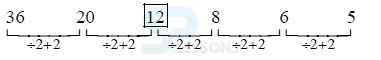Introduction
Introduction
Career in Banking is one of the most lucrative and most sought after careers. In India, Bank Recruitment Exams are primarily conducted for recruitment of Probationary Officers, Clerks & Specialist Officers. India currently[2019] has 93 commercial and 27 public sector banks out of which 19 are nationalized and 6 are SBI and its associate banks and rest two are IDBI Bank and Bharatiya Mahila Bank, which are categorized as other public sector banks. Recruitment for Bank Probationary Officers, Management Trainees, Clerks and for various other posts generally follow a 3 step recruitment process: Preliminary Exam + Mains Exam + Interview & Group Discussion. The article IBPS CLERK Prelims Practice Set presents a practice set for the most sought after SBI PO recruitment. Until the year 2013, All Public Sector Banks used to conduct their own entrance test, GDs and Personal Interview for recruiting candidates. However, after 2014, IBPS started conducting recruitment Tests for 12 PSU Banks. SBI holds a separate entrance test for recruitment.
Prelims exams are very important to clear every government sector or bank related recruitment process in India. Prelims are also known as Screening Tests. Only those candidates who are selected in the prelims round are allowed to move further up in the recruitment process. The marks obtained in the preliminary exams are not considered for the final merit list. Preliminary Exams are only meant to be screening tests. Preliminary exams usually consist of 3 sections, with 100 questions with a time duration of 1 hour. Preliminary exams most certainly have negative marking.
 Quiz
Quiz
Directions Q (1 - 5): What should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following questions.
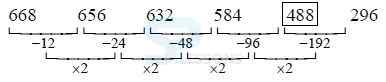
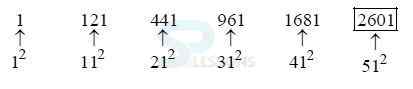
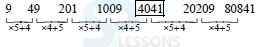
1. 36 20 ? 8 6 5 ?
-
A. 10
B. 12
C. 14
D. 16
E. None of these
-
A. 392
B. 438
C. 488
D. 536
E. None of these
-
A. 2701
B. 2511
C. 2611
D. 2801
E. None of these
-
A. 4054
B. 4049
C. 4050
D. 4041
E. None of these
-
A. 121
B. 111
C. 109
D. 97
E. None of these
-
A. 224
B. 58
C. 121
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
-
A. Rs 84,500
B. Rs 5, 30, 000
C. Rs 3, 25, 200
D. Rs 4, 34, 400
E. None of these
-
A. 18 : 13 : 24
B. 13 : 18 : 23
C. 17 : 3 : 23
D. 18 : 11 : 23
E. None of these
-
A. 8 years
B. 12 years
C. 9 years
D. 10 years
E. None of these
-
A. 273
B. 87
C. 264
D. 92
E. None of these
-
A. 9
B. 729.
C. 6561
D. 81
E. None of these
-
A. 2 : 3
B. 21 : 31
C. 7 : 10
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
-
A. Rs 1,100
B. Rs 1,111
C. Rs 1,110
D. Rs 1,000
E. None of these
-
A. 1525
B. 1650
C. 1700
D. 1575
E. None of these
-
A. 374
B. 388
C. 362
D. 391
E. None of these
-
A. 7
B. 21
C. 18
D. 11
E. 16
-
A. 350
B. 345
C. 355
D. 340
E. 335
-
A. 525
B. 556
C. 534
D. 550
E. 540
-
A. 18
B. 14
C. 11
D. 9
E. 21
-
A. 63
B. 67
C. 76
D. 72
E. 80
-
A. if x > y
B. if [latex]{x}^{3}[/latex] y
C. if x < y
D. if x ≤ y
E. if x = y or the relationship cannot be established
-
A. if x > y
B. if [latex]{x}^{3}[/latex] y
C. if x < y
D. if x ≤ y
E. if x = y or the relationship cannot be established
-
A. if x > y
B. if [latex]{x}^{3}[/latex] y
C. if x < y
D. if x ≤ y
E. if x = y or the relationship cannot be established
-
A. if x > y
B. if [latex]{x}^{3}[/latex] y
C. if x < y
D. if x ≤ y
E. if x = y or the relationship cannot be established
-
A. if x > y
B. if [latex]{x}^{3}[/latex] y
C. if x < y
D. if x ≤ y
E. if x = y or the relationship cannot be established
-
A. 361
B. 529
C. 441
D. 625
E. None of these
-
A. 1156
B. 1136
C. 1096
D. 1116
E. None of these
-
A. 396
B. 216
C. 432
D. 576
E. None of these
-
A. 5060
B. 5200
C. 4880
D. 4500
E. None of these
-
A. 90.25
B. 94.386
C. 95.50
D. 91.875
E. None of these
-
A. Rs. 1,393.405
B. Rs. 1,326
C. Rs. 1,384.50
D. Rs. 1340
E. None of these
-
A. Rs. 3
B. Rs. 2.5
C. Rs. 1.5
D. Rs. 2
E. None of these
-
A. 324
B. 16
C. 256
D. 144
E. None of these
-
A. 86
B. 95
C. 68
D. 77
E. None of these
-
A. 10
B. 7
C. 12
D. 8
E. 6
-
A. 86
B. 95
C. 68
D. 77
E. None of these
36. ‘Talk’ is related to ‘Speak’ in a certain way. Similarly, ‘Honest’ is related to ‘Truthful’. Following the same logic, ‘Listen’ is related to ‘.............’.
-
A. Music
B. Ears
C. Hear
D. Ignore
E. Sound
-
A. Bird
B. Insect
C. Aeroplane
D. Kite
E. None of these
-
A. Restrict
B. Rocket
C. Robber
D. Random
E. Restaurant
-
A. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B. 3, 2, 1, 4, 5
C. 5, 2, 3, 4, 1
D. 5, 1, 2, 3, 4
E. None of these
-
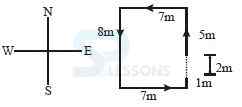
A. 3 m
B. 6 m
C. 4 m
D. 2 m
E. 7 m
-
A. 2
B. 3
C. 6
D. 5
E. None of these
-
A. 381191
B. 381911
C. 394132
D. 562134
E. None of these
-
A. pot
B. cot
C. chair
D. filter
E. None of these
-
A. Uncle
B. Daughter-in-law
C. Cousin
D. Brother
E. None of these
-
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. Fourth
E. None of these
-
A. All follow
B. None follows
C. Only I and III follow
D. Only II and IV follow
E. None of these
-
A. None follows
B. Only I or IV and II follow
C. Only either I or II and IV follow
D. Either I or II follows
E. None of these
-
A. None follows
B. Only I and III follow
C. Only I and II follow
D. Only III and IV follow
E. None of these
-
A. Only I and IV follow
B. Only I and II follow
C. Only III and IV follow
D. Either II or III follows
E. None of these
-
A. Only I and IV follow
B. Only II follows
C. Only I and II follow
D. Only IV follows
E. None of these
-
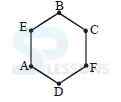
A. B
B. C
C. E
D. F
E. None of these
-
A. F
B. D
C. C
D. B
E. None of these
-
A. B
B. C
C. D
D. F
E. None of these
-
A. B & F
B. C & F
C. D & F
D. A & E
E. None of these
-
A. B, C, F
B. A, F, B
C. D, A, B
D. F, A, E
E. None of these
-
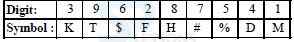
A. %$DTFK
B. K$DTFK
C. X$DTFX
D. K$DTF%
E. None of these
-
A. $%HFD#
B. #%HFD$
C. %$HFD#
D. %#HFD$
E. None of these
-
A. DK$T%D
B. DK$T%H
C. HK$T%H
D. #%$HK#
E. None of these
-
A. #%$HKD
B. D%$HK#
C. D%$HKD
D. #%$HK#
E. None of these
-
A. FTMK#H
B. XTMK#X
C. HTMK#F
D. FTMK#F
E. None of these
-
A. XFH%DX
B. XFH#DX
C. MFH%DX
D. XFH%D#
E. None of these
-
A. If only conclusion I is true.
B. If only conclusion II is true.
C. If neither I nor II is true.
D. If both I and II are true.
E. None of these
-
A. If only conclusion I is true.
B. If only conclusion II is true.
C. If neither I nor II is true.
D. If both I and II are true.
E. None of these
-
A. If only conclusion I is true.
B. If only conclusion II is true.
C. If neither I nor II is true.
D. If both I and II are true.
E. None of these
-
A. If only conclusion I is true.
B. If only conclusion II is true.
C. If neither I nor II is true.
D. If both I and II are true.
E. None of these
-
A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. More than three
-
A. V1F
B. EK8
C. R % #
D. 6V9
E. $G3
-
A. None
B. One
C. Tow
D. Three
E. More than three
-
A. G
B. 2
C. E
D. *
E. None of these
-
A. H
B. I
C.
D. 9
E. None of these
Directions Q (71 - 75): Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Govind’s father was a rich landlord, who was loved and respected by all his tenants. When he died, he left large tracts of land to Govind. But Govind did not spend a single day looking after his land. He had a funny idea, that there existed a magic potion which, if it was poured on any object, would turn it into gold. He spent all his time trying to learn more about this potion. People took advantage of him and cheated him. His wife grew anxious. Given the amount of money Govind was spending, she was sure that they would soon be paupers.
One day, a widely respected sage who had been to the Himalayas came to their town. Govind asked him about the potion. To his surprise, the sage answered, “I have learned how to brew such a potion. But it is a difficult process.” “Tell me!” insisted Govind, hardly able to believe his luck. “You have to collect the dew which settles on the leaves of a banana tree every morning during winter. There is a condition, though. The tree should be planted and watered regularly with your own hands. Store the collected dew in an earthen vessel and when you have five liters, bring it to me. I will recite a sacred mantra to transform the dough into the potion. A drop of the potion will be sufficient to change any object into gold.”
Govind was worried “Winter is only for a few months in the year. It will take me years to collect the dew.” “You can plant as many trees as you want,” replied the sage. Govind went home and after talking to his wife, began clearing the large fields which has been lying vacant for years. He planted rows of banana saplings. He tended them with great care. His wife helped him too. She would take the banana crop to market and get a good price. Over the years the plantation grew and finally, after six years, Govind had five liters of dew. He went to the sage who
smiled, uttered a mantra and sprinkled a few drops of dew on a copper vessel. To Govind’s dismay, nothing happened. “you have cheated me!” he shouted at the sage.
The sage however smiled. Govind’s wife then came forward with a box. The sage opened it and revealed stacks of gold coins inside. Turning to Govind he said, “you worked hard on your land and created a plantation. Your wife sold the produce in the market. It was your hard work which created this wealth, not magic. If I had told you this earlier, you would not have listened.” Govind understood the wisdom behind the sage’s words and worked even harder from that day on.
71. Why did Govind’s father give him large tracts of land?
-
A. It was his way of instilling a sense of responsibility in his son
B. Govind was his only son and sole heir
C. To provide Govind with sufficient funds to pursue his the interest in discovering a magic potion
D. He wanted Govind to continue to look after the tenants
E. None of these
-
A. He was cunning and plotted with Govind’s wife to cheat him.
B. He had no magical powers as such and used to swindle people
C. He was a good judge of people
D. He did not deserve his good reputation
E. He was dishonest because he had cheated Govind out of his gold
-
A. Govind had no knowledge of farming and could not cultivate the land he had inherited from his father
B. Govind had no friended because he was obsessed with finding a potion which would turn anything into gold
C. Govind was only interested in studying under different sages and neglected his family duties
D. Since Govind had devoted all his time and wealth to finding a magic potion, they would soon be poor
E. Govind’s experiments to find a magic potion were dangerous
-
A. Only (B)
B. Only (A)
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
E. None of these
-
A. The soil of his land was suitable only for cultivating bananas
B. It was the most highly prized commodity in the region
C. It could be grown at any time of the year including winter
D. His wife pressurized him to do so
E. The ingredient for the magic potion could only be obtained from a banana tree
-
A. His proposal had
B. to be send to
C. the President of the company
D. for her approval
E. No error
-
A. Each tuesday evening we visited
B. the farmers in the area
C. and held a meeting
D. to discuss the problems they faced
E. No error
-
A. Though our training facilities
B. are limited only a
C. few employees have been
D. selected for training
E. No error
-
A. During the interview
B. the panel asked me
C. several technical questions
D. and I answered all of it
E. No error
-
A. He decided to work for
B. an NGO, but most of his
C. classmates opted for high paid
D. jobs in multinational companies
E. No error
-
A. firstly
B. freshly
C. foremost
D. initially
E. recently
-
A. copied
B. observed
C. learned
D. understood
E. improving
-
A. asked
B. insisted
C. demanded
D. settled
E. lend
-
A. severe
B. no
C. additionally
D. variety
E. plenty
-
A. time
B. process
C. return
D. event
E. action
-
A. neglected
B. abandoned
C. defaulted
D. depended
E. disappointed
-
A. benefit
B. easier
C. reckless
D. disorganized
E. secure
-
A. sense
B. confidence
C. challenge
D. doubt
E. believe
-
A. a red and sore tongue
B. is an indicator from
C. lack of iron and Vitamin-[latex]{B}_{12}[/latex]
D. in the body
E. No error
-
A. in the high-strung life
B. of over-crowded metros
C. there a constant tug of war
D. over space and resources
E. No error
-
A. The foremost criterion of selection we adopted
B. were the number of years of training
C. a singer had received
D. under a particular guru
E. No error
-
A. excess weight is the result of
B. unhealthy eating habits
C. which are inherent risk factors
D. responsible for many diseases
E. No error
-
A. the therapeutic benefits
B. at helping others
C. have long been
D. recognised by people
E. No error
-
A. D
B. B
C. C
D. E
E. A
-
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. E
E. D
-
A. A
B. B
C. E
D. C
E. D
-
A. D
B. B
C. C
D. E
E. A
-
A. A
B. B
C. E
D. D
E. C
-
A. compel those employees
B. compelling all employees
C. compelling the employee
D. compel employees
E. No correction required
-
A. easily way to
B. easier ways for
C. easiest way to
D. easier way from
E. No correction required