Description
Description
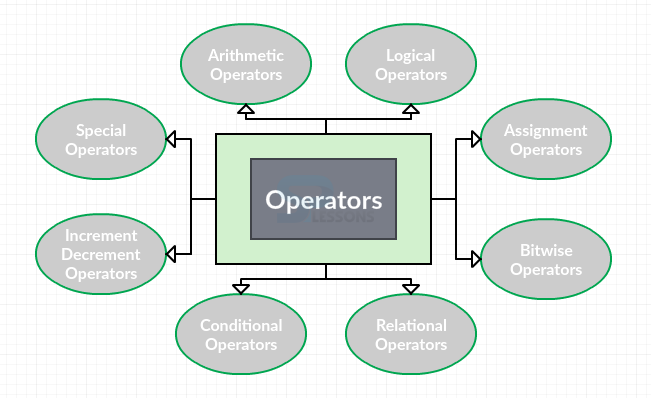
C Operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform mathematical or logical operation on the variables or a value. C language has rich set of built-in operators.
For better understanding, C Operators are classified into 8 categories and are described as follows.
 Description
Description
Arithmetic operators performs
mathematical calculations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus.  Operators
Operators
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Two operands are added | x+y gives 30 |
| - | Subtracts second operand from the first | x-y gives -10</td |
| * | Multiplies operands | x*y gives 200 |
| / | Divide numerator by denominator | x/y gives 2 |
| % | Modulus operator and remainder of after an integer division | y%x gives 0 |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num1,num2;
int sum,sub,mult,div,mod;
printf("\nEnter First Number :");
scanf("%d",&num1);
printf("\nEnter Second Number :");
scanf("%d",&num2);
sum = num1 + num2;
printf("\nAddition is : %d",sum);
sub = num1 - num2;
printf("\nSubtraction is : %d",sub);
mult = num1 * num2;
printf("\nMultiplication is : %d",mult);
div = num1 / num2;
printf("\nDivision is : %d",div);
mod = num1 % num2;
printf("\nModulus is : %d",mod);
return(0);
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
Enter First Number :6
Enter Second Number :3
Addition is : 9
Subtraction is : 3
Multiplication is : 18
Division is : 2
Modulus is : 0
[/c]
 Description
Description
Assignment C operator
assigns values to variables.  Operators
Operators
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Assignment operator: Assigns right-hand side(called rvalue)to left-hand side(called lvalue) | z=x+y assigns value of x+y to z |
| += | Add AND Assignment operator: Adds right operand to left operand and assigns the result to left operand | y+=x is equivalent to x=y+x |
| -= | Subtract AND Assignment operator: Subtracts right operand from left operand and assigns result to left operand | y-=x is equivalent to y=y-x |
| *= | Multiply AND Assignment operator: Multiplies right operand from left operand and assigns result to left operand | y*=x is equivalent to x=y*x |
| /= | Divide AND Assignment operator: Divides right operand from left operand and assigns result to left operand | y/=x is equivalent to x=y/x |
| %= | Modulus AND Assignment operator: Takes modulus using two operands and assigns result to left operand | y%=x is equivalent to x=y%x |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a=5;
a+= 3;
printf("\n Result of op1 = %d",a);
a=5;
a-=3;
printf("\n Result of op2 = %d",a);
a=5;
a*=3;
printf("\n Result of op3 = %d",a);
a=5;
a/=3;
printf("\n Result of op4 = %d",a);
a=5;
a%=3;
printf("\n Result of op5 = %d",a);
return 0;
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
Result of op1 = 8
Result of op2 = 2
Result of op3 = 15
Result of op4 = 1
Result of op5 = 2
[/c]
 Description
Description
Relational operators can be used to
compare two variables.  Operators
Operators
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | Checks equal or not, if yes then condition returns true |
| != | Checks equal or not, if values are not equal then returns true |
| > | Checks for greater value |
| < | Checks for lower value |
| >= | Checks for greater than or equal to the value |
| <= | Checks for less than or equal to the value |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num1 = 30;
int num2 = 40;
printf("Value of %d > %d is %d\n",num1,num2,num1> num2);
printf("Value of %d >=%d is %d\n",num1,num2,num1>=num2);
printf("Value of %d <=%d is %d\n",num1,num2,num1<=num2);
printf("Value of %d < %d is %d\n",num1,num2,num1< num2);
printf("Value of %d ==%d is %d\n",num1,num2,num1==num2);
printf("Value of %d !=%d is %d\n",num1,num2,num1!=num2);
return(0);
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
Value of 30 > 40 is 0
Value of 30 >=40 is 0
Value of 30 <=40 is 1
Value of 30 < 40 is 1
Value of 30 ==40 is 0
Value of 30 !=40 is 1
[/c]
 Description
Description
Increment and Decrement Operators are used to
increment or decrement the value assigned to a variable by 1.  Operators
Operators
| Operators | Operator type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ++i | Pre-increment | Value of i incremented before assigning it to variable i |
| i++ | Post-increment | Value of i incremented after assigning it to variable i |
| - -i | Pre-decrement | Value of i decremented before assigning it to variable i |
| i- - | Post-decrement | Value of i decremented after assigning it to variable i |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
void main()
{
int a,b,c,d,x=10,y=10;
a=x++;
b=++y;
c=x--;
d=--x;
printf("Value of a : %d\n",a);
printf("Value of b : %d\n",b);
printf("Value of c : %d\n",c);
printf("Value of d : %d\n",d);
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
Value of a : 10
Value of b : 11
Value of c : 11
Value of d : 9
[/c]
 Description
Description
Logical operators performs
logical operations on given expressions.  Operators
Operators
| Operator | Name of Operator | Output |
|---|---|---|
| && | AND Operator | Output is 1 only when conditions on both sides of operator becomes true |
| || | OR Opeator | Output is 0 only when conditions on both sides of operator becomes false |
| ! | NOT Operator | Gives inverted output |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int a=40,b=20;
int c=20,d=10;
if (a>b && b!=0)
{
printf("&& operator : Both conditions are true\n");
}
if (c>d || d!=20)
{
printf("|| Operator : Only one condition is true\n");
}
if (!(a>b && a!=0))
{
printf("!=Operator : Both conditions are true\n");
}
else
{
printf("!Operator : Both conditions are true but are reversed as false");
}
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
&& operator : Both conditions are true
|| Operator : Only one condition is true
!Operator : Both conditions are true but are reversed as false[/c]
 Description
Description
Bitwise operators are used to
convert values into binary digits.  Operators
Operators
| Operator | Symbol | Form | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Right shift | >> | x>>y | all bits in x shifted right y bits |
| Left shift | << | x<<y | all bits in x shifted left y bits |
| Bitwise AND | & | x&y | each bit in x AND each bit in y |
| Bitwise OR | | | x|y | each bit in x OR each bit in y |
| Bitwise XOR | ^ | x^y | each bit in x XOR each bit in y |
| Bitwise NOT | ~ | ~x | all bits in x flipped |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int a=10,b=20,AND_op,NOT_op,XOR_op,OR_op;
AND_op=(a&b);
OR_op=(a|b);
NOT_op=(~a);
XOR_op=(a^b);
printf("AND_op value = %d\n",AND_op );
printf("OR_op value = %d\n",OR_op);
printf("NOT_op value = %d\n",NOT_op );
printf("XOR_op value = %d\n",XOR_op );
printf("left_shift value = %d\n",a<<1);
printf("right_shift value = %d\n",a>>1);
}
[/c]
[c]
AND_op value = 0
OR_op value = 30
NOT_op value = -11
XOR_op value = 30
left_shift value = 20
right_shift value = 5
[/c]
 Description
Description
Conditional C operator is used to make for
making decisions. It can also be called as "Ternary operator".  Syntax
Syntax
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Condition ? X : Y | Conditional Opeator | Checks the condition. If condition is true, then it returns value X, otherwise value Y</td |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=5,b;
b=(a==5?10 : 0 ) ;
printf("x value is %d\n",a);
printf("y value is %d",b);
}
[/c]
Output:
[c]
x value is 5
y value is 10
[/c]
 Description
Description
Special operators are used along with the above operators. C-language provides some special operators.
 Operators
Operators
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sizeof | Size of operator | Returns the size of a variable |
| * | Pointer Operator | Points to a variable |
| & | Pointer Operator | Returns the address of a variable |
 Example
Example
[c]#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double a;
printf("Size of double=%d bytes\n",sizeof(a));
int *ptr,b;
b=10;
ptr=&b;
printf("%d",*ptr);
return 0;
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
Size of double=8 bytes
10
[/c]
 Key Points
Key Points
- C Operator performs mathematical and logic operations.
- Arithmetic, Assignment, Relational,Increment and Decrement, Logical, Bitwise, Conditional are few types of operators.
 Programming
Tips
Programming
Tips
- Other than variable identifier, do not use increment and decrement C operator with any expression.
- Do not use variable without assigning any value to it.
- Don't confuse between equality operator == with assignment operator =