Description
Description
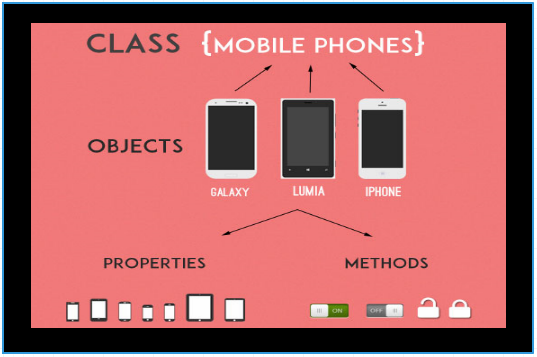
Objects of a class are similar to the variables of a basic C++ program. CPP Object can be declared with a class data type. They represents the divisions of a class. The below diagram shows "Classes and Objects" related to the real world.
Below is the syntax to represent an Object.
class_name object_name;
 Differences
Differences
| Class | Object |
|---|---|
| Class is a data type | CPP Object is an instance of class |
| Class does not occupy memory location | |
| Class generates objects | Objects gives life to class |
| The class cannot demanipulate as it is not available in memory | Objects can be manipulated |
 Description
Description
Access operator . retrieves the data in the CPP object of a class. To access the class members certain rules are available. It depends on the modifiers (Public, Private or Protected) attached to that member.
 Example
Example
[c]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Triangle
{
public:
int base;
int height;
};
int main( )
{
Triangle Tri1;
Triangle Tri2;
int Area = 0.0;
// Triangle 1 specification
Tri1.base = 3.0;
Tri1.height = 4.0;
// Triangle 2 specification
Tri2.base = 5.0;
Tri2.height = 6.0;
// Area of Triangle 1
Area = Tri1.base * Tri1.height ;
cout << "Area of triangle 1 : " << Area <<endl;
// Area of Triangle 2
Area = Tri2.base * Tri2.height ;
cout << "Area of triangle 2 : " << Area <<endl;
return 0;
}[/c]
Output
[c]Area of triangle 1 : 12
Area of triangle 2 : 30[/c]
 Description
Description
The main aim of Object Oriented Programming is to hide the data and provide security to the application users. Modifiers of classes are used to achieved them as they restrict the hackers without providing the access to the class members and data present in it. So, modifiers also called as " Access Specifiers". Three access specifiers are available. They are:
Access Specifiers :
- Public
- Private
- Protected
 Description
Description
The member of a class with Public Access Specifier is accessed anywhere outside the class but only inside the program. The variables declared with public keyword can be retrieved and accessed without member function.
 Example
Example
[c]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Triangle
{
public:
double base;
void setBase( double bas );
double getBase( void );
};
// Member functions definitions
double Triangle::getBase(void)
{
return base ;
}
void Triangle::setBase( double bas )
{
base = bas;
}
// Main function for the program
int main( )
{
Triangle tri;
// set line base
tri.setBase(3.0);
cout << "Base of triangle : " << tri.getBase() <<endl;
// set line length without member function
tri.base = 6.0; // base is public
cout << "Base of triangle is : " << tri.base <<endl;
return 0;
}[/c]
Output
[c]
Base of triangle : 3
Base of triangle is : 6
[/c]
 Description
Description
The member of a class with Private Access Specifier is not accessible and viewed outside of the class. The variables declared with private keyword can be retrieved and accessed only by class and neighbour functions. By default, all the members of class are declared as private.
 Example
Example
[c]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Triangle
{
public:
double base;
void setHeight( double hei );
double getHeight( void );
private:
double height;
};
// Member functions definitions
double Triangle::getHeight(void)
{
return height ;
}
void Triangle::setHeight( double hei )
{
height = hei;
}
// Main function for the program
int main( )
{
Triangle tri;
// set box base without member function
tri.base = 15.0; // OK: because base is public
cout << "base of box : " << tri.base <<endl;
// set box width without member function
// tri.height = 10.0; // Error: because height is private
tri.setHeight(25.0); // Use member function to set it.
cout << "height of box : " << tri.getHeight() <<endl;
return 0;
}[/c]
Output
[c]
base of box : 15
height of box : 25[/c]
 Description
Description
The member of a class with Protected Access Specifier is not accessible and viewed outside the class same as Private Access Specifier. But, the advancement in protected is, the child class members can access it otherwise called as Derived Classes. It is a sub class of a class.
 Example
Example
[c]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Pyramid
{
protected:
double base;
};
class Triangle:Pyramid // SmallBox is the derived class.
{
public:
void setSmallBase( double bas );
double getSmallBase( void );
};
// Member functions of child class
double Triangle::getSmallBase(void)
{
return base ;
}
void Triangle::setSmallBase( double bas )
{
base = bas;
}
// Main function for the program
int main( )
{
Triangle pyramid;
// set box width using member function
pyramid.setSmallBase(25.0);
cout << "Base of pyramid : "<< pyramid.getSmallBase() << endl;
return 0;
}[/c]
Output
[c]
Base of pyramid : 25
[/c]
 Key Points
Key Points
- CPP Object is an instance of class.
- Modifiers also called as Access Specifiers (Public, Private and Protected)