Introduction
Introduction
Doing some work or process is called Thread. More threads can run concurrently within a code, every thread in Java is created and managed by the
java.lang.Thread class. To create a Java Threads developer has to follow some points as below explained.
- Write a class that extends the thread class or implements the Runnable interface. Java Thread class and Runnable interface are available in
java.lang.package. - Write public void run() method in that class, this method is executed by any thread by default.
- Create an object to the class.
- Create a Java Threads and attach the object of class into Thread.
- Start running the Thread.
 Life Cycle
Of Thread
Life Cycle
Of Thread
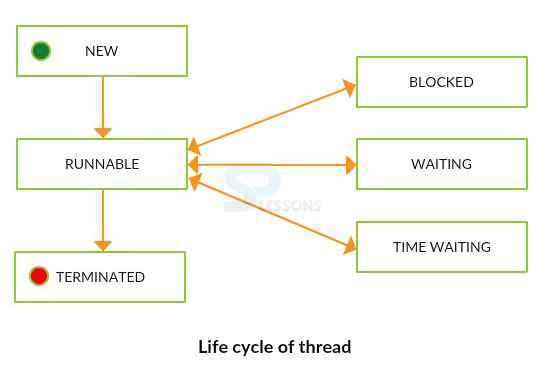
While starting any thread, the thread can be any one of the states as follows. According to sun micro thread life cycle only follows 4 states, for the better understanding purpose Running state is also added.
New: When creating an object to the Thread class, then the thread will be in New state, but this process will be started before invoking start().
Runnable: The thread is in runnable state after the invocation of start() method, but the thread scheduler has not selected it to be the running thread.
Running: The Thread is in Running state if the thread scheduler selected it.
Non-Runnable(Blocked): Here some methods will be performed like sleep().
Terminated: The Thread goes to dead state after the completion of the task.
 Methods
Methods
Following are the common repeating methods of Thread in the code.
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| activeCount() | Gives back the present number of dynamic Threads in this Thread group. |
| checkAccess() | To check whether the present Thread is permitted to alter this Thread. |
| currentThread() | Gives back a reference to the as of now executing Thread object. |
| destroy() | To destroy the thread. |
| getPriority() | To get the priority of the thread |
| isDaemon() | To provide the services. |
| sleep(long) | To stop the thread for a particular interval of time. |
 Example
Example
DemoThread.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
public class DemoThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
t.setName("Admin Thread");
// set thread priority to 1
t.setPriority(1);
// prints the current thread
System.out.println("Thread = " + t);
int count = Thread.activeCount();
System.out.println("currently active threads = " + count);
Thread th[] = new Thread[count];
// returns the number of threads put into the array
Thread.enumerate(th);
// prints active threads
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.println(i + ": " + th[i]);
}
}
}
[/java]
The
currentThread() method is used to reference to the presently executing object. Thread priority ranges from 1 to 10, where 1 is the minimum priority of the thread and 10 is the maximum priority of the thread, 5 is the default priority of the thread.
Output: The result will be as follows.
[java]
Thread = Thread[Admin Thread,1,main]
currently active threads = 1
0: Thread[Admin Thread,1,main]
[/java]
DemoThread.java
[java]package com.SPlessons;
import java.lang.*;
public class DemoThread {
public static void main(String args[]){
new ThreadClass("X");
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
try {
t.checkAccess();
System.out.println("Hey You have permission to modify");
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
class ThreadClass implements Runnable {
Thread t;
String str;
ThreadClass(String str) {
this.str = str;
t = new Thread(this);
// this will call run() function
t.start();
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("This is run() function");
}
}
[/java]
The checkAccess() method determines if the currently running thread has permission to modify this thread or not. If the current thread is not allowed to access this thread, then it results in throwing a SecurityException.
Output: The result will be as follows.
[java]
Hey You have permission to modify
This is run() function
[/java]
DemoThread.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.lang.*;
public class DemoThread extends Thread{
public void run(){
if(Thread.currentThread().isDaemon()){//checking for daemon thread
System.out.println("The daemon thread is working");
}
else{
System.out.println("user thread work");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
DemoThread t1=new DemoThread();//creating thread
DemoThread t2=new DemoThread();
DemoThread t3=new DemoThread();
t1.setDaemon(true);//now t1 is daemon thread
t1.start();//starting threads
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
class ThreadClass implements Runnable {
Thread t;
String str;
ThreadClass(String str) {
this.str = str;
t = new Thread(this);
// this will call run() function
t.start();
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("This is run() function");
}
}
[/java]
The functionality of daemon thread is to provide the services to the user, internally there are many daemon threads such as finalizer and gc(gabage colector). Runnable interface is used define the run() method.
Output: The result will be as follows.
[java]
The daemon thread is working
user thread work
user thread work
[/java]
DemoThread.java
[java]
package com.SPlessons;
import java.lang.*;
public class DemoThread implements Runnable {
Thread t;
public void run() {
for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
try {
// thread to sleep for 2000 milliseconds
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread t = new Thread(new DemoThread());
// this will call run() function
t.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(new DemoThread());
// this will call run() function
t2.start();
}
} [/java]
The sleep() method is used to resume the thread for a particular interval of time, in the above example, the developer has given 2000 milli seconds .
Output: The result will be as follows.
[java]
Thread-0 5
Thread-1 5
Thread-1 6
Thread-0 6
Thread-1 7
Thread-0 7
Thread-1 8
Thread-0 8
Thread-1 9
Thread-0 9
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The default priority of thread is 5.
- Once the developer start the thread then it is not possible to start again.
- The purpose join() method in thread to wait for the thread to die.