Description
Description
The functionality of
java.util.Scanner class is used to read the data from the keyboard, The Scanner class will break the input as tokens by utilizing a delimiter. It gives numerous techniques to peruse and parse different values of primitive. Following is the syntax declaration for java.util.Scanner class.
[java]
public final class Scanner
extends Object
implements Iterator<String>
[/java]
An iterator replaces Enumeration in the Java Collections Framework. Iterators permit the guest to expel components.
 Methods
Methods
Following are the common using methods of java.util Scanner Class.
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| java.util.Scanner.next() | To give back the following token from the scanner. |
| java.util.Scanner.nextLine() | To move the scanner position to the following line and returns the esteem as a string. |
| java.util.Scanner.nextByte() | To scan the following token as a byte. |
| java.util.Scanner.nextInt() | To scan the following token as an int. |
| java.util.Scanner.nextLong() | To scan the following token as a long. |
 Description
Description
The functionality of the
java.util.Scanner.nextInt() method is to scan the following token as an int. The following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public int nextInt()[/java]
DemoScanner.java
[java]
import java.util.Scanner;
class ReverseNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int temp=0;
System.out.println("Enter the number to be reverse");
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=s.nextInt();
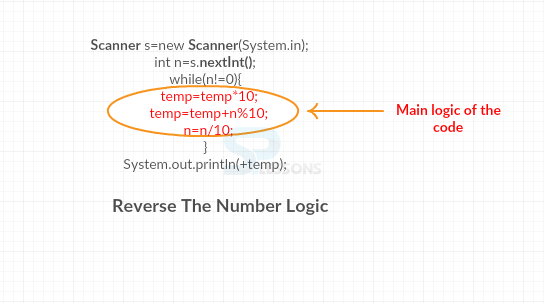
while(n!=0){
temp=temp*10;
temp=temp+n%10;
n=n/10;
}
System.out.println(+temp);
}
}
[/java]
Following is the interactive diagram for the above reverse the number code.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Enter the number to be reverse
45264
46254
[/java]
 Description
Description
The functionality of the
java.util.Scanner.next() method is to give back the following token from the scanner. The following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public String next()[/java]
DemoScanner.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoScanner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "SPLessons Stop Thinking Start Coding...!";
// create a new scanner with the specified String Object
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(s);
// find the next token and print it
System.out.println("" + scanner.next());
// find the next token and print it
System.out.println("" + scanner.next());
System.out.println("" + scanner.next());
System.out.println("" + scanner.next());
System.out.println("" + scanner.next());
// close the scanner
scanner.close();
}
}
[/java]
In the above example, A total token is gone before and took after by input that matches the delimiter design.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
SPLessons
Stop
Thinking
Start
Coding...!
[/java]
 Description
Description
The functionality of the
java.util.Scanner.nextLine() method is to move the scanner position to the following line and returns the esteem as a string. The following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public String nextLine()[/java]
DemoScanner.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoScanner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "Welcome to SPlessons...! \n Start Coding ";
// create a new scanner with the specified String Object
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(s);
// print the next line
System.out.println(scanner.nextLine());
// print the next line again
System.out.println(scanner.nextLine());
// close the scanner
scanner.close();
}
}
[/java]
The java.util.Scanner.nextLine() technique gives back whatever remains of the present line, barring any line separator toward the end.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Welcome to SPlessons...!
Start Coding
[/java]
 Description
Description
The functionality of the
java.util.Scanner.nextByte() method is to scan the following token as a byte. The following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public byte nextByte()[/java]
DemoScanner.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoScanner {
public static void main(String[] args){
// Declare File object
// initialize the scanner
Scanner scan = new Scanner("12 13 -21 -7 1A");
// tokenize the string on the constructor input
while(scan.hasNext()){
// get the byte tokens
System.out.println(scan.nextByte(16));
}
scan.close();
}
}
[/java]
The hasNext() strategy is used to return true if this scanner has other token in its input.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
18
19
-33
-7
26
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Java.util Scanner - The
java.util.Scanner.close()method is used to close the scanner. - Java.util Scanner - The
java.util.Scanner.locale()method is used to indicate the locale of the scanner. - Java.util Scanner - The
java.util.Scanner.radix()method is used to return the default radix of the scanner.