Introduction
Introduction
Electric Circuits and Fields is a core course in every Electrical Engineering curriculum, with a wide range of applications to a variety of problems related to electrical in general. The chapter includes some of basic fundamental questions of Electric Circuits and Fields primarily instrumental for aspirants of recruitment exams in India and also for aspirants of The Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering [GATE] in India.
 Quiz
Quiz
Q1. Coulomb’s law is true for
- A. atomic distances ([latex]= {10}^{–11m}[/latex])
B. nuclear distances ([latex]= {10}^{–15m}[/latex])
C. charged as well as uncharged particles
D. all the distances
Answer: D
- A. positive
B. negative
C. zero
D. none of these
Answer: C
- A. increases
B. decreases
C. remains constant
D. may increase or decrease depending on the actual temperature.
Answer: C
- A. joule
B. henry
C. farad
D. ampere
Answer: C
- 1. Kirchoff’s junction law follows from conservation of charge.
2. Kirchoff’s loop law follows from conservative nature of electric field.
- A. [latex]{m}^{–1}[/latex]
B. [latex]{m}^{1}[/latex]
C. m
D. 2.5m
Answer: C
- A. diode
B. copper wire
C. filament lamp
D. carbon resistor
Answer: A
- A. charge
B. energy
C. momentum
D. angular momentum
Answer: A
- A. 36 × 105joule
B. 36 × 103joule
C. 103joule
D. 105joule
Answer: A
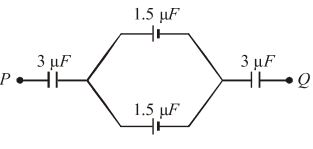
- A. 1mF
B. 1.5mF
C. 9
D. 6.75mF
Answer: A
Q11. Specific resistance of a conductor depends upon:
- A. composition of the conductor
B. length of the conductor
C. area of cross-section of the conductor
D. resistance of the conductor
Answer: A
- A. decreases
B. increases
C. becomes zero
D. remains constant
Answer: D
- A. ohm/m
B. m/ohm
C. mho/m
D. mho
Answer: C
- A. 36 × 105 Watts
B. 36 × 105 ergs
C. 36 × 105 Joules
D. 36 × 105 B.T.V
Answer: C
- A. closed loops in a network
B. electronic circuits
C. junctions in a network
D. electric circuits
Answer: D
- A. nichrome
B. carbon
C. tungsten
D. copper
Answer: C
- A. D.c. circuits
B. High currents
C. Small resistors
D. Semiconductors
Answer: D
- A. copper
B. carbon
C. steel
D. nichrome
Answer: D
- A. kg wt
B. newton
C. joule
D. N-m
Answer: D
- A. power resistor
B. non-metallic resistor
C. carbon resistor
D. variable resistor
Answer: B
Q21. In MKS system one Kilowatt is equal to
- A. 1.36 HP
B. 1.34 HP
C. 1.5 HP
D. 1.6 HP
Answer: C
- A. current stabilizers
B. as heating elements
C. for inductive circuits
D. to suppress surges
Answer: B
- A. LDR
B. NTC thermistors
C. Nichrome conductors
D. ACSR conductors
Answer: D
- A.
B.
C.
D. None of the above
Answer: B
- A. [latex]\frac {q}{0}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {0}{q}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac {2q}{0}[/latex]
D. Zero
Answer: C
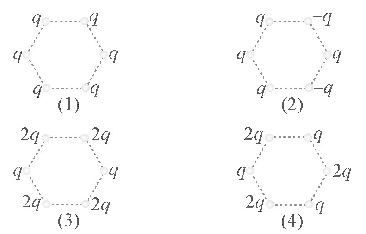
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: D
- A. E is necessarily zero on the surface
B. E is perpendicular to the surface at every point
C. The total flux through the surface is zero
D. The flux is only going out of the surface
Answer: B
- A. electric field is zero but potential is not zero
B. electric field is not zero but potential is zero
C. neither electric field nor potential is zero
Answer: C
- A. 2F
B. [latex]\frac {F}{2}[/latex]
C. 0
D. [latex]\sqrt{2}F[/latex]
Answer: A
- A. [latex]{3}\sqrt{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]{4}\sqrt{2}[/latex]
C. [latex]{5}\sqrt{2}[/latex]
D. 7
Answer: D
Q31. The RMS value of the voltage u(t)=3+4cos(3t)is
- A. [latex]\sqrt{17}V[/latex]
B. 5V
C. 7V
D. ([latex]3+2\sqrt{2}V[/latex]
Answer: A
- A. [latex]O \overrightarrow{E}[/latex]
B. E
C. Null Vector
D. Zero
Answer: C
- A. [latex]\frac {3}{4{\pi}_{o}} \frac {{q}_{r}}{{R}^{3}}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {4}{3{\pi}_{o}} \frac {{q}_{r}}{{R}^{3}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac {3}{2{\pi}_{o}} \frac {{q}_{r}}{{R}^{2}}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {3}{4{\pi}_{o}} \frac {{q}_{r}}{{R}^{4}}[/latex]
Answer: A
- A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
Answer: A
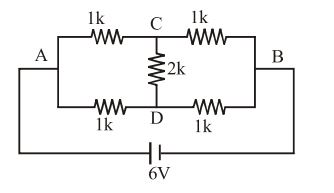
- A. zero
B. 1 mA
C. 2 mA
D. 6 mA
Answer: A
- A. A capacitor resists an abrupt change in the voltage across it in a manner analogous to the way a spring resists abrupt change in the current flowing through it.
B. A capacitor resists an abrupt change in the current flowing through it.
C. It is impossible to change the voltage across a capacitor by a finite amount in zero time, for this requires infinite current through the capacitor.
D. A finite amount of energy can be stored in a capacitor even if the current through the capacitor is zero, such as when the voltage across it is a constant.
Answer: B
- A. increase
B. Decrease
C. remain nearly the same
D. become in determinant
Answer: B
- A. Area of the conductor.
B. Length of the conductor.
C. Type of material.
D. None of these.
Answer: A
- A. 0.02 F
B. 0.5 F
C. 0.05 F
D. 0.2 F
Answer: C
- A. 1ohm of resistance
B. Ratio of 1 V to 1 C
C. Ratio of 1 C to 1 V
D. None of these
Answer: C
Q41. Which of the followings is/are active element?
- A. Voltage source
B. Current source
C. Both
D. None of these.
Answer: C
- A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Zero
D. A finite value
Answer: C
- A. Resistor
B. Bulb
C. Both
D. None of these.
Answer: C
- A. Zero
B. Infinite
C. Finite
D. 100 ohms
Answer: A
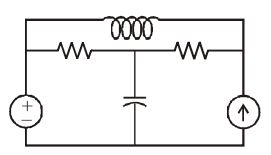
- A. Planar networks
B. Non planar networks
C. Both planar & non-planar networks.
D. Neither planar nor non planar networks
Answer: A
- A. Law of conservation of charge
B. Law of conservation of energy
C. Both
D. None of the above
Answer: A
- A. Zero
B. Minimum
C. Maximum
D. Any of the above
Answer: A
- A. Law of conservation of charge
B. Law of conservation of energy
C. Both
D. None of the above
Answer: B
- A. Current calculations
B. Voltage calculations
C. Power calculations
D. None of the above
Answer: C
- A. Zero
B. Infinite
C. Finite
D. 100 ohms
Answer: B