Description
Description
The java.util.Dictionary class is the abstract parent of any class, for instance, Hashtable, which maps keys to values. Here each key and esteem will be dealt with as a protest and key partners with one esteem. Taking after is the linguistic synatx of java.util.Dictionary class.
[java]
public abstract class Dictionary<K,V>
extends Object
[/java]
The java.util.Dictionary class will have only single constructor that is
Dictionary() and methods will be inherited by java.util.Object class.
 Methods
Methods
Following are the methods of java.util Dictionary Class.
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| elements() | To give back the values in dictionary. |
| get(Object) | To give back the esteem to which the key is mapped in this lexicon. |
| isEmpty() | Tests if this word reference maps no keys to esteem. |
| keys() | An enumeration of the keys will be returned. |
| put(Object, Object) | Maps the predefined key to the predetermined esteem in this word reference. |
| remove(Object) | To remove the key from the dictionary. |
| size() | To return the entries in dictionary. |
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public abstract Enumeration<V> elements()[/java]
DemoDictionary.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoDictionary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a new hashtable
Dictionary d = new Hashtable();
// add 2 elements
d.put(5, "SP");
d.put(6, "SPLessons" + "Tutorial");
System.out.println("\"5\" is " + d.get(5));
System.out.println("\"6\" is " + d.get(6));
// generates a series of elements, one at a time
for (Enumeration e = d.elements(); e.hasMoreElements();) {
System.out.println(e.nextElement());
}
}
}
[/java]
The Hashtable was a piece of the first java.util and is a solid usage of a Dictionary.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
"5" is SP
"6" is SPLessonsTutorial
SPLessonsTutorial
SP
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public abstract V get(Object key)[/java]
DemoDictionary.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoDictionary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a new hashtable
Dictionary dict = new Hashtable();
// add elements in the hashtable
dict.put("4", "SP");
dict.put("5", "Lesson");
dict.put("6", "SPLesson");
// returns the elements associated with the key
System.out.println(dict.get("6"));
}
}
[/java]
In the above code, the given value has been returned.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
SPLesson
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public abstract Enumeration<K> keys()[/java]
DemoDictionary.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoDictionary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a new hashtable
Dictionary d = new Hashtable();
// add some elements
d.put("4", "SP");
d.put("5", "Lesson");
d.put("6", "SPLessons");
// return an enumeration of the keys from this dictionary.
for (Enumeration e = d.keys(); e.hasMoreElements();) {
System.out.println(e.nextElement());
}
}
}
[/java]
Following is the syntax for Enumeration.hasMoreElements() method.
[java]boolean hasMoreElements()[/java]
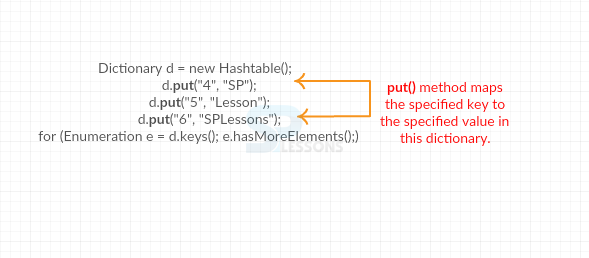
Following is the figure to explain the functionality of put() method.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
6
5
4
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public abstract V put(K key,V value)[/java]
DemoDictionary.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoDictionary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a new hasthtable
Dictionary d = new Hashtable();
// put some elements
d.put("4", "SP");
d.put("5", "Lesson");
d.put("6", "SPLessons");
// print how many times put was called
System.out.println("Number of times put was called:" + d.size());
}
}
[/java]
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]Number of times put was called:3
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public abstract V remove(Object key)[/java]
DemoDictionary.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoDictionary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a new hasthtable
Dictionary d = new Hashtable();
// put some elements
d.put("4", "SP");
d.put("5", "Lesson");
d.put("6", "SPLessons");
// remove one element
System.out.println(d.get("5"));
System.out.println(d.remove("5") + " has been removed");
System.out.println(d.get("5"));
}
}
[/java]
In the above example, the developer selected the value 5 to remove.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Lesson
Lesson has been removed
null[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public abstract int size()[/java]
DemoDictionary.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoDictionary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a new hasthtable
Dictionary d = new Hashtable();
// put some elements
d.put("4", "SP");
d.put("5", "Lesson");
d.put("6", "SPLessons");
System.out.println("Size of dictionary:" + d.size());;
}
}
[/java]
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]Size of dictionary:3[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public abstract boolean isEmpty()[/java]
DemoDictionary.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoDictionary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a new hasthtable
Dictionary d = new Hashtable();
// put some elements
d.put("4", "SP");
d.put("5", "Lesson");
d.put("6", "SPLessons");
// return true if this dictionary maps no keys to value.
boolean b = d.isEmpty();
System.out.println("Dictionary is empty:" + b);
}
}
[/java]
The
java.util.Dictionary.isEmpty() method returns true if this dictionary has no keys to values otherwise returns false.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]Dictionary is empty:false[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Java.util Dictionary - The java.util.Dictionary class will hire the methods from
java.util.Object class. - Java.util Dictionary - The
Dictionary()is the single constructor of the java.util.Dictionary class - The
keys()method is used to return an enumeration of the keys.