Introduction
Introduction
This chapter demonstrates about the SSL - TLS these are the some security applications and side effects of HTTP/2. Following are the concepts covered in this chapter.
- HTTP/2 and Security
- TLS, SSL
 Description
Description
HTTP/2 work on a plain text by using the SSL/TLS which is not required any security, in spite majority of the browser vendors said that they would not support HTTP/2 over a plain text if which have any implementation which required TLS. Now a days all are moving to the more secured internet and here also raise the question of weather TLS adding more impact to the browsers or not, the figure below demonstrates the HTTP/2 and Security is as shown below.
 Description
Description
SSL and TLS have the same things technically but the TLS some more secured when compared to SSL. SSl stands for Secure Socket Layer and the TLS stands for Transport Layer Security. TSL is basically build on SSL 3 and considered as more secured. Most of the people while talking about the SSL or TLS they commonly referred as HTTP/2. TLS provides the three things which is shown below.
- Encryption Which allows communication to be transmitted securely with out is doping and is does by using the symmetrical encryption.
- Authentication TLS also provide authentication i.e client can identify the server and server can identify the client in the seance no one know who one can talking with the whom.
- Integrity Finally TLS provide integrity in which it validate the data again is being tampered with modified during the connection.
 Description
Description
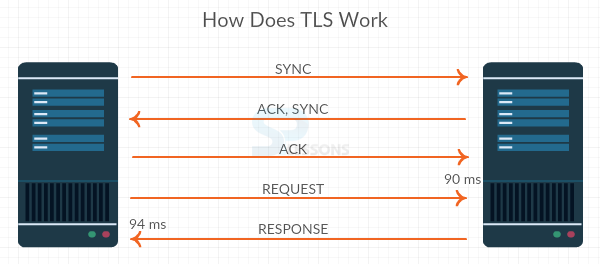
In three way handshake of TCP when establishing the connection initially a SYNC request would be sent and the ACK, SYNK request would be sent back now ACK would be sent in between the client and server then closing in three way hand shake which acts like 90 ms or more over time but which have the initial impact on the setup. When ever the Request comes and Response go out in three way handshake it will take 94 ms of time the figure below demonstrates the working of the TLS is as shown.
 Description
Description
In order to provide the more features TLS need to do the two things like namely selecting the version of the protocols going to use and exchange the validation certificates, if applicable which are provides to use the encryption all of these are some overhead to three way handshaking. Now once handshake is takes place, offer the communication is some what more efficiency and the reason for these handshake takes place using asymmetric encryption.
In the asymmetric encryption it use one private key and one public key in which one used to encrypt and another one used to decrypt and then from their on they establish a private key session which is used to moving forward and it is the procedure used for the Symmetrical encryption which is much faster then the Asymmetric encryption. The figure below demonstrates the TLS Handshake is as shown below.
Application Layer Protocol Negotiation
ALPN is known as the Application Layer Protocol Negotiation which is an extension to TLS which was added save on additional round trips. It allows us to define the protocol to be used part of the handshake which is an extension and built in to save on round trips and negotiate the actual protocol being used as part of the TLS hand shake. The figure below demonstrates the ALPN is as shown below
 Key Points
Key Points
- TLS is the extension of the SSL 3.
- TLS is the more secured the tha SSL.
- ALPN is the extension to the TLS.