Description
Description
Enum is only an information sort and it comprises of gathering of constants and in the meantime enum can be utilized for headings and weeks, for example, SUNDAY, MONDAY, WEDNESDAY, and so forth. An Enum has been presented from JDK 1.5 rendition. Enum guide is a guide usage for the enum. Taking after is the syntax of the java.util EnumMap Class.
[java]
public class EnumMap<K extends Enum<K>,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Serializable, Cloneable
[/java]
Where the
Serializable and Cloneable are the interfaces that needs to be implemented.
 Methods
Methods
Following are the common using methods of java.util EnumMap Class.
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| java.util.EnumMap.clear() | To remove the mappings. |
| java.util.EnumMap.containsKey() | To specify a particular key for the mapping. |
| java.util.EnumMap.containsValue() | To specify one or more keys for the mapping. |
| java.util.EnumMap.get() | To return the particular value to which mapping will be done. |
| java.util.EnumMap.values() | To return the collection view. |
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public void clear()[/java]
DemoEnumMap.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoEnumMap {
// create an enum
public enum Numbers{ONE, TWO, THREE, FOUR, FIVE};
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Numbers,String> map =
new EnumMap<Numbers,String>(Numbers.class);
// associate values in map
map.put(Numbers.ONE, "1");
map.put(Numbers.TWO, "2");
map.put(Numbers.THREE,"3");
map.put(Numbers.FOUR, "4");
// print the whole map
System.out.println(map);
// clear the mappings
map.clear();
// print the map again
System.out.println(map);
}
}
[/java]
Now understand the code without using clear() method. Following is the result.
[java]
{ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4}
{ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4}
[/java]
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
{ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4}
{}
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public boolean containsKey(Object key)[/java]
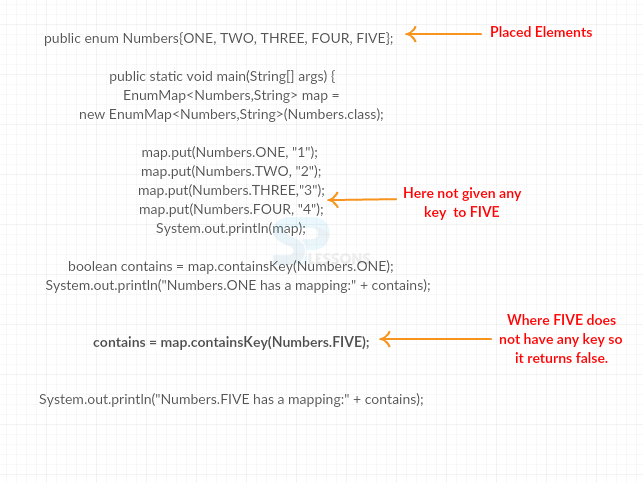
DemoEnum.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoEnumMap {
// create an enum
public enum Numbers{ONE, TWO, THREE, FOUR, FIVE};
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Numbers,String> map =
new EnumMap<Numbers,String>(Numbers.class);
// associate values in map
map.put(Numbers.ONE, "1");
map.put(Numbers.TWO, "2");
map.put(Numbers.THREE,"3");
map.put(Numbers.FOUR, "4");
// print the whole map
System.out.println(map);
// check if map contains a mapping at specified key
boolean contains = map.containsKey(Numbers.ONE);
// print the result
System.out.println("Numbers.ONE has a mapping:" + contains);
// check if map contains a mapping at another specified key
contains = map.containsKey(Numbers.FIVE);
// print the result
System.out.println("Numbers.FIVE has a mapping:" + contains);
}
}
[/java]
In the above example, while mapping the keys with values
FIVE was not used so it returns false.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
{ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4}
Numbers.ONE has a mapping:true
Numbers.FIVE has a mapping:false
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public boolean containsValue(Object value)[/java]
DemoEnum.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoEnumMap {
// create an enum
public enum Numbers{ONE, TWO, THREE, FOUR, FIVE};
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Numbers,String> map =
new EnumMap<Numbers,String>(Numbers.class);
// associate values in map
map.put(Numbers.ONE, "1");
map.put(Numbers.TWO, "2");
map.put(Numbers.THREE,"3");
map.put(Numbers.FOUR, "4");
// print the whole map
System.out.println(map);
// check if map contains a mapping for specified key
boolean contains = map.containsValue("1");
// print the result
System.out.println("Map contains '1':" + contains);
// check if map contains a mapping at another specified key
contains = map.containsValue("5");
// print the result
System.out.println("Map contains '5':" + contains);
}
}
[/java]
In the above example, values of the code will be returned, where the value 5 has not been mentioned so it returns false.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
{ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4}
Map contains '1':true
Map contains '5':false
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public V get(Object key)[/java]
DemoEnum.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoEnumMap {
// create an enum
public enum Numbers {
ONE, TWO, THREE, FOUR, FIVE
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Numbers, String> map =
new EnumMap<Numbers, String>(Numbers.class);
// associate values in map1
map.put(Numbers.ONE, "1");
map.put(Numbers.TWO, "2");
map.put(Numbers.THREE, "3");
map.put(Numbers.FOUR, "4");
// print the map
System.out.println(map);
// get the value for Numbers.ONE
String value = map.get(Numbers.ONE);
// print the result
System.out.println("Numbers.ONE value:" + value);
System.out.println("Numbers.FIVE value:" + map.get(Numbers.FIVE));
System.out.println("Numbers.FOUR value:" + map.get(Numbers.FOUR));
}
}
[/java]
In above example, The developer used
get() method, where FIVE does not have any value so it returns false in the result.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
{ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4}
Numbers.ONE value:1
Numbers.FIVE value:null
Numbers.FOUR value:4
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public Collection<V> values()[/java]
DemoEnum.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoEnumMap {
// create an enum
public enum Numbers {
ONE, TWO, THREE, FOUR, FIVE
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumMap<Numbers, String> map =
new EnumMap<Numbers, String>(Numbers.class);
// assosiate values in map
map.put(Numbers.ONE, "1");
map.put(Numbers.TWO, "2");
map.put(Numbers.THREE, "3");
map.put(Numbers.FOUR, "4");
map.put(Numbers.FIVE, "5");
// print the map
System.out.println("Map: " + map);
// create a new collection and create the view
Collection<String> values = map.values();
// print the collection view
System.out.println("Collection:" + values);
}
}
[/java]
In the above example, the developer used five values and 5 keys so the total collection will be printed in the result.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Map: {ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4, FIVE=5}
Collection:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Java.util EnumMap - The
java.util.EnumMap.size()method is used to return the size of the keys in map. - Java.util EnumMap - The
java.util.EnumMap.remove()method is used to remove the mapping in map. - The
java.util.EnumMap.put()method is used to return particular key with particular value.