Introduction
Introduction
IDBI Executive - Online Test, conducted in online Mode, has: a duration of 90 Minutes, a total of 150 questions, a maximum score of 150 marks, and, consists of 3 sections, namely – Reasoning Ability, English Language and Quantitative Aptitude. There is a Negative marking in IDBI Executive Online Test and 0.25 marks are deducted for each wrong answer. Candidates must clear the cut-off in all 3 sections to qualify for the IDBI Executive Document verification and Pre-Recruitment Medical test.
 Pattern
Pattern
| S.No. | Name of Tests | No. of Questions | Maximum Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reasoning Ability | 50 | 50 | 90 Minutes |
| 2 | English Language | 50 | 50 | |
| 3 | Quantitative Aptitude | 50 | 50 | |
| Total | 150 | 150 |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
| Topic | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Direction and Distance | 1-3 |
| Order & Ranking | 2-4 |
| Arrangement & Pattern | 3-5 |
| Coding Decoding | 3-5 |
| Blood Relation | 3-5 |
| Seating Arrangement | 4-5 |
| Mathematical Inequalities | 5 |
| Syllogism | 5 |
| Input Output | 5 |
| Floor Puzzle | 5 |
| Non-Verbal Reasoning | 4 |
Penalty for Wrong Answers:
There will be negative marks for wrong answers in the Objective tests. 1/4th of mark assigned for question will be deducted for each wrong answer.
 Samples
Samples
1. One evening before sunset two friends sumit and mohit were talking to each other face to face. If mohit's shadow was exactly to his right side, which direction was sumit facing,
A. North
B. South
C. Data inadequate
D. West
Answer: B
2. I am facing east. I turn 100° in the clock wise direction and then 45° in the anticlock wise direction. Which direction am I facing now?
A. East
B. South - east
C. North
D. South - west
E. none of the above
Answer: B
1. In a row of persons, position of A from left side of the row is 27th and position of A from right side of the row is 34th. Find total no. of persons in the row?
A. 60
B. 70
C. 80
D. 90
Answer: A
2. In a row of 16 persons, position of A from left side of the row is 12th. Find the position of A from right side of the row?
A. 5th
B. 6th
C. 7th
D. 8th
Answer: A
3. In a row of persons, position of A from left side of the row is 27th and there are 5 persons after A in the row. Find total no. of persons in the row?
A. 31
B. 32
C. 33
D. 34
Answer: B
Direction (1-3): These questions are based on the following arrangement of letter, numbers and symbols.
C # F? 2 I 3 M ⋆ Q 6 T 7 & G 5 4 % D 1 E $ 8 W Z 9
1. If all the numbers are deleted from the arrangement, then which element will be 9th to the right of the 16th element from the right end?
A. &
B. T
C. %
D. G
E. None of these
Answer: D
2. Four of the following five are alike in certain way based on their element’s position in the arrangement and hence, forma group. Which one does not belong to the group?
A. F?I
B. *QT
C. 1E8
D. 4DE
E. ^T&
Answer: D
3. If all the symbols are deleted from the arrangement, then which element will be 7th to the left of 13th element from the left end?
A. 9
B. Q
C. M
D. 3
E. None of these
Answer: C
1. If in a certain language, MADRAS is coded as NBESBT, how is BOMBAY coded in that code?
A. CPNCBX
B. CPNCBZ
C. CPOCBZ
D. CQOCBZ
E. None of these
Answer: B
2. In a certain code, TRIPPLE is written as SQHOOKD. How is DISPOSE written in that code?
A. CHRONRD
B. DSOESPI
C. ESJTPTF
D. ESOPSID
E. None of these
Answer: A
3. If in a code language, COULD is written as BNTKC and MARGIN is written as LZQFHM, how will MOULDING be written in that code?
A. CHMFINTK
B. LNKTCHMF
C. LNTKCHMF
D. NITKHCMF
E. None of these
Answer: C
1. Pointing to a photograph of a boy Suresh said, "He is the son of the only son of my mother." How is Suresh related to that boy?
A. Brother
B. Uncle
C. Cousin
D. Father
Answer: D
2. If A + B means A is the mother of B; A - B means A is the brother B; A % B means A is the father of B and A x B means A is the sister of B, which of the following shows that P is the maternal uncle of Q?
A. Q - N + M x P
B. P + S x N - Q
C. P - M + N x Q
D. Q - S % P
Answer: C
3. If A is the brother of B; B is the sister of C; and C is the father of D, how D is related to A?
A. Brother
B. Sister
C. Nephew
D. Cannot be determined
Answer: D
1. A, P, R, X, S and Z are sitting in a row. S and Z are in the centre. A and P are at the ends. R is sitting to the left of A. Who is to the right of P?
A. A
B. X
C. S
D. Z
Answer: B
2. A, B, C, D and E are sitting on a bench. A is sitting next to B, C is sitting next to D, D is not sitting with E who is on the left end of the bench. C is on the second position from the right. A is to the right of B and E. A and C are sitting together. In which position A is sitting?
A. Between B and D
B. Between B and C
C. Between E and D
D. Between C and E
Answer: B
3. Six friends are sitting in a circle and are facing the centre of the circle. Deepa is between Prakash and Pankaj. Priti is between Mukesh and Lalit. Prakash and Mukesh are opposite to each other. Who is sitting right to Prakash?
A. Mukesh
B. Deepa
C. Pankaj
D. Lalit
Answer: D
Directions (1-3): In the question below relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. The statements are followed by two conclusions.
1. Statements: H ≥ J; L = M; K ≤ L; J ≤ K
Conclusions:
I. H K
A. Only conclusion I is true.
B. Only conclusion II is true.
C. Either conclusion I or conclusion II is true.
D. Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II is true.
E. Both the conclusion I and conclusion II are true.
Answer: D
2. Statements: H ≥ J; L = M; K ≤ L; J ≤ K
Conclusions:
I. L ≥ J
II. L < H
A. Only conclusion I is true.
B. Only conclusion II is true.
C. Either conclusion I or conclusion II is true.
D. Neither conclusion I nor conclusion II is true.
E. Both the conclusion I and conclusion II are true.
Answer: A
3. Statements: A < Y = Z ≥ W; Z < P
Conclusions:
P > A
W < P
A. Only Conclusion I is true
B. Only Conclusion II true
C. Either Conclusion I or II is true
D. Neither Conclusion I nor II is true
E. Both Conclusion I and II are true
Answer: E
Directions (1-5): In each of the following questions two statements are given and these statements are followed by two conclusions numbered (1) and (2). You have to take the given two statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the two given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Give answer:
(A) If only (1) conclusion follows
(B) If sonly (2) conclusion follows
(C) If either (1) or (2) follows
(D) If neither (1) nor (2) follows and
(E) If both (1) and (2) follow.
1. Statements: Some actors are singers. All the singers are dancers.
Conclusions:
1. Some actors are dancers.
2. No singer is actor.
A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
Answer: A
2. Statements: All the harmoniums are instruments. All the instruments are flutes.
Conclusions:
1. All the flutes are instruments.
2. All the harmoniums are flutes.
A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
Answer: B
3. Statements: Some mangoes are yellow. Some tixo are mangoes.
Conclusions:
1. Some mangoes are green.
2. Tixo is a yellow.
A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
Answer: D
4. Statements: Some ants are parrots. All the parrots are apples.
Conclusions:
1. All the apples are parrots.
2. Some ants are apples.
A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
Answer: B
5. Statements: Some papers are pens. All the pencils are pens.
Conclusions:
1. Some pens are pencils.
2. Some pens are papers.
A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
Answer: E
Directions (1-2): Read the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
A word-number arrangement machine, when given an input as a set of words and numbers, rearranges them following a particular rule and generates stepwise outputs until the rearrangement is complete following that rule.
Following is an illustration of input and steps of rearrangement until the last step.
Input: pour ask 57 dear 39 fight 17 28
Step I: ask pour 57 dear 39 fight 17 28
Step II: ask 57 pour dear 39 fight 17 28
Step III: ask 57 dear pour 39 fight 17 28
Step IV: ask 57 dear 39 pour fight 17 28
Step V: ask 57 dear 39 fight pour 17 28
Step VI: ask 57 dear 39 fight 28 pour 17
In addition, Step VI: is the last step.
As per the rule followed in the above steps, find out the answer to each of the following questions.
1. Input: ‘19 feat 34 28 dog bag take 43’, which of the following steps would be “bag 43 dog 19 feat 34 28 take”?
A. IInd
B. IVth
C. Ist
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
Answer: E
2. Input: ‘zeal for 49 31 high 22 track 12’, which of the following will be the IIIrd step?
A. For 49 high 31 track 22 zeal 12
B. For 49 high 31 zeal 22 track 12
C. For 49 high zeal 31 22 track 12
D. For 49 high 31 track zeal 22 12
E. None of these
Answer: C
Directions (3-4): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
A word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of words and numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of the input and various steps of rearrangement. (All the numbers are two digit numbers).
Input: 11 day 34 night 93 pace 27 easy 44 joy
Step I: 93 11 day 34 night pace 27 easy 44 joy
Step II: 93 11 34 night pace 27 easy 44 joy day
Step III: 93 44 11 34 night pace 27 easy joy day
Step IV: 93 44 11 34 night pace 27 joy day easy
Step V: 93 44 34 11 night pace 27 joy day easy
Step VI: 93 44 34 11 night pace 27 day easy joy
Step VII: 93 44 34 27 11 night pace day easy joy
Step VIII: 93 44 34 27 11 pace day easy joy night
Step IX: 93 44 34 27 11 day easy joy night pace
Step IX is the last step of the rearrangement as the desired arrangement is obtained. As per rules followed in the above steps, find out in each of the questions the appropriate step for the given input.
Input for the question: class 25 war 15 race 73 heap 58 just 88 take 38
3. Which of the following represents the Step X?
A. 88 73 58 38 25 war 15 race take class heap just
B. 88 73 58 38 25 15 class heap just race take war
C. 88 73 58 38 25 15 war class heap just race take
D. 88 73 58 38 25 15 war take class heap just race
E. There is no such Step
Answer: C
4. How many steps are required to complete this arrangement?
A. Eleven
B. Twelve
C. Ten
D. Nine
E. None of these
Answer: A
5. An arrangement machine, when given a particular input, rearranges it following a particular rule. The following is the illustration of the input and the steps of arrangement.
Input: 19 say 16 empty on 17 meat 18
Step1: on 19 say 16 empty 17 meat 18
Step2: on say 19 16 empty 17 meat 18
Step3: on say meat 19 16 empty 17 18
Step4: on say meat empty 19 16 17 18
Step5: on say meat empty 19 18 16 17
Step6: on say meat empty 19 18 17 16
Input: 44 make 43 42 in day angle 41.
In step 2, which element occurs at the end?
A. 41
B. 42
C. 43
D. 44
E. None of these
Answer: A
Directions (1-5): Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Eight persons from different bank viz. UCO bank, Syndicate bank, Canara bank, PNB, Dena Bank, Oriental Bank of Commerce, Indian bank and Bank of Maharashtra are sitting in two parallel rows containing four people each, in such a way that there is an equal distance between adjacent persons. In row 1: A, B, C and D are seated and all of them are facing south. In row 2: P, Q, R and S are seated and all of them are facing north. Therefore, in the given seating arrangements each member seated in a row faces another member of the other row. (All the information given above does not necessarily represent the order of seating as in the final arrangement).
- C sits second to right of the person from Bank of Maharashtra. R is an immediate neighbor of the person who faces the person from Bank of Maharashtra.
- Only one person sits between R and the person for PNB. Immediate neighbour of the person from PNB faces the person from Canara Bank.
- The person from UCO bank faces the person from Oriental Bank of Commerce. R is not from Oriental Bank of Commerce. P is not from PNB. P does not face the person form Bank of Maharashtra
- Q faces the person from Dena Bank. The one who faces S sits to the immediate left of A.
- B does not sit at any of the extreme ends of the line. The person from Bank of Maharashtra does not face the person from Syndicate Bank.
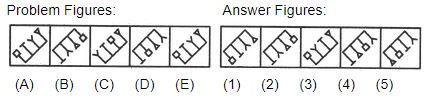
Directions (1-5): Each of the following questions consists of five figures marked A, B, C, D and E called the Problem Figures followed by five other figures marked 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 called the Answer Figures. Select a figure from amongst the Answer Figures which will continue the same series as established by the five Problem Figures.
1. Select a figure from amongst the Answer Figures which will continue the same series as established by the five Problem Figures.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Answer: B
2. Select a figure from amongst the Answer Figures which will continue the same series as established by the five Problem Figures.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Answer: A
3. Select a figure from amongst the Answer Figures which will continue the same series as established by the five Problem Figures.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Answer: A
4. Select a figure from amongst the Answer Figures which will continue the same series as established by the five Problem Figures.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Answer: D
5. Select a figure from amongst the Answer Figures which will continue the same series as established by the five Problem Figures.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Answer: E