder location using the Workspaces Preference window as shown in the image below.
 Example
Example
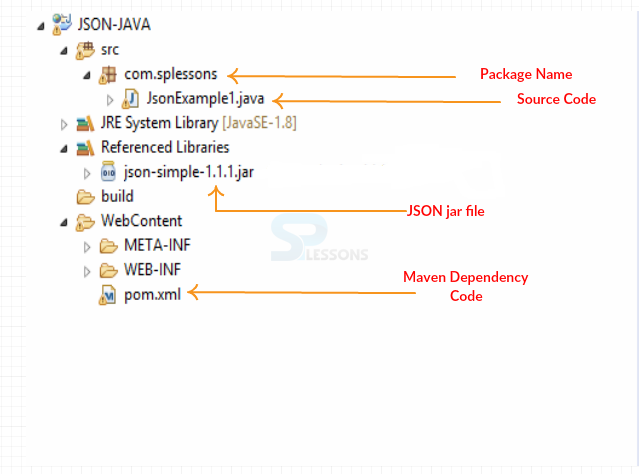
Following is the code structure for JAVA with JSON.
JsonExample1.java
[java]
package com.splessons;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
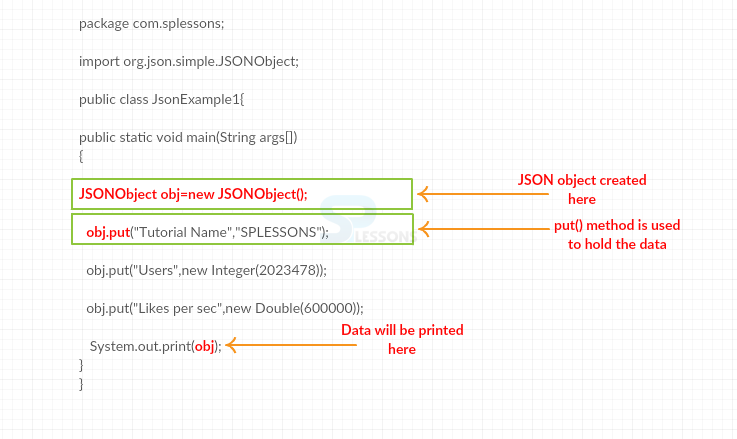
public class JsonExample1{
public static void main(String args[]){
JSONObject obj=new JSONObject();
obj.put("Tutorial Name","SPLESSONS");
obj.put("Users",new Integer(2023478));
obj.put("Likes per sec",new Double(600000));
System.out.print(obj);
}
}
[/java]
In the above code, object has been created that is obj, where put() method is used to hold the data. Following is an image for the code description.
pom.xml
Following is the code to add maven dependency to the project.
[xml]
<dependency>
<groupId>com.googlecode.json-simple</groupId>
<artifactId>json-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
</dependency>
[/xml]
Where POM stands for Project Object Model, POM is a XML representation of a Maven extend held in a document named
pom.xml.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
{"Tutorial Name":"SPLESSONS","Likes per sec":600000.0,"Users":2023478}
[/java]
 Example
Example
Following is an example for JSON Encode using Map.
JsonExample2.java
[java]
package com.splessons;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.json.simple.JSONValue;
public class JsonExample2{
public static void main(String args[]){
Map obj=new HashMap();
obj.put("Tutorial Name","SPLESSONS");
obj.put("Users",new Integer(2023478));
obj.put("Likes per sec",new Double(600000));
String jsonText = JSONValue.toJSONString(obj);
System.out.print(jsonText);
}
}
[/java]
The JSONObject class doesn't have a
toJSONString() strategy. Rather it supersedes the toString() technique to produce json. To get the json object, just utilize obj.toString().
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]{"Tutorial Name":"SPLESSONS","Likes per sec":600000.0,"Users":2023478}[/java]
 Example
Example
Following is an example for Java JSON Array Encode.
JsonExample3.java
[java]
package com.splessons;
import org.json.simple.JSONArray;
public class JsonExample3{
public static void main(String args[]){
JSONArray arr = new JSONArray();
arr.add("SPLESSON");
arr.add(new Integer(2733));
arr.add(new Double(3600000));
System.out.print(arr);
}}
[/java]
To understand the above code user need to have an ArrayList concept in JAVA, where added three objects and package is also added that is
import org.json.simple.JSONArray;.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
["SPLESSON",2733,3600000.0]
[/java]
 Example
Example
Following is an example for Java JSON Decode.
JsonExample4.java
[java]
package com.splessons;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import org.json.simple.JSONValue;
public class JsonExample4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="{\"Tutorial Name\":\"SPLESSONS\",\"Users\":2023478.0,\"Likes per sec\":600000}";
Object obj=JSONValue.parse(s);
JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) obj;
String name = (String) jsonObject.get("Tutorial Name");
double salary = (Double) jsonObject.get("Users");
long age = (Long) jsonObject.get("Likes per sec");
System.out.println(name+" "+salary+" "+age);
}
}
[/java]
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
SPLESSONS 2023478.0 600000
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The
POMstands forProject Object Model. - The HashMap is used to maintain key and value and it will be represented as.