Description
Description
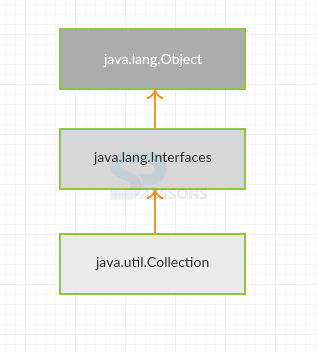
Collections is a structure that gives an outline to store and control the social occasion of things. Each one of the operations that you perform on a data, for instance, looking for, sorting, consideration, control, deletion thus on can be performed by Java Collections. Taking after is the grammar revelation for java.util.Collections class.
[java]
public class Collections
extends Object
[/java]
Following are the fields of java.util.Collections class.
- EMPTY_LIST-->It is the empty list.
- EMPTY_SET-->It is the empty set.
- EMPTY_MAP-->It is the empty map.
 Conceptual
Figure
Conceptual
Figure
 Methods
Methods
Following are the regular methods for java.util Collections Class.
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| java.util.Collections.addAll() | To include the majority of the predetermined components to the predefined collection. |
| java.util.Collections.asLifoQueue() | To give back a perspective of a Deque as a LIFO Queue. |
| java.util.Collections.binarySearch() | To search the list for the object using the binary search concept. |
| java.util.Collections.checkedList() | To get a powerfully typesafe perspective of the predetermined list. |
| java.util.Collections.checkedSortedMap() | To get a powerfully typesafe perspective of the predefined sorted map. |
| java.util.Collections.enumeration() | To get the enumeration for the collection. |
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration.
[java]public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T.. a) [/java]
Where c is the collection and a is the element to inserted.
DemoCollection.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoCollection {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create array list object
List arrlist = new ArrayList();
// populate the list
arrlist.add("S");
arrlist.add("A");
arrlist.add("I");
System.out.println("Initial collection value: "+arrlist);
// add values to this collection
boolean b = Collections.addAll(arrlist, "1","2","3");
System.out.println("Final collection value: "+arrlist);
}
}
[/java]
Here the developer added three elements by using the
ArrayList() method.
Output:Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Initial collection value: [S, A, I]
Final collection value: [S, A, I, 1, 2, 3]
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public static <T> Queue<T> asLifoQueue(Deque<T> deque)[/java]
DemoCollection.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoCollection {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create Deque object
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>(7);
// populate the object
deque.add(8);
deque.add(9);
deque.add(10);
deque.add(11);
deque.add(12);
deque.add(13);
deque.add(14);
// get queue from the deque
Queue nq = Collections.asLifoQueue(deque);
System.out.println("View of the queue is: "+nq);
}
}
[/java]
The java.util.Collections.asLifoQueue() method follows Last-In-First-Out concept.
Output:Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]View of the queue is: [8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14][/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public static <T> int binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key)[/java]
DemoCollection.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoCollection {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create arraylist
ArrayList<String> arlst=new ArrayList<String>();
// populate the list
arlst.add("StackOverFlow");
arlst.add("Dice");
arlst.add("SPlessons");
arlst.add("TUTORIALS");
// search the list for key 'QUALITY'
int index=Collections.binarySearch(arlst, "SPlessons");
System.out.println("'SPlessons' is available at index: "+index);
}
}
[/java]
Here the developer created the ArrayList to store the strings and given four strings to search.
Output:Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
'SPlessons' is available at index: 2
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public static <E> List<E> checkedList(List<E> list,Class<E> type)[/java]
DemoCollection.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoCollection {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create arraylist
ArrayList<String> arlst=new ArrayList<String>();
// populate the list
arlst.add("StackOverFlow");
arlst.add("Dice");
arlst.add("SPlessons");
arlst.add("TUTORIALS");
// create typesafe view of the list
Collection<String> tslst;
tslst = Collections.checkedList(arlst,String.class);
System.out.println("Dynamically typesafe view is: "+tslst);
}
}
[/java]
The java.util.Collections.checkedList() method is used to return a dynamically typesafe perspective view of the list.
Output:Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Dynamically typesafe view is: [StackOverFlow, Dice, SPlessons, TUTORIALS]
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public static <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> checkedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m,Class<K> keyType,Class<V> valueType)[/java]
Where
m is the guide for which a powerfully typesafe view is to be returned.
DemoCollection.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoCollection {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create sorted map
SortedMap smap = new TreeMap();
// populate the map
smap.put("1", "WWW.");
smap.put("2", "SPLESSONS");
smap.put("3", ".COM");
// get typesafe view of the sorted map
SortedMap tsmap;
tsmap = Collections.checkedSortedMap(smap,String.class,String.class);
System.out.println("Typesafe view of the sorted map: "+tsmap);
}
}
[/java]
Output:Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Typesafe view of the sorted map: {1=WWW., 2=SPLESSONS, 3=.COM}
[/java]
 Description
Description
Following is the syntax declaration of the method.
[java]public static <T> Enumeration<T> enumeration(Collection<T> c)[/java]
Where c is the collection.
DemoCollection.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.util.*;
public class DemoCollection {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create array list object
List arrlist = new ArrayList();
// populate the list
arrlist.add("S");
arrlist.add("P");
arrlist.add("L");
arrlist.add("E");
arrlist.add("S");
arrlist.add("S");
arrlist.add("O");
arrlist.add("N");
// create Enumeration
Enumeration e = Collections.enumeration(arrlist);
System.out.println("Print the enumeration");
while(e.hasMoreElements()){
System.out.println("Value is: "+e.nextElement());
}
}
}
[/java]
Enum in java is an information sort that contains settled arrangement of constants. It can be utilized for a considerable length of time of the week, bearings and so on.
Output:Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]
Print the enumeration
Value is: S
Value is: P
Value is: L
Value is: E
Value is: S
Value is: S
Value is: O
Value is: N
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Java.util Collections - The java.util.Collections.max() technique is used to give back the most outrageous segment of the given collection.
- The java.util.Collections.min() strategy is used to give back the base segment of the given collection.