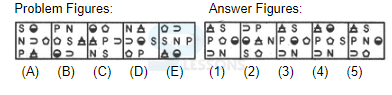
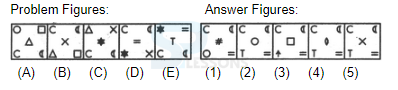
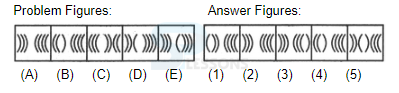
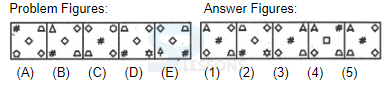
Introduction
Introduction
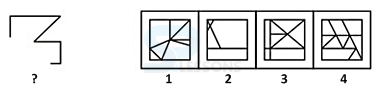
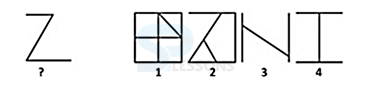
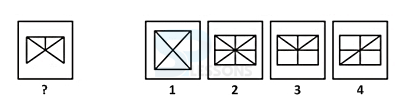
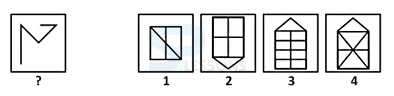
 Pattern
Pattern
Scheme of Preliminary Examination for recruitment to the post of Upper Division Clerk (UDC) in ESIC is as follows:
- Preliminary Examination is an objective test.
- The test will have four sections.
- The overall test duration is for 1 hour (No separate sectional duration).
- The test contain 200 questions with Maximum of 200 marks.
- Phase –I Preliminary Examination is qualifying in nature and marks will not be reckoned for final merit.
- The candidates will be shortlisted for Phase-II in the ratio of 1:10 i.e. about 10 times the number of vacancies in each category on the basis of their performance in Phase - I.
| Name of the Test (Objective Tests) | No. of Qs. | Max. Marks | Duration | Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Intelligence and Reasoning | 25 | 50 | 1 hour | Bilingual |
| General Awareness | 25 | 50 | Bilingual | |
| Quantitative Aptitude | 25 | 50 | Bilingual | |
| English Comprehension | 25 | 50 | English | |
| Total | 100 | 200 |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
[Click Here] for ESIC UDC Reasoning Syllabus
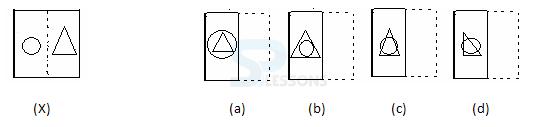
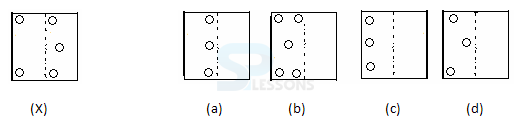
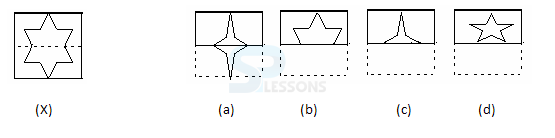
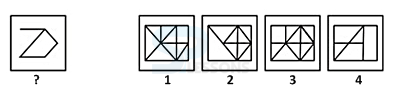
 Samples
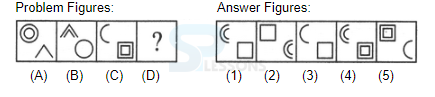
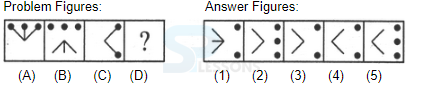
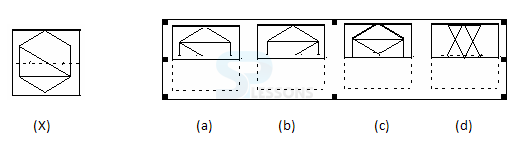
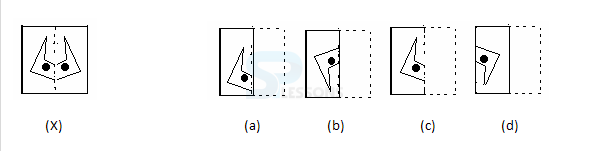
Samples
Syllogism
Direction (1- 5): In each of the questions below are given three statements, followed by conclusions: I, II, III, IV. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
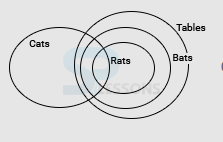
1. Statements: Some Cats are Rats. All bats are tables. All Rats are Bats.
Conclusion:
I. Some Cats are bats
II. All bats are rats
III. All tables are cats
IV. All bats are cats
- A. Only I & II follow
B. Only II follows
C. Only I & IV follow
D. None of these
- A. All follow
B. Only II and III follow
C. Only III follows
D. Only IV follows
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Only I and III follow
D. Only III follows
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II and III follow
C. Only I and III follow
D. Only II follows
- A. Only I and II follow
B. Only I and III follow
C. Only II and III follow
D. All follow
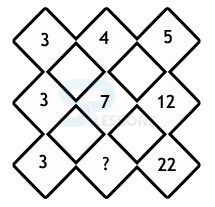
- A. 12
B. 13
C. 11
D. 15
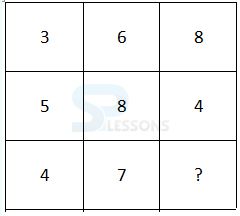
- A. 65
B. 70
C. 80
D. 75
- A. 11
B. 12
C. 10
D. 15
- A. 11
B. 10
C. 12
D. 15
- A. 5
B. 6
C. 7
D. 9
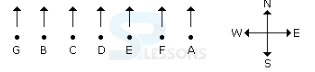
- A. Only B
B. G, B, and D
C. G and B
D. D, E, F and A
- A. E is to the immediate left of D
B. A is at one of the ends
C. G is to the immediate left of B
D. F is second to the right of D
- A. C and D
B. C and G
C. G and F
D. C and E
- A. Between E and D
B. Extreme left
C. Centre
D. Extreme right
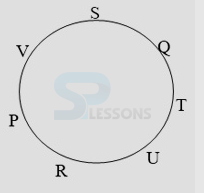
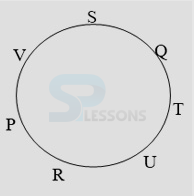
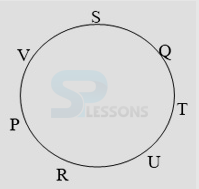
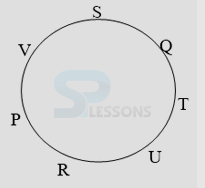
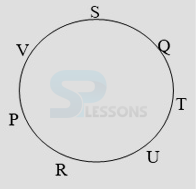
- A. P is fourth to the right of T.
B. U is to the immediate right of R.
C. U is third to the right of S.
D. Q is to the immediate left of S.
- A. R is fourth to the right of T.
B. P is to the immediate right of V.
C. S is second to the left of T.
D. Q is second to the right of V.
- A. QT
B. RP
C. VS
D. SV
- A. URT
B. TUQ
C. STQ
D. None of these
- A. Fourth to the right of S
B. To the immediate left of R
C. Between P and T
D. To the immediate right of P
- A. IV
B. III
C. V
D. VI
E. None of these
- A. the job will now the do you how
B. the job now will the do you how
C. the job will how the do you now
D. the job will the now do you how
E. None of these
- A. clever good is the very she girl
B. clever good the is she very girl
C. clever good the very is she girl
D. None of these
- A. is not to sharp point pin the
B. is not to point sharp pin the
C. is not to sharp point pin the
D. is not to point sharp
E. None of these
- A. VI
B. VII
C. VIII
D. None of these
- A. Brother
B. Uncle
C. Father
D. Grandfather
- A. Mother
B. Sister
C. Aunt
D. Grandmother
- A. Cousin
B. Daughter
C. Niece
D. Friend
- A. Daughter
B. Granddaughter
C. Mother
D. Sister
- A. Son
B. Father
C. Brother
D. Father-in.law
- A. TXCDE
B. KOPJH
C. GHOOX
D. EHRGF
- A. JGNNO
B. LGHNO
C. TYUIO
D. EHFDE
- A. IZXFDY
B. IZBJDS
C. POKUYT
D. WWWREI
- A. TTT
B. SDG
C. POK
D. SJL
- A. WERFD
B. DIJQT
C. SAERT
D. SJLKI
- A. only I follows
B. only II follows
C. either I or II follows
D. neither I nor II follow
E. both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. only II follows
C. either I or II follows
D. neither I nor II follows
E. both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. only II follows
C. either I or II follows
D. neither I nor II follows
E. both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. only II follows
C. either I or II follows
D. neither I nor II follows
E. both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. only II follows
C. either I or II follows
D. neither I nor II follows
E. both I and II follow
- A. B
B. E
C. D
D. C
E. A
- A. B
B. A
C. D
D. E
E. Either E or B
- A. B
B. E
C. D
D. C
E. A
- A. B
B. F
C. K
D. W
E. None of these
- A. 60
B. 61
C. 62
D. 58
E. None of these
- A. North-East
B. Norst-West
C. North
D. West
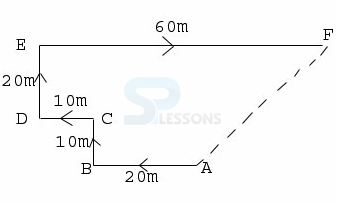
- A. 35 meter, North
B. 30 meter, South
C. 35 meter, East
D. 30 meter, North
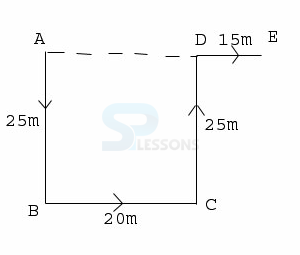
- A. 30 meters, West
B. 10 meters, West
C. 30 meters, North
D. 10 meters, North
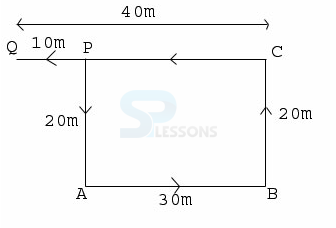
- A. East
B. North
C. West
D. South
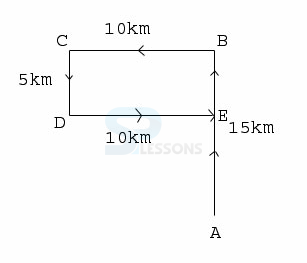
- A. In the South-West
B. In the North-West
C. In the East
D. At the starting Point
- A. Q # 7
B. $ R F
C. 3 3 C
D. 3 # 7
E. E 3 6
- A. & Y V
B. U V N
C. C F E
D. 1 N L
E. None of these
- A. F
B. C
C. 7
D. $
E. None of these
- A. One
B. Two
C. None
D. Three
E. More than three
- A. L
B. 6
C. N
D. 1
E. None of these
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. Fossiles
B. History
C. Tissues
D. Hormones
- A. Sad
B. Despair
C. Pain
D. Cry
- A. Carbohydrates
B. Minerals
C. Vitamins
D. Proteins
- A. Ink
B. Cap
C. Paper
D. Word
- A. Sculptor
B. Cobbler
C. Chef
D. Mason
- A. Duckling
B. Cub
C. Kitten
D. Puppy
- A. Darjeeling
B. Shimla
C. Agra
D. Ooty
- A. Ear
B. Eye
C. Nose
D. Throat
- A. Mumbai
B. Chennai
C. Vishakhapatnam
D. Delhi
- A. GEETA
B. QURAN
C. BIBLE
D. PANCHSHEEL
- A. Nurse
B. Doctor
C. Treatment
D. Patient
- A. Lawn
B. Garden
C. Park
D. Field
- A. Editor
B. Reader
C. Paper
D. Press
- A. Governor
B. M.P
C. Legislator
D. Minister
- A. Food
B. Laziness
C. Hunger
D. Race
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 19, 13
B. 19, 15
C. 21, 13
D. 19, 13
E. 19, 17
- A. 30
B. 29
C. 900
D. 961
E. 31
- A. 25, 27, 25
B. 20, 25, 27
C. 17, 23, 29
D. 13, 20, 29
E. 12, 20, 31
- A. 444
B. 44444
C. 444444
D. 4444
E. 44
- A. 500000
B. 400000
C. 50000
D. 6000000
E. 5000
- A. 326
B. 248
C. 392
D. 414
- A. 84
B. 63
C. 98
D. 91
E. 65
- A. 20-10
B. 15-12
C. 45-27
D. 30-18
- A. 27
B. 39
C. 42
D. 48
E. 24
- A. 7324
B. 9611
C. 1754
D. 2690
- A. 629
B. 667
C. 713
D. 693
E. 824
- A. 5271
B. 5269
C. 5259
D. 5283
E. 5536
- A. 6228
B. 6230
C. 6218
D. 6229
E. 6231
- A. 125
B. 216
C. 64
D. 512
E. 343
- A. 3013
B. 3007
C. 3017
D. 3023
E. 2983
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B .2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 74 years
B. 78 years
C. 86 years
D. 80 years
- A. Rs. 4, Rs. 23
B. Rs. 13, Rs. 17
C. Rs. 15, Rs. 14
D. Rs. 17, Rs. 13
- A. 2/13
B. 1/40
C. 13/40
D. Data inadequate
- A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. Data inadequate
- A. 45
B. 60
C. 75
D. 90
- A. During the 40s and the 50s claws, antlers, horns, tusks and other animal parts were in great demand for their medicinal uses which prompted most tribals to kill animals.
B. During the 40s and the 50s, the government built a dam in the vicinity of North Indian forest.
C. The extensive government-sponsored logging operations of the 40s and the 50s in the North Indian forests led to the immediate extinction of rodents, a major prey of snakes.
D. The government undertook a forestation to receive the forests to prevent the extinction of snakes in North India but failed miserably.
E. None of these
- A. The producers and directors in Bollywood actually keep in mind the public mood while making movies.
B. A movie's success does not depend upon various parameters like who the hero or heroine is, whose music it has, who's directing or producing it etc.
C. Many movies that copied the formula of a successful movie went on to become, some of the great flops.
D. Almost all the Bollywood authors are uninnovative and have run out of ideas and so tend to simply 'redesign' a recent hit.
E. None of these
- A. Most other booksellers in the market charge almost the same as what this book manufacturer does.
B. The fashion of reading books is fast catching up with the people in urban society and they are unmindful of the price.
C. Most readers are unmindful of the quality of books so far as the print is legible.
D. The WTO predicated that inflation in cities would come down in the coming days.
E. None of these.
- A. The cost of manufacturing mobiles in Japan is 8% more than that in China.
B. The labor cost in China is 12% more than in Japan.
C. China and India have a mutually supportive cultural relationship.
D. Japan has had an undue competitive edge over China.
E. None of these
- A. Most people from Rampur work at Jaipur and buy food items at Jaipur which they leave at home.
B. The population of Jaipur is not less than Rampur's.
C. Lakhs of devotees from cities visit Rampur's ancient temple of Lord Rama on weekends.
D. A recent survey found that on an average a person from Rampur eats four times the quantity of chat a person from Jaipur eats.
E. None of these.