Introduction
Introduction
In the last quarter of 1906, the capital of Tamil Nadu, now called Chennai was hit with the financial crises. Because of this, the three best known British commercial names of the 19th century nearly collapsed.
One had crashed, the second one has to be resurrected by a distress sale and the third one was bailed out by a benefactor. The first one, Arbuthnot & Co., was considered soundest of the three in its time. A key figure in this was Mr. V. Krishnaswamy Iyer who was then a Madras lawyer.
In order to support the Swadeshi movement, Mr. V. Krishnaswamy Iyer founded the Indian bank with the support of Nagarthae Chettairs authored by Mr. Ramasamy Chettiar, elder brother of Annamalai Chettiar.
Indian Bank commenced its operation on 15th August 1907 with both Mr. Ramasamy Chettiar and Mr. V. Krishnaswamy Iyer as the first directors of the bank. The head office was then in parry's Building, Parry Corner, Madras.
 History
History
In 1932, Indian bank established its first international branch in Colombo. Since then, it has managed to widen its operations across many countries. However, in 1969, Government of India nationalized top 14 banks in India and Indian Bank was one such bank.
By this time, Burmese and the Malayan government has also nationalized banks in their counties because of which Indian banks overseas was forbidden to continue its operations as a branch of the parent bank. This has changed the whole scenario of the banking sector.
While the bank was overcoming the damages it has faced because of this, in 1992, a multi-crore scam was exposed. The chairman, Mr. M. Gopalakrishnan has lent INR 13 billion small corporates and exporters of the South. These borrowings were never paid and the bank had to face huge financial crises. Still continuing its operations with various ups and down, Indian Bank still holds strong with the business crossing the milestone target of INR 30 lakh crores in 2015.
Headquartered in Chennai, Indian Bank is a state-owned financial service. It has been serving the nation with a tea of dedicated 19843 staff members in India. As of March 2018, the total business of the bank has touched to INR 3,71, 020 crores with an operating profit of INR 5000.99 crores. The core banking solution provided in all 2820 branches has added value to the net profit of worth INR 1258.99 crores.
Indian bank has information systems and security processes certified with ISO 27001:2013. It is one of the very few banks of the world who has been certified. Indian Bank has 227 overseas correspondent banks in 75 countries of the world.
The overseas branches are located in Singapore and Colombo. There is Foreign Currency banking Unit owned by the bank in Colombo and Jaffna. Besides, the bank has diversified its banking activities through two of its subsidies; Indian Merchant Banking Services Ltd. and IndBank Housing Ltd.
 CEO
CEO
CEO [18 March 2017 – Present]: Mr. Kishor Kharat
Aged 59 years, Mr. Kishor Kharat has been the Managing Director and CEO of India Bank. A graduate in commerce and law, Mr. Kishor Kaharat assumed charge on April 4, 2017. Mr. Kishor Kharat also holds a Degree of Master of Business Administration and is a certified Associate of the Indian Institute of Bankers.
Starting a career with Bank of Baroda and working for over 37 years, Mr. Kishore Kharat holds immense experience in the banking sector and the complexities that banks shall face. As a member of the RBI Committee on Financial Inclusion, Mr. Kishor Kharat was entitled to draw a medium-term roadmap for bringing financial inclusion in the country.
Presently working as a member of the Managing Committee of IBA, CII National Committee on Banking, Insurance Advisory Committee of IRDAI, Governing Board of NIBM, and Director of Governing Board of NIBM.
Besides, Mr. Kishor Kharat is also a member in PGDM Executive Council of NIBM. It is because of the pragmatic approach that Mr. Kishor Kharat posses, Indian Bank does not confine to its competitive landscape to its public sector. The bank does not believe in Sarkari culture and provides a high level of services and efficiency matching the levels of a good private sector bank.
According to the CEO, Mr. Kishor Kharat, the bank is becoming a public sector bank with characteristics those of a private sector. The bank has the lowest non-performing assets in the industry. This is because Indian bank does not lend carelessly. Neither does the bank invested in problematic sectors of road, power, cement, or textiles. This is how Indian Bank has managed to make a decent profit.
 Organization
Organization
What does Indian Bank do?
1. Specialized Banking: As a forefront runner in specialized banking;
- Indian Bank has 99 Forex Authorized branches including the Treasury Branch in Mumbai.
- 73 Specialized MSME Branches that exclusively extend finance to MSME units.
- The credit departments have a Project Appraisal and Debt Syndication (PA&DS) that has been operationalized at the corporate office.
- 2975 Sub Service Areas (SSA) have been allotted under the Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojna.
- Of these 2517 SSAs have Bank Mitrs or Bank Correspondents to provide banking services,
- 458 SSAs are already functioning through Brick and Mortar branches.
- Indian Bank is Pioneer in introducing the concept of Self Helped Groups and Financial Inclusion Projects in rural India.
- Indian Bank has been awarded for its microfinance activities going on in the state of Kerela, Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Specialised verticals for MSME segment and Mid Corporate Segment.
- Fully business computerization.
- Fully Core Banking Solution (CBS) Branches
- Launched the IB Credit Card.
- E-payment facility for corporate customers.
- 3399 Buch Note Acceptors
- 2,36,835 ATMs providing 24 x 7 services.
- Aadhar Enabled Payment System (AEPS) through Business Correspondents.
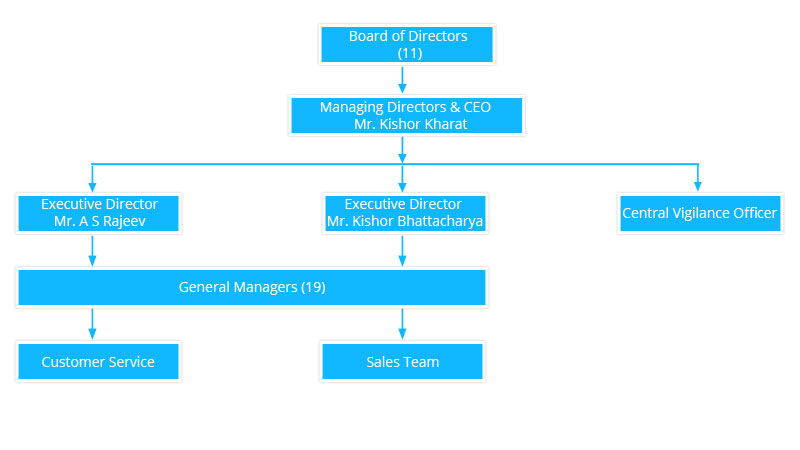
- Two executive directors: Mr. A S Rajeev and Shri M. K. Bhattacharya
- A government nominee director: Shri Amit Aggarwal
- RBI nominee director: Mr. J. K. Dash
- Non-Official Directors: Mr. Vijay Kumar Goel, Mr. Padmanaban Vittal Dass
- Shareholder Director: Mr. Vinod Kumar Nagar, Dr. Bharath Krishna Sankar
- Part-time Non-official Director: Mr. Sahil Kumar Jha
- and the bank's executives overlook all business areas including marketing, operation, and finance. Each of the financial division has its own dedicated staff.
- International Banking
- Domestic Foreign Business
- Treasury
- Rural & Agri-Business
- Retail Marketing and Banking
- Credit Recovery
- MSME & Credit Policy
- Central Audit & Inspections
- Human Resources
- Corporate Communication
- Large Corporates
- Risk Management