Description
Description
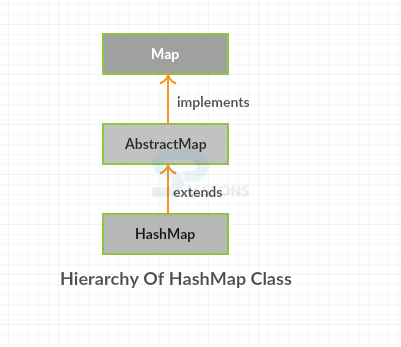
The HashMap class uses a hashtable to complete the Map interface. This allows the execution time of key operations, for instance, get( ) and put( ). A HashMap contains values in perspective of the key and amplifies AbstractMap class, includes exceptional components. Following is the syntax declaration for java.util HashMap Class.
[java]
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
[/java]
The Cloneable interface portrays no people. It is used to demonstrate that a class allows a bitwise copy of an example to be made. The Serializable interface is used to check java classes so that examples of the classes will get limit.
 Conceptual
Figure
Conceptual
Figure
 Constructors
Constructors
Following are the constructors of
java.util HashMap Class.
| Constructors | Description |
|---|---|
| HashMap( ) | To construct default HashMap. |
| HashMap(int capacity) | To initialize the capacity of the hash map to the given integer. |
| HashMap(Map m) | To initialize the hash map by utilizing the elements of object m. |
 Methods
Methods
Following are the basic and regular using methods of
java.util HashMap Class.
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| Collection values() | To return the collection view of the values |
| Set keySet() | To Return a set view of the keys. |
| void clear() | To vanish the all mappings. |
| Object clone() | To return a copy of HashMap instance. |
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public Collection<V> values()[/java]
DemoHashMap.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoHashMao {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create hash map
HashMap newmap = new HashMap();
// populate hash map
newmap.put(1, "SPLessons");
newmap.put(2, "Start Coding");
newmap.put(3, "Stop Thinking");
// checking collection view of the map
System.out.println("Collection view is: "+ newmap.values());
}
}
[/java]
The
put() strategy is utilized to relate the value with the key in the map.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Collection view is: [SPLessons, Start Coding, Stop Thinking]
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public Set<K> keySet()[/java]
DemoHashMap.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoHashMao {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create hash map
HashMap newmap = new HashMap();
// populate hash map
newmap.put(1, "SPLessons");
newmap.put(2, "Start Coding");
newmap.put(3, "Stop Thinking");
// get keyset value from map
Set keyset=newmap.keySet();
// check key set values
System.out.println("Key set values are: " + keyset);
}
}
[/java]
The
put() strategy is utilized to relate the value with the key in the map. By using keyset() method values of the map will be returned.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Key set values are: [1, 2, 3]
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public void clear()[/java]
DemoHashMap.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoHashMao {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create hash map
HashMap newmap = new HashMap();
// populate hash map
newmap.put(1, "SPLessons");
newmap.put(2, "Start Coding");
newmap.put(3, "Stop Thinking");
System.out.println("First map elements: " + newmap);
// clear hash map
newmap.clear();
System.out.println("Map elements after clear: " + newmap);
}
}
[/java]
In the above example, all the mapping data is going to remove after using
clear() method.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Initial map elements: {1=SPLessons, 2=Start Coding, 3=Stop Thinking}
Map elements after clear: {}
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public Object clone()[/java]
DemoHashMap.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoHashMao {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create two hash maps
HashMap newmap1 = new HashMap();
HashMap newmap2 = new HashMap();
// populate hash map
newmap1.put(1, "SPLessons");
newmap1.put(2, "Start Coding");
newmap1.put(3, "Stop Thinking");
// clone 1st map
newmap2=(HashMap)newmap1.clone();
System.out.println("1st Map: " + newmap1);
System.out.println("Cloned 2nd Map: " + newmap2);
}
}
[/java]
The
clone() is a technique in the Java programming dialect for object duplication. In Java, objects are controlled through reference variables.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
1st Map: {1=SPLessons, 2=Start Coding, 3=Stop Thinking}
Cloned 2nd Map: {1=SPLessons, 2=Start Coding, 3=Stop Thinking}
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The HashMap Class maintains
no order. - The HashMap Class may have multiple null values and single null value.
- The
HashMapextends AbstractMap andAbstractMapimplements Map interface.