Description
Description
Termination or sudden problem in C-program may lead to loss of data. So, to overcome this problem in C-language, C-files are used and can be accessed by using C File I/O functions.
File can be defined as the collection of similar data stored permanently in a disk. The data stored in this can be changed if needed and can be used at any time by using C File I/O functions. File is declared in <stdio.h> header file and can be accessed with a pointer.
To declare a file in C language, structure pointer of file type is used.
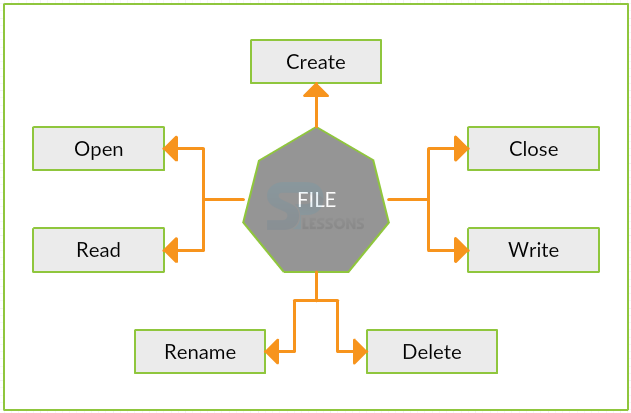
Some of the basic C File IO operations are as shown below.
FILE *fp;
High level C File IO functions can be categorized as:- Text file
- Binary file
| Function | description |
|---|---|
| fopen() | Used to create a new file or open a existing file. |
| fclose() | Used to close a file. |
| fscanf() | Used to read a dataset from a file. |
| fprintf() | Used to write data to a file. |
| getc() | Used to read characters from files. |
| putc() | Used to write a character to a file. |
| getw() | Used to read an integer from a file. |
| putw() | Used to write an integer to a file. |
| rewind() | Used to set the position to the beginning point. |
| ftell() | Used to give current position in the file. |
| fseek() | Used to set the position to required point. |
 Description
Description
The first step in opening a file goes with creating a file by declaring a file pointer and then open the created file. Opening a file is done with
fopen() function.  Syntax
Syntax
*fp = FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode);
(or)
fp=fopen("filename","mode");
In the above syntax,
filename is the name of the file to be opened.
mode in the syntax which denotes the purpose of creating a file.
*fp refers to the opened(or created) file.  Mode Types
Mode Types
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| r | Represents open a file for read |
| w | Represents open empty file for writing |
| a | Represents open a file to append |
| r+ | Represents open a binary file for read and write |
| w+ | Represents open a binary file for write and read |
| r+ | Represents open a binary file for append and read |
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char a;
fp= fopen ("splessons.C");
if(fp==NULL)
{
printf("can't open");
exit(1);
}
}[/c]
exit() function in above program is similar to the return function the C main section.  Description
Description
Various file I/O functions are discussed in the above table which performs reading and writing operations on file.
getc() and putc() are two simple functions to read and write individual characters to a file.
When the user inputs the data, data is written and stored in the file. This can be done by using C File I/O function, fprintf() function. f in the starting represents the file argument pointed to file structure.
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
FILE *fp;
fp=fopen("C:\\splessons.txt");
if(fp==NULL)
{
printf("no file exists");
exit(1);
}
printf"Enter a:");
scanf("%d",&a);
fprintf(fp,"%d",a);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}[/c]
To read the data from a file fscanf() function is used.
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
FILE *fp;
if ((fp=fopen("C:\\aplessons.txt")==NULL)
{
printf("Cannot open the file");
exit(1);
}
fscanf(fp,"%d",&a);
printf("Value of n=%d",a);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}[/c]
 Description
Description
When there is no action to be performed with a file, it can be closed. This can be done by using C File I/O function,
fclose(ptr). Compiler returns zero if the action is complete (or) returns eof if there is any error in closing the file.
[c]
/* fclose example */
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
FILE * pFile;
pFile = fopen ("myfile.txt","wt");
fprintf (pFile, "fclose example");
fclose (pFile);
return 0;
}
[/c]  Description
Description
A file can be renamed as per the requirement. Renaming actually means that the user can give their own names to the file according to their convenience.This can be done with
rename() function.
int rename(const char *old_filename, const char *new_filename)
If the file is renamed zero is returned.Otherwise, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
[c]
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int r;
char oldname[] = "file.txt";
char newname[] = "newfile.txt";
r = rename(oldname, newname);
if(r == 0)
{
printf("File renamed successfully");
}
else
{
printf("Error: unable to rename the file");
}
return(0);
}
[/c]
Output:
[c]
Error: unable to rename the file[/c]
 Description
Description
A file can be deleted if there is no use with it in future. Once the file is deleted, it cannot be restored.This can be done with
remove() function.
int remove(const char *filename)
[c]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main ()
{
int r;
FILE *fp;
char filename[] = "file.txt";
fp = fopen(filename, "w");
fprintf(fp, "%s", "This is splessons.com");
fclose(fp);
r = remove(filename);
if(r == 0)
{
printf("File deleted successfully");
}
else
{
printf("Error: unable to delete the file");
}
return(0);
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
File deleted successfully
[/c]
 Key Points
Key Points
- File is collection of data.
- Opening, closing, writing, reading,deleting and renaming are C File I/O functions.
 Programming
Tips
Programming
Tips
- It is better practice to delete the files if not necessary to save the memory.
- When using string literal as the argument,do not forget to use double backslashes rather than a single backslash as double backslashes \\ escapes the \ key, so the string works as it is expected