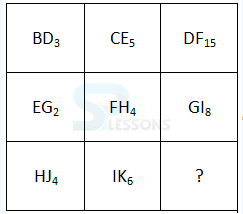
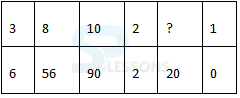
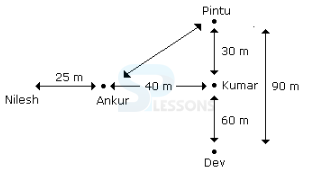
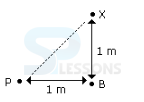
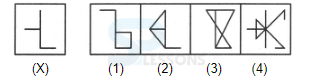
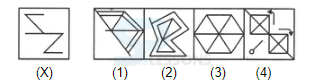
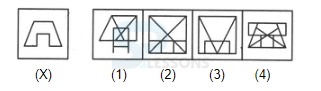
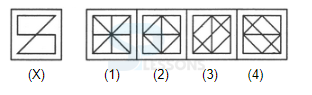
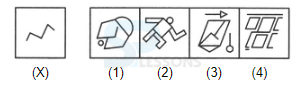
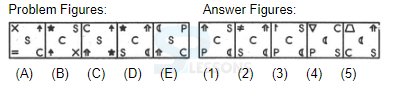
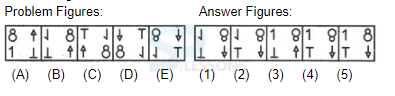
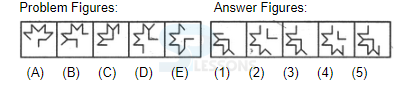
Introduction
Introduction
 Pattern
Pattern
Scheme of Main Examination for recruitment to the post of Stenographer in ESIC is as follows:
- Main Examination is an objective test.
- The test will have three sections (with separate timings for each section).
- The marks obtained in Phase – I will be considered for final selection.
- The candidates will be shortlisted for Phase-II in the ratio of 1:10 i.e. about 10 times the number of vacancies in each category on the basis of their performance in Phase - I.
| Name of the Test | No. of Qs | Max. Marks | Duration | Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English Language & Comprehension | 100 | 100 | 70 minutes | Hindi and English except English Language & Comprehension |
| Reasoning Ability | 50 | 50 | 35 minutes | |
| General Awareness | 50 | 50 | 25 minutes |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
[Click Here] for ESIC Steno Reasoning Ability Syllabus.
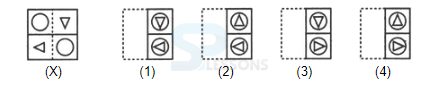
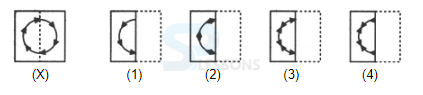
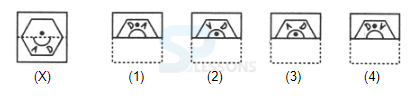
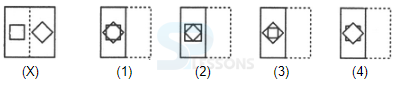
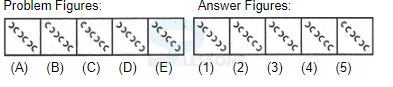
 Samples
Samples
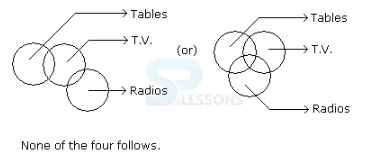
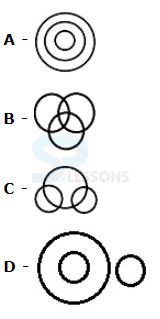
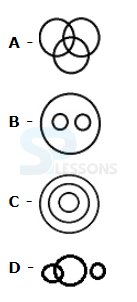
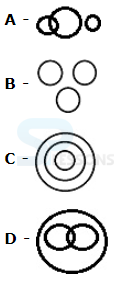
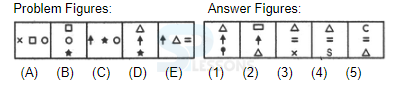
Syllogism
Directions (1-5): In each of the following questions two statements are given. Which are followed by four conclusions (1), (2), (3) and (4). Choose the conclusions which logically follow from the given statements.
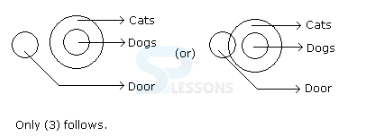
1. Statements: No door is dog. All the dogs are cats.
Conclusions:
1. No door is a cat.
2. No cat is a door.
3. Some cats are dogs.
4. All the cats are dogs.
- A. Only (2) and (4)
B. Only (1) and (3)
C. Only (3) and (4)
D. Only (3)
E. All four
- A. Only (1) and (2)
B. Only (1) and (3)
C. Only (1) and (4)
D. Only (2) and (4)
- A. Only (4)
B. Only (2)
C. Only (3)
D. Only (1)
E. Only (1) and (3)
- A. Only (1) and (4)
B. Only (3) and (4)
C. Only (2) and (4)
D. Only (1) and (2)
E. Only (1) and (3)
- A. Only (2) and (4)
B. Only (1) and (3)
C. Only (4)
D. Only (1) and (4)
E. None of the four.
- A. 10B
B. 10C
C. 9C
D. 7C
- A. E12
B. D12
C. H10
D. G12
- A. 28E
B. 28C
C. 28G
D. 28K
- A. KS24
B. JL24
C. DG24
D. BP24
- A. 5
B. 0
C. 7
D. 3
- A. Immediate Left
B. Second Left
C. Third Left
D. Immediate Right
E. None of the above
- A. R
B. W
C. E
D. T or E
E. None of the above
- A. Q
B. Q or R
C. R or E
D. E
E. R or W
- A. QT
B. TR
C. RW
D. WE
E. QE
- A. QTR
B. TRW
C. EWR
D. TRE
E. TQR
- A. Romil
B. Rohit
C. Anil
D. Abhishek
E. Rahul
- A. Ramesh and Rakesh
B. Rahul and Rohit
C. Anil and Ramesh
D. Abhishek and Rahul
E. Rohit and Abhijeet
- A. Romil-Bhopal
B. Anil-Bengaluru
C. Rohit-Delhi
D. Abjijeet-Delhi
E. Abhishek-Patna
- A. Third to the right
B. Fourth to the left
C. Fifth to the right
D. Second to the right
E. Third to the left
- A. Third to the left
B. Third to the right
C. Second to the left
D. Immediate left
E. None of these
- A. 38
B. Professor
C. Study
D. 51
E. None of these
- A. 9th from the left
B. 2nd from the right
C. 8th from the left
D. 5th from the right
E. None of these
- A. 38
B. 57
C. Correct
D. Doctor
E. None of these
- A. Step V
B. Step VI
C. Step VII
D. There is no such step.
E. None of these
- A. Five
B. Six
C. Seven
D. Eight
E. None of these
- A. Daughter
B. Grand-daughter
C. Mother
D. Sister
- A. Son
B. Brother
C. Cousin
D. Grand-Son
- A. Son
B. Grandfather
C. Uncle
D. Brother
- A. Brother
B. Brother-in-law
C. Cousin
D. Father-in-law
- A. His son’s
B. His father's
C. His nephew’s
D. His own
- A. CPNCBX
B. CPNCBZ
C. CPOCBZ
D. CQOCBZ
E. None of these
- A. CHRONRD
B. DSOESPI
C. ESJTPTF
D. ESOPSID
E. None of these
- A. CHMFINTK
B. LNKTCHMF
C. LNTKCHMF
D. NITKHCMF
E. None of these
- A. QDFHS
B. SDFHS
C. SHFDQ
D. UJHFS
E. None of these
- A. EOJDJEFM
B. EOJDEJFM
C. MFEJDJOE
D. MFEDJJOE
E. None of these
- A. Only II, III and IV are true
B. Only I, III and IV are true
C. Only I and II are true
D. Only II and IV are true
E. None of these
- A. Only Conclusion I is true
B. Either Conclusion I or II is true
C. Only Conclusion II is true
D. Both Conclusion I and II are true
E. Neither conclusion I nor II is true
- A. Only Conclusion II is true
B. Neither conclusion I nor II is true
C. The only conclusion I is true
D. Either conclusion I or II is true
E. Both conclusion I or II are true
- A. The only conclusion I is true
B. Either conclusion I or II is true
C. Neither conclusion I nor II is true
D. Only conclusion II is true
E. Both conclusion I and II are true
- A. Both conclusion I and II are true
B. Neither conclusion I nor II is true
C. Either conclusion I or II is true
D. Only conclusion II is true
E. The only conclusion I is true
- A. 6
B. 7
C. 8
D. 11
E. 5
- A. R
B. S
C. T
D. Either (b) or (c)
E. None of these
- A. U
B. P
C. S
D. CND
E. R
- A. 36
B. 35
C. 33
D. 34
E. None of these
- A. 51
B. 50
C. 49
D. CND
E. None of these
- A. Dev
B. Nilesh
C. Ankur
D. Pintu
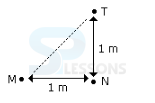
- A. 215 m
B. 155 m
C. 245 m
D. 185 m
- A. North
B. South
C. North-East
D. South-West
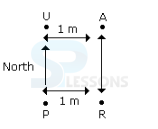
- A. North-West
B. North-East
C. South-West
D. South-East
- A. East
B. West
C. North
D. South
- A. H9R
B. H10Q
C. H10R
D. I10R
- A. Y44B
B. Y66B
C. Y88B
D. Z88B
- A. 36I19
B. 36J21
C. 48J21
D. 48J23
- A. I11T
B. L11S
C. L12T
D. L12S
- A. 5FU
B. 15LS
C. 9IT
D. 17OR
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
E. Both A and R are false.
- A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
E. Both A and R are false.
- A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
E. Both A and R are false.
- A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
E. Both A and R are false.
- A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
E. Both A and R are false.
- A. Ears
B. Vestibular
C. Eyes
D. Nose
- A. Potato
B. Tamarind
C. Lemon
D. Orange
- A. RAM
B. Cache
C. LAN
D. PROM
- A. Nickel
B. Cobalt
C. Aluminium
D. Iron
- A. Error
B. Howler
C. Slip
D. Blurred
- A. Hidden
B. Forthright
C. Outcome
D. Forward
- A. Ear
B. Hearing
C. Noise
D. Commotion
- A. Fish: River
B. Aeroplane: Sky
C. Bouquet: Flower
D. Ship: Fleet
- A. Pen: Ink
B. Ball: Stick
C. Fruit: Juice
D. Grass: Horses
- A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Humidity
D. Altitude
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 12
B. 19
C. 42
D. 32
E. None of the above
- A. 41
B. 61
C. 52
D. 31
E. 6
- A. 5
B. 19
C. 39
D. 26
E. 54
- A. 1
B. 16
C. 26
D. 9
E. 49
- A. 2177
B. 729
C. 125
D. 1
E. 121
- A. 39
B. 21
C. 83
D. 51
- A. 19
B. 17
C. 29
D. 23
E. 27
- A. 34, 4, 8
B. 22, 4, 5
C. 54, 4, 13
D. 37, 4, 9
- A. 5
B. 3
C. 13
D. 11
E. 9.
- A. 161
B. 115
C. 391
D. 253
E. 345
- A. 7: 343
B. 9: 243
C. 10: 500
D. 5: 75
- A. 6: 216
B. 7: 1029
C. 8: 448
D. 9: 729
- A. 30: 100
B. 23: 72
C. 19: 58
D. 11: 43
- A. 562
B. 471
C. 382
D. 281
- A. 453
B. 417
C. 336
D. 255
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
- A. 13
B. 15
C. 17
D. 20
- A. 40 years
B. 45 years
C. 50 years
D. 60 years
- A. 18
B. 22
C. 42
D. 43
- A. 120 grams
B. 140 grams
C. 240 grams
D. 280 grams
E. None of these
- A. Rs. 236
B. Rs. 240
C. Rs. 248
D. Rs. 252
- A. if only argument I is strong.
B. if only argument II is strong.
C. if either I or II is strong.
D. if neither I nor II is strong.
E. if both I and II are strong.
- A. if only argument I is strong.
B. if only argument II is strong.
C. if either I or II is strong.
D. if neither I nor II is strong.
E. if both I and II are strong.
- A. if only argument I is strong.
B. if only argument II is strong.
C. if either I or II is strong.
D. if neither I nor II is strong.
E. if both I and II are strong.
- A. if only argument I is strong.
B. if only argument II is strong.
C. if either I or II is strong.
D. if neither I nor II is strong.
E. if both I and II are strong.
- A. if only argument I is strong.
B. if only argument II is strong.
C. if either I or II is strong.
D. if neither I nor II is strong.
E. if both I and II are strong.