Description
Description
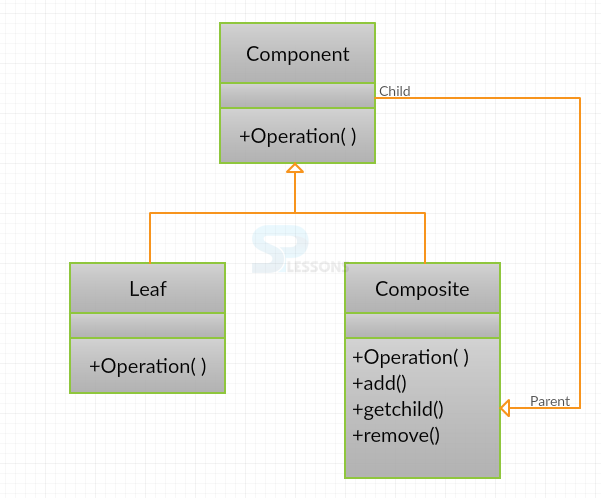
Composite Pattern is used when a set of objects are to be considered as a single object. It is a type of structural pattern. The objects in composite pattern will be represented in tree structure and forms the whole hierarchy. Tree structure consists of leaf, nodes, and root.
 Advantages
Advantages
- Primitive and complex objects can be defined inside the class hierarchy.
- New components can be added easily.
- Class contains its own objects.
- Structure of the class and interface is flexible.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
- Component: Component is the abstraction for leafs and composites. It is used to define the interface that is to be implemented by the objects in the composition.
- Leaf : Leaf objects do not have children. Leaf implements the services described by the Component interface.
- Composite : A Composite can be used to store the child components in addition to implementing the methods that are defined by the component interface. Composites provide additional methods for adding, deleting, and getting components as well.
 Examples
Examples
Creating an interface Shape
[java]public interface Shape
{
public void draw(String fillColor);
}[/java]
Creating a class Rectangle that implements the interface Shape.
[java]
public class Rectangle implements Shape
{
public void draw(String fillColor)//overrides the interface method
{
System.out.println("Drawing Rectangle with color "+fillColor);
}
}[/java]
Creating a class Oval that implements the interface Shape.
[java]
public class Ovel implements Shape
{
public void draw(String fillColor)//overrides the interface method
{
System.out.println(" Ovel Circle with color "+fillColor);
}
}[/java]
Importing the packages java.util.Arraylist and java.util.List.
Creating a class Drawing and implementing the interface Shape.
[java]import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Drawing implements Shape
{
private List;Shape; shapes = new ArrayList;Shape();
public void draw(String fillColor)//overrides the interface method
{
for(Shape sh : shapes)
{
sh.draw(fillColor);
}
}
public void add(Shape s)
{
this.shapes.add(s);
}
public void remove(Shape s)
{
shapes.remove(s);
}
public void clear()
{
System.out.println("Clearing all the shapes from drawing");
this.shapes.clear();
}
}[/java]
Creating a main class TestCompositePattern.
[java]
public class TestCompositePattern
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Shape tri = new Rectangle();
Shape tri1 = new Rectangle();
Shape cir = new Ovel();
Drawing drawing = new Drawing();
drawing.add(tri1);
drawing.add(tri1);
drawing.add(cir);
drawing.draw("Red");
drawing.clear();
drawing.add(tri);
drawing.add(cir);
drawing.draw("Green");
}
}[/java]
 Output
Output
Result will be as follows.
[java]Drawing Rectangle with color Red
Drawing Rectangle with color Red
Drawing Ovel with color Red
Clearing all the shapes from drawing
Drawing Rectangle with color Green
Drawing Ovel with color Green[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Composite Pattern - Whole Structure is defined in tree structure in hierarchy form.
- Composite Pattern are mostly used in swings.