Introduction
Introduction
HTML5 Geolocation is used to allow the geographical position of the user by using Geolocation APIs.Following are the concepts covered.
- What is Geolocation
- Options
- Browser Support
 Description
Description
The HTML5 Geolocation is used to share the current location with the Web browsers. The Location comprises of a couple of directions meaning the latitude and longitude of the subject. GeloLocation is also used to find the business locations and users locations on a map.
Several types of sources have to be used for the API of Geolocation which can be defined as follows.
- IP Address of the User Used to find the location of the user Internet Service Provider but not the exact location.
- Global Positioning System (GPS) Used to triangulating the area taking into account signals from GPS satellites circling the earth.
- Cell Phone ID Used to triangulation of location based on separation from cell towers.
- Wi Fi Location Used to traingulating the location based from separation from WiFi access focuses.
- Address By utilizing the Address, Zip Code, road name and so on, so not precise.
 Description
Description
HTML5 Geolocation introduced some options to increase the functionality of the geolocation API those methods are described below.
- getcurrentpoisition()
- Error Handling
- poisitionoptions
- watchPoisition()
- clearWatch()
 Description
Description
The method is used to get the current position of the user. Geolocation object is used to retrieve the current location, which is present in the navigator.geolocation property. There are 3 methods to get the current position as follows.
The code below is used to demonstrate the getting the current position.
[html]<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
button{font:1em Arial; background:#fa4b2a; color:#fff;}
p{font:1em Verdana; color:#fa4b2a;}
</style>
<body>
<p id="output"></p>
<button onclick="getCoordinates()">
Click here to find your current location</button>
<script>
var geo=document.getElementById("output");
function getCoordinates()
{
if (navigator.geolocation)
{
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(currentPosition);
}
else{geo.innerHTML="Yikes!! Please upgrade your dinasaur browser.";}
}
function currentPosition(pos)
{
geo.innerHTML="(Latitude , Longitude)" + "<br>" + "("
+ pos.coords.latitude + " , " +
+ pos.coords.longitude + ")";
}
</script>
</body>
</html> [/html]
Result
By running the above code in a preferred browser following output appears.
- callback Indicates the capacity to be called when the area information is accessible.
- error Indicates the capacity that will be called when the local information in distracted, which is optional.
- options Used To determine a choices item to be utilized to calibrate the information recovery handle, which is optional.
 Description
Description
While working with the Geolocation API frequently user can get some errors, to solve those errors HTML5 introduced error codes as shown below.
The code below demonstrates about the error handling.
[html]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
button{font:1em Arial; background:#0000FF; color:#fff;}
p{font:1em Verdana; color:#FE642E;}
body{font:1em helvetica; color:#FF0000;}
</style>
<body>
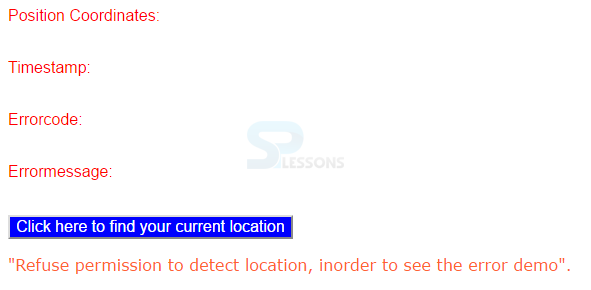
Position Coordinates:<p id="output"></p><br>
Timestamp:<p id="timestamp"></p><br>
Errorcode:<p id="errorcode"></p><br>
Errormessage:<p id="errormsg"></p><br>
<button onclick="getCoordinates()">
Click here to find your current location</button>
<script>
var geo=document.getElementById("output");
function getCoordinates()
{
if (navigator.geolocation)
{
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(currentPosition, error_callback);
}
else{geo.innerHTML="Yikes!! Please upgrade your dinasaur browser.";}
}
function currentPosition(pos)
{
geo.innerHTML="(Latitude , Longitude)" + "<br>" + "("
+ pos.coords.latitude + " , " +
+ pos.coords.longitude + ")";
document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
}
function error_callback(error) {
document.getElementById("errorcode").innerHTML = error.code;
document.getElementById("errormsg").innerHTML = error.message;
}
</script>
<p>"Refuse permission to detect location, inorder to see the error demo".</p>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
Result
By running the above code in a preferred browser, the following output is obtained.
- code 0 - UNKNOWN_ERROR Error occured that is not characterized by any other error codes.
- code 1 - PERMISSION_DENIED User should not be given permission to access the location
- code 2 – POISITION_UNAVALABLE Strategy used to recover user location failed.
- code 3 – TIMEOUT Try to recover user location if the time exceeded.
 Description
Description
The method is used to define how location data is gathered in a getCurrentPoisition() method properties of this method as follows.
The code below demonstrate how to position options.
[html]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
button{font:1em Arial; background:#0000FF; color:#fff;}
p{font:1em Verdana; color:#fa4b2a;}
body{font:1em helvetica; color:#0F0694;}
</style>
<body>
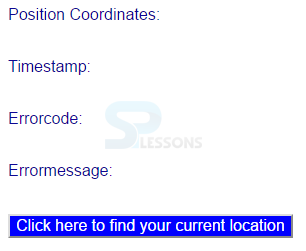
Position Coordinates:<p id="output"></p><br>
Timestamp:<p id="timestamp"></p><br>
Errorcode:<p id="errorcode"></p><br>
Errormessage:<p id="errormsg"></p><br>
<button onclick="getCoordinates()">
Click here to find your current location</button>
<script>
var geo=document.getElementById("output");
// Position Object Options
var options = { enableHighAccuracy: high,
timeout:500,
maximumAge:5000 };
//----------------------------------------------------//
function getCoordinates()
{
if (navigator.geolocation)
{
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(currentPosition, error_callback, options);
}
else{geo.innerHTML="Yikes!! Please upgrade your dinasaur browser.";}
}
function currentPosition(pos)
{
geo.innerHTML="(Latitude , Longitude)" + "<br>" + "("
+ pos.coords.latitude + " , " +
+ pos.coords.longitude + ")";
document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
}
function error_callback(error) {
document.getElementById("errorcode").innerHTML = error.code;
document.getElementById("errormsg").innerHTML = error.message;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
Result
By running the above code in a preferred browser, the following output is obtained.
- enableHighAccuracy Signals the browser to utilize high precision recognition mode, default value is false.
- timeout Sets the most extreme time permitted to process the present location, in milliseconds.
- maximumAge Signifies most extreme age of a stored position after which the program must begin to recalculate the location.
 Description
Description
watchPoisition() method is used to monitor updating the positions with Geolocation API. The location Update always called when the position get changes as shown below.
watchPoisition(locationUpdate, handleError, options)
The code below demonstrates the watch position options.
[html]<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
button{font:1em Arial; background:#0000FF; color:#fff;}
p{font:1em Verdana; color:#fa4b2a;}
body{font:1em helvetica; color:#FF0000;}
</style>
<body>
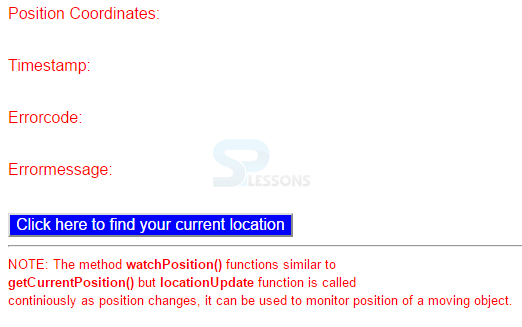
Position Coordinates:<p id="output"></p><br>
Timestamp:<p id="timestamp"></p><br>
Errorcode:<p id="errorcode"></p><br>
Errormessage:<p id="errormsg"></p><br>
<button onclick="getCoordinates()">
Click here to find your current location</button> <br>
<script>
var geo=document.getElementById("output");
var options = { enableHighAccuracy: high,
timeout:500,
maximumAge:5000 };
function getCoordinates()
{
if (navigator.geolocation)
{
navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(currentPosition, error_callback, options);
}
else{geo.innerHTML="Yikes!! Please upgrade your dinasaur browser.";}
}
function currentPosition(pos)
{
geo.innerHTML="(Latitude , Longitude)" + "<br>" + "("
+ pos.coords.latitude + " , " +
+ pos.coords.longitude + ")";
document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
}
function error_callback(error) {
document.getElementById("errorcode").innerHTML = error.code;
document.getElementById("errormsg").innerHTML = error.message;
}
</script>
<hr>
<small>NOTE: The method <b>watchPosition()</b> functions similar to <br><b>getCurrentPosition()</b> but <b>locationUpdate</b>
function is called <br>continiously as position changes,
it can be used to monitor position of a moving object.</small>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
Result
By running the above code in a preferred browser, the following output is obtained.
 Description
Description
By using clearWatch() method user can stop monitoring the location which gives signals to the Geolocation service about stop gathering location updates as shown below.
clearWatch(watchId)
The code below is used to demonstrate the clear watch as follows.
[html]<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
button{font:1em Arial; background:#0000FF; color:#fff;}
p{font:1em Verdana; color:#fa4b2a;}
body{font:1em helvetica; color:#FF0000;}
</style>
<body>
Position Coordinates:<p id="output"></p><br>
Timestamp:<p id="timestamp"></p><br>
Errorcode:<p id="errorcode"></p><br>
Errormessage:<p id="errormsg"></p><br>
<button onclick="getCoordinates()">
Click here to find your current location</button> <br>
<button onclick="clearwatch">
Stop Position Monitoring</button><br>
<script>
var geo=document.getElementById("output");
var options = { enableHighAccuracy: high,
timeout:500,
maximumAge:5000 };
document.getElementById("clearwatch").onclick = function() {
navigator.geolocation.clearWatch(watchID);}
function getCoordinates()
{
if (navigator.geolocation)
{
navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(currentPosition, error_callback, options);
}
else{geo.innerHTML="Yikes!! Please upgrade your dinasaur browser.";}
}
function currentPosition(pos)
{
geo.innerHTML="(Latitude , Longitude)" + "<br>" + "("
+ pos.coords.latitude + " , " +
+ pos.coords.longitude + ")";
document.getElementById("timestamp").innerHTML = pos.timestamp;
}
function error_callback(error) {
document.getElementById("errorcode").innerHTML = error.code;
document.getElementById("errormsg").innerHTML = error.message;
}
</script>
<small>You can stop Monitoring position by using Geolocation API's method <b>clearWatch(watchID)</b> </small>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
Result
By running the above code in a preferred browser, the following output is obtained.
- watchId Indicates the arrival values from watchPosition() call, such that the one of a kind solicitation is recognized and then cancelled.Thus, quit receiving any further area updates.
 Description
Description
HTML5 Geolocation is supported by all the latest browsers.Following are the browser versions supported by HTML5.
The code below demonstrates how to check the users Browser supports or not.
[html]<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="check"> </p>
<button onclick="checkSupport()">Check Browser Support</button>
<script>
function checkSupport() {
if(navigator.geolocation) {
document.getElementById("check").innerHTML =
"Awesome! Your Browser supports HTML5 Geolocation API.";
} else {
document.getElementById("check").innerHTML =
"Yikes! Upadate your Dinasaur Browser.";
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
Result
By running the above code in a preferred browser, the following output is obtained.
- Chrome 4.0
- Mozilla Firefox 3.5
- Safari 4.0
- Internet Explorer 9.0
- Opera 10.5
 Points
Points
- To detect the location, latitude and longitudes are mandatory.
- JavaScript is used to capture latitude and longitude.
- Now-a-days most of the devices support geolocation.