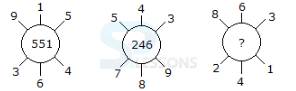
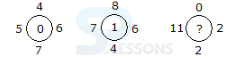
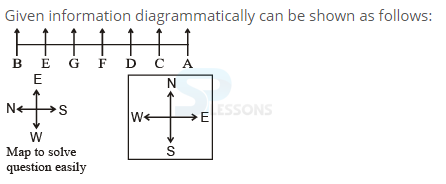
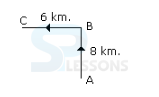
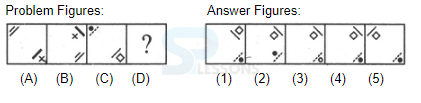
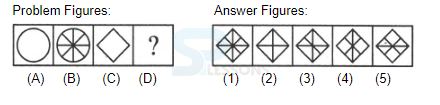
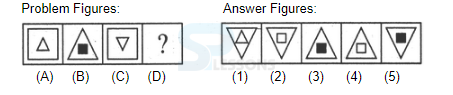
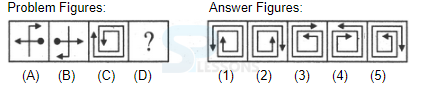
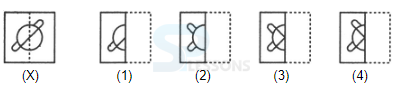
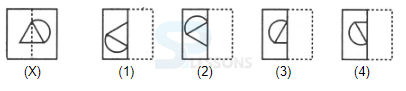
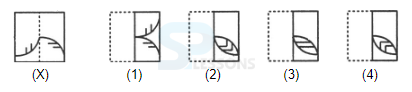
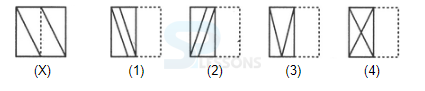
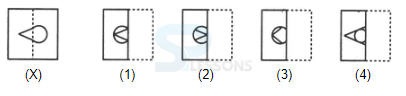
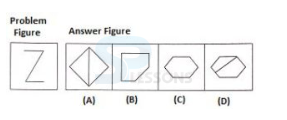
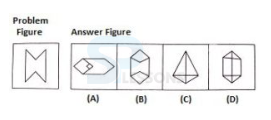
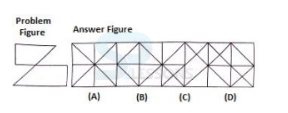
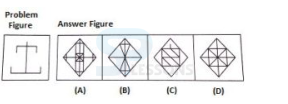
Introduction
Introduction
 Pattern
Pattern
Scheme of Main Examination for recruitment to the post of Upper Division Clerk (UDC) in ESIC is as follows:
- Main Examination is an objective test.
- The test will have four sections.
- The overall test duration is for 2 hour (No separate sectional duration).
- The test contain 200 questions with Maximum of 200 marks.
- The marks obtained in Phase – II will be considered for final selection.
- The candidates will be shortlisted for Phase-III in the ratio of 1:5 i.e. about 5 times the number of vacancies in each category on the basis of their performance in Phase - II.
| Name of the Test (Objective Tests) | No. of Qs. | Max. Marks | Duration | Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Intelligence and Reasoning | 50 | 50 | 2 hour | Bilingual |
| General Awareness | 50 | 50 | Bilingual | |
| Quantitative Aptitude | 50 | 50 | Bilingual | |
| English Comprehension | 50 | 50 | English | |
| Total | 100 | 200 |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
[Click Here] for ESIC UDC Reasoning Syllabus
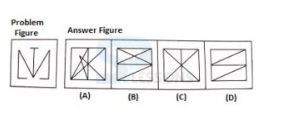
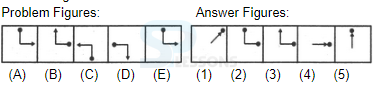
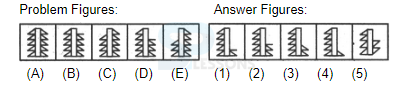
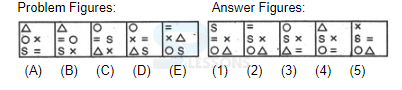
 Samples
Samples
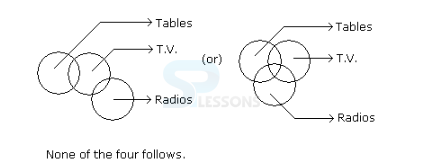
Syllogism
Direction (1 - 5): In each of the following questions two statements are given. Which are followed by four conclusions (1), (2), (3) and (4). Choose the conclusions which logically follow from the given statements.
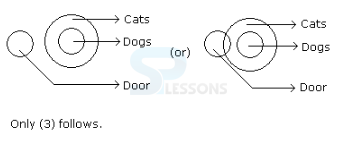
1. Statements: No door is a dog. All the dogs are cats.
Conclusions:
1. No door is a cat.
2. No cat is the door.
3. Some cats are dogs.
4. All the cats are dogs.
- A. Only (2) and (4)
B. Only (1) and (3)
C. Only (3) and (4)
D. Only (3)
E. All four
- A. Only (1) and (2)
B. Only (1) and (3)
C. Only (1) and (4)
D. Only (2) and (4)
- A. Only (4)
B. Only (2)
C. Only (3)
D. Only (1)
E. Only (1) and (3)
- A. Only (1) and (4)
B. Only (3) and (4)
C. Only (2) and (4)
D. Only (1) and (2)
E. Only (1) and (3)
- A. Only (2) and (4)
B. Only (1) and (3)
C. Only (4)
D. Only (1) and (4)
E. None of the four.
- A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
- A. 36
B. 48
C. 38
D. 30
- A. 13
B. 14
C. 12
D. 15
- A. 262
B. 622
C. 631
D. 824
- A. 0
B. 2
C. 11
D. 12
- A. A E
B. A B
C. F B
D. C B
E. None of these
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. All information is necessary
E. None of these
- A. C F
B. A C
C. C F
D. A F
E. None of these
- A. G
B. F
C. E
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
- A. F
B. D
C. C
D. A
E. None of these
- A. None
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
E. Four
- A. R
B. P
C. U
D. T
E. None of these
- A. T, V
B. V, Q
C. W, P
D. R, P
E. None of these
- A. S
B. R
C. V
D. Q
E. None of these
- A. W, T
B. P, U
C. S, Q
D. R, P
E. P, Q
- A. IV
B. V
C. VI
D. VII
E. None of these
- A. III
B. II
C. VII
D. IV
E. No step like this is possible
- A. aim 49 can zen 16 yet vast 33 54 87 82
B. vast last can aim zen 16 yet 33 87 82 54 49
C. zen 49 last zen 16 82 yet can vast 33 aim 54 87
D. aim 49 last zen 82 yet can vast 33 87 54 16
E. None of these
- A. 87
B. 16
C. 33
D. zen
E. aim
- A. zen yet vast last can aim 16 33 49 54 82 87
B. aim can last vast yet zen 16 33 49 54 82 87
C. aim can last vast yet zen 87 82 54 49 33 16
D. zen yet vast last can aim 87 82 54 49 33 16
E. None of these
- A. Brother
B. Sister
C. Brother-in-law
D. Sister-in-law
- A. Father
B. Brother
C. Grandfather
D. Uncle
- A. Nephew
B. Uncle
C. Son
D. Cousin
- A. Daughter
B. Grand-daughter
C. Mother
D. Sister
- A. Son
B. Brother
C. Cousin
D. Grand-Son
- A. ATSSTS
B. EQDDYD
C. ESDDYD
D. EQDDZD
- A. SQBHOHOF
B. UQBHOIOF
C. UQBHOHOI
D. UQBHOHOF
- A. ATAETNR
B. OTAETNR
C. OTAESNR
D. STAETNR
- A. CPNCBZ
B. CPNCBX
C. DPNCBZ
D. DPNCBX
- A. EJTQPTF
B. EJTQPTG
C. CHRPNRD
D. CHRONRD
- A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Only 3 & 4
D. Only 3
E. None of these
- A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Only 3
D. Only 3 & 4
E. None of these
- A. Only 1
B. Either 2 or 3
C. Only 2
D. Either 3 or 4
E. None of these
- A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Only 2 & 3
D. Either 3 or 4
E. None of these
- A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Either 1 or 2
D. Only 4
E. None of these
- A. B
B. F
C. K
D. W
E. None of these
- A. 60
B. 61
C. 62
D. 58
E. None of these
- A. 29
B. 36
C. 27
D. 35
E. None of these
- A. A
B. C
C. B
D. D
E. None of these
- A. R
B. S
C. T
D. Q
E. None of these
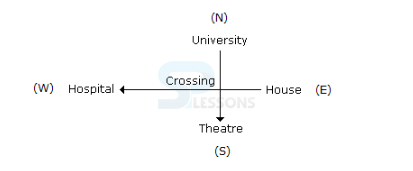
- A. East
B. West
C. South
D. Data inadequate
- A. 10 km.
B. 16 km.
C. 14 km
D. 2 km.
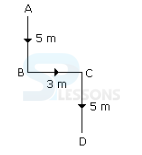
- A. West
B. South
C. South-West
D. South-East
- A. North-East
B. South
C. North
D. South-West
- A. North
B. South
C. East
D. West
- A. U-121
B. U-122
C. V-122
D. V-128
- A. 9
B. 10
C. 12
D. 19
- A. BX17
B. BY17
C. CY17
D. CY18
E. CZ17
- A. K25P
B. L25P
C. L25O
D. L27P
- A. 27U24
B. 45U15
C. 47U15
D. 47V14
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. Nurse
B. Doctor
C. Treatment
D. Patient
- A. Lawn
B. Garden
C. Park
D. Field
- A. Editor
B. Reader
C. Paper
D. Press
- A. Governor
B. M.P
C. Legislator
D. Minister
- A. Food
B. Laziness
C. Hunger
D. Race
- A. Asia
B. Europe
C. Australia
D. India
- A. Sindhi
B. Arabic
C. German
D. Hindi
- A Hen
B Foal
C Leveret
D Lamb
- A. Delhi
B. Lucknow
C. Hyderabad
D. Jaipur
- A. AIDS
B. Cholera
C. Health
D. Cancer
- A. Food
B. Laziness
C. Hunger
D. Race
- A. Build
B. Construction
C. Destruction
D. Manufacture
- A. Cage
B. Sky
C. Nest
D. Water
- A. Cells
B. Power
C. Terminals
D. Energy
- A. Cap
B. Tie
C. Coat
D. Gown
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 194
B. 192
C. 196
D. 195
E. 197
- A. 40
B. 50
C. 56
D. 42
E. 38
- A. 3172
B. 3414
C. 3192
D. 3429
E. 3439
- A. 130
B. 123
C. 102
D. 132
E. 120
- A. 36
B. 72
C. 100
D. 112
E. 20
- A. 39
B. 21
C. 83
D. 51
- A. 19
B. 17
C. 29
D. 23
E. 27
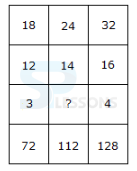
- A. 34, 4, 8
B. 22, 4, 5
C. 54, 4, 13
D. 37, 4, 9
- A. 5
B. 3
C. 13
D. 11
E. 9
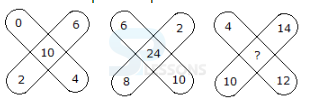
- A. 161
B. 115
C. 391
D. 253
E. 345
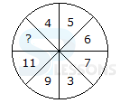
- A. 63
B. 81
C. 90
D. 99
- A. 23
B. 82
C. 97
D. 113
- A. 12
B. 13
C. 15
D. 31
- A. 169
B. 248
C. 261
D. 268
- A. 18
B. 132
C. 136
D. 140
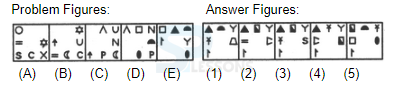
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 22
B. 23
C. 25
D. 35
- A. Rs. 4, Rs. 23
B. Rs. 13, Rs. 17
C. Rs. 15, Rs. 14
D. Rs. 17, Rs. 13
- A. 71 years
B. 72 years
C. 74 years
D. 77 years
- A. Thumb
B. Index finger
C. Middle finger
D. Ring finger
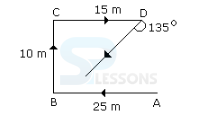
- A. 20 m
B. 22 m
C. 24 m
D. 26 m
- A. Only I follows
B. Only I and II follow
C. Only II and III follow
D. Only III follows
E. All follow
- A. Only I follows
B. Only I and II follow
C. Only II follows
D. All follow
E. None of these
- A. Only I and II follow
B. Only I follows
C. Only II follows
D. All follow
E. None follows
- A. Only I follows
B. Only I and II follow
C. Only I and III follow
D. All follow
E. None of these
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Only I and III follow
D. Only I and II follow
E. None follows