Introduction
Introduction
When a number of colored pixels are grouped together in an area, it forms a image. AWT Image Processing refers to a process of calculating a new color to each pixel depending on the existing color or the surrounding color.
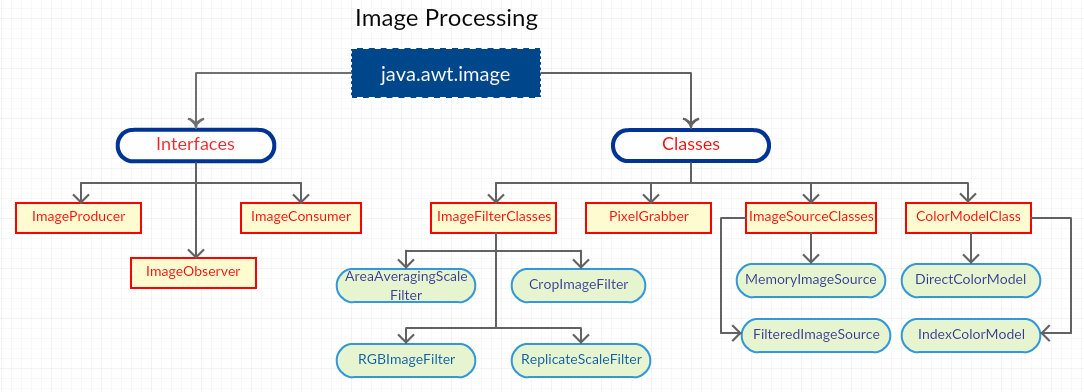
AWT Image Processing chapter covers the following topics that are related to images.
- Interfaces
- Classes
 Description
Description
 Description
Description
The methods of ImageProducer interface are responsible for generating the pixel data and send that data to the Image Consumer, which needs to get registered before sending. This can be done by using the setPixels() method of ImageConsumer interface.
Methods:
- addConsumer() : Adds consumers to the consumer list.
- startProduction() : Tells the producer to send the data to the consumer.
- isConsumer() : Checks the consumer is registered or not.
- removeConsumer() : Removes a consumer if not found registered in the list.
- requestTopDownLeftRightResend() : This method is called to send the pixel data again.
 Description
Description
ImageConsumer interface is responsible to handle the pixel data sent by the producer. There are 7 methods to handle the data in which 2 methods override the setPixels() method.
Methods:
- setHints() : This method is called before the pixel data is sent to decide the type and order of the data. The below table gives the flags of setHinds() method.
Flag Description RANDOMPIXELORDER Data sent in random order. TOPDOWNLEFTRIGHT Data sent from left to right andd top to bottom. COMPLETESCANLINES Complete scan lines are sent when called setPixels() method. SINGLEPASS Single pixel is sent only once. SINGLEFRAME These pixels represents a single image.
- setDimensions() : This method is called to adjust the width and height.
- setProperties() : Image properties are stored in a table and are sent to the consumer when called this method.
- setColorModel() : This method is called to set the color for the pixels data.
- setPixels() : This method is the combination of arguments like height, width, scanLength, pixels, offset, and colorModel.
- imageComplete() : If the image is completely delivered, then this method is called by the consumer.
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| STATICIMAGEDONE | Only one static image is done. |
| SINGLEFRAMEDONE | Only a single frame of the image is done. |
| IMAGEERROR | Occurrence of error while creating an image |
 Description
Description
ImageObserver interface is used to spy on the image generation and function.
Methods:
- imageUpdate() : This method is called to report the status of image. It returns true if asked for more information about the image and returns false if not required. The following arguments are used to know about the image:
Flag Description HEIGHT This returns the image height. WIDTH This is returned if the width of the image is available. FRAMEBITS This is returned if a frame is passed out of multiple frames. SOMEBITS This is returned if the width of the image is available. ALLBITS It is returned when the image is complete. ABORT This method is returned when Image loading is aborted. ERROR Image processing interruption is given by this method.
 Description
Description
PixelGrabber stores the pixel data by capturing them in an array format in MemoryImageSource and this saved image file can be recreated when required. It create subsets for pixels and can send it through the web.
PixelGrabber can modify the images by flipping, rotating and obtaining the mirror image.
Methods:
public PixelGrabber (ImageProducer ip, int x, int y, int width, int height, int pixels[], int offset, int scansize)public synchronized boolean grabPixels (long ms) throws InterruptedExceptionpublic synchronized void startGrabbing()public synchronized void abortGrabbing()public synchronized ColorModel getColorModel()
 Description
Description
It is an other source to modify the images. It has a subclass ImageFilter.
- RGBImageFilter : This modifies the image pixel color and position depending on the existing image by using the method filterRGB().
- CropImageFilter : This filter class will crop an image into an area. It uses the method Graphics.drawImage().
- ReplicateScaleFilter() : This filter will scale the image by removing the rows and columns. It uses the method getScaledInstance().
- AreaAveragingScaleFilter : This filter will increase the quality of the image when compared to the ReplicateScaleFilter by blending the pixels. It overrides the getScaledInstance() method.
 Description
Description
There are two sub classes here.
- FilteredImageSource : It is the combination of ImageFilter & ImageProducer and is used for creation of new images. This filter applies modifications to the created new image.
- MemoryImageSource : Image creation can be done in the memory space.
 Description
Description
These classes help in applying the colors to the pixels. It consists of two sub-classes.
- DirectColorModel : This class depicts the entire color information (green,red,alpha,blue values) in each pixel.
- IndexColorModel : This class prepares a lookup table instead of storing in each pixel.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Production of image in pixels format using colors is known as AWT Image Processing.
- Producer, Consumer and Observer are the interfaces.
- PixelGrabber and FilterClasses are similar.
- ColorModel is applied to observe the images with colors.