Description
Description
Interpreter Pattern is used for representing the language and provides an interpreter to work with the syntax of the language. Interpreter Pattern comes under Behavioral Pattern. For example, compiler converts the user defined language to machine understandable language.
 Advantages
Advantages
- Mapping of domain and syntax to a language can be done easily.
- One can easily understand and change the syntax of the language.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
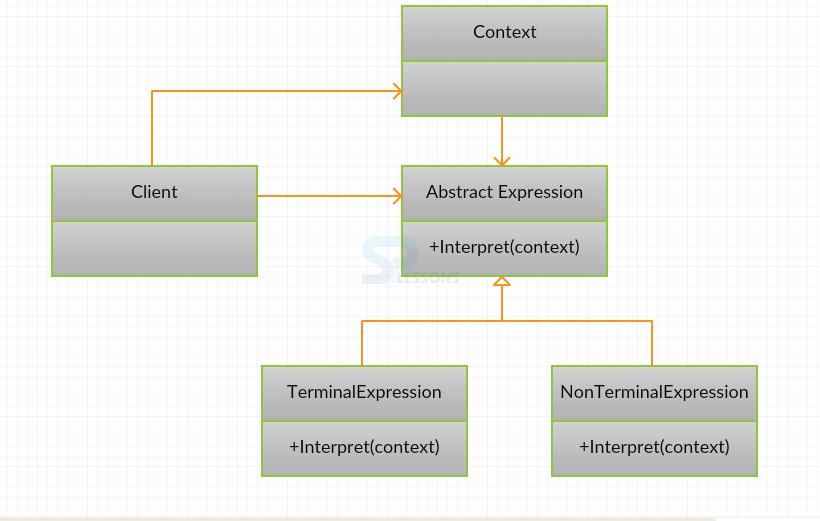
- Client: Client is used to represent the consumer of the interpreter. Client objects represent the expression tree that further represents the commands that are to be executed.
- Context : The context class is used for storing the information, which is used for expression objects.
- AbstractExpression: AbstractExpression is an abstract class and a base class for all expressions. It defines the Interpret method, which must be implemented for each subclass.
- TerminalExpression: Terminal expressions are interpreted in a single object. These are created as concrete subclasses of the ExpressionBase class.
- NonterminalExpression: Non-terminal expressions represent the concrete subclass of the ExpressionBase.
 Examples
Examples
Creating a interface Name and importing Java.util Package.
[java]
import java.util.*;
public interface Name
{
public String change(String exp);
} [/java]
Creating a class InfxToPostfxPattern that implements the interface Name. Infx is taken as input in the form of String and is converted to postfx.
[java]
public class InfxToPostfxPattern implements Name
{
public String change(String exp)
{
int priority = 0;// for the priority of operators.
String postfix = "";
StackCharacter s1 = new StackCharacter();
for (int i = 0; i < exp.length(); i++)
{
char ch = exp.charAt(i);
if (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/'||ch=='%')
{
if (s1.size() = 0)//size is checked
s1.push(ch);
}
else
{
Character chTop = (Character) s1.peek();
if (chTop == '*' || chTop == '/')
priority = 1;
else
priority = 0;
if (priority == 1)//priority is equal to 1
{
if (ch == '*' || ch == '/'||ch=='%')
{
postfix += s1.pop();
i--;
}
else
{
postfix += s1.pop();
i--;
}
}
else
{
if (ch == '+' || ch == '-')//any one condition is true
{
postfix += s1.pop();
s1.push(ch);
}
else
s1.push(ch);
}
}
}
else
{
postfix += ch;
}
}
int len = s1.size();//length is assigned as integer
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++)
postfix += s1.pop();
return postfix;
}
}// End of the InfxToPostfxPattern class. [/java]
Creating a Main class Interpreter and an object for the InfixToPostfixPattern class.
[java]
public class Interpreter {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String infix = "x*y+z";
InfixToPostfixPattern ip=new InfixToPostfixPattern();
String postfix = ip.conversion(infix);
System.out.println("Infix: " + infix);
System.out.println("Postfix: " + postfix);
}
}
[/java]
 Output
Output
The result will be as follows.
[java]
Infx: x*y+c
Postfx: xyz*+ [/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Interpreter Pattern are applied for parsing light expressions.
- Interpreter pattern can be applied to a limited area.