Introduction
Introduction
AP VRO 2019, conducted in offline Mode, has a duration of 150 Minutes, a total of 150 questions, a maximum score of 150 marks, and consists of 2 Parts, namely –
- Part – A: General Studies And Mental Ability
- Part – B: Drawing And Survey
 Exam Pattern
Exam Pattern
AP VRO Exam Pattern
| S. No. | Name of the Test | Questions | Maximum Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | General studies and mental ability | 50 | 50 | 50 Minutes |
| 2. | Drawing and survey | 100 | 100 | 100 Minutes |
| Total | 150 | 150 | 150 Minutes | |
Note: for each correct answer 1 mark will be awarded and each wrong answer will carry negative mark.
 Syllabus
Syllabus
For Detailed Syllabus: Click Here
 Samples
Samples
Importance of Lettering and Numbering
1. Which grade of pencil is used for drawing arrowheads?
-
A. 2H
B. 2B
C. 7H
D. H
-
A. Dimension line
B. Extension line
C. Centre line
D. Short-break line
-
A. Construction line
B. Long-break lines
C. Short-break line
D. Irregular line
-
A. Inner line
B. Outline
C. Outer line
D. Boundary line
-
A. Cursive writing
B. Uniformity in letters as obtained in one stroke of the pencil
C. Writing in one stroke without lifting the pencil
D. Writing only with hard, small diameter lead-pencil
Construction of Plain Geometric Figures
1. Which of the following is not a line segment?
-
A. Bamboo
B. Ruler
C. Laser beam
D. Pencil
-
A. Perpendicular
B. 60 degree
C. Half
D. Any ratio
-
A. One side
B. One angle
C. Two side
D. One angle and one side
-
A. A square is a particular case of a rectangle and a rhombus simultaneously.
B. A square is a parallelogram with right angles and equal sides.
C. The diagonals of a square cut at 90 degree
D. A square is a particular case of a rectangle only.
-
A. 37.5
B. 33.75
C. 40
D. 120
Construction of Ordinary Scale
1. When drawings are drawn smaller than the actual size of the objects the scale used is said to be_________
-
A. Enlarging scale
B. Reducing scale
C. Small scale
D. Decreasing scale
-
A. Resulting fraction
B. Representative figure
C. Representative fraction
D. Representative index
-
A. Chords
B. Lines
C. Angles
D. Diameter
-
A. Measuring small angle
B. Measuring large angle
C. Measuring required accurate angle
D. Normal angle
-
A. Plain
B. Comparative
C. Diagonal
D. Vernier
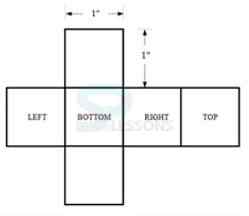
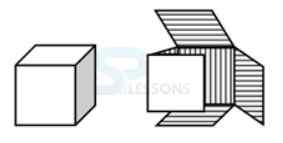
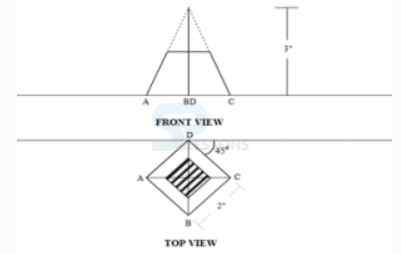
Drawing Plan and Elevation of Points, Lines, Surfaces & Solids.
1. Which among these is not the method of surface development?
-
A. Parallel-line development
B. Radial-line development
C. Triangulation development
D. Geometric development
-
A. Cube
B. Cuboid
C. Triangular prism
D. Cone
-
A. Square
B. Triangle
C. Trapezium
D. Rectangle
-
A. Triangle
B. Square
C. Trapezium
D. Circle
-
A. Square
B. Rectangle
C. Triangle
D. Circle
Conventional Signs and Symbols as per IS Code for Engineering Drawings and Buildings Drawings
1. Identity the below symbol.
-
A. Well
B. Dam
C. Boundary pillar
D. Statue
-
A. Well
B. Dam
C. Boundary pillar
D. Statue
-
A. Well
B. Earthwork dam
C. Boundary pillar
D. Statue
-
A. Well
B. Earthwork dam
C. Boundary pillar
D. Statue
-
A. Temple
B. Church
C. Police station
D. Statue
Drawing and detailing of Brick arrangements – Various types of Bonds
1. In ______ type of bond, all the brakes are arranged in the stretcher courses.
-
A. English bond
B. Header bond
C. Stretcher bond
D. Flemish bond
-
A. Header bond
B. Flemish bond
C. Dutch bond
D. Facing bond
-
A. English bond
B. Raking bond
C. Garden-wall bond
D. Dutch bond
-
A. Stretcher bond
B. Flemish bond
C. Header bond
D. English bond
-
A. English cross bond
B. Facing bond
C. Raking bond
D. Garden-wall bond
Surveying of Buildings Sites with Chain, Field Book Entries – Plotting – Calculation of Areas
1. An offset is a _________ distance of an object measured from the survey line.
-
A. Lateral
B. Horizontal
C. Normal
D. Inclined
-
A. Cross staff
B. Site square
C. Optical staff
D. Prism square
-
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 8
-
A. 500
B. 50
C. 1000
D. 100
-
A. Aligning
B. Extending
C. Ranging
D. Offsetting
Use of Prismatic Compass, Handling of Leveling Instrument
1. In which of the following compass sighting and reading taking can be done simultaneously from one position of the observer?
-
A. Prismatic compass
B. Surveyor’s compass
C. Theodolite
D. Sextant
-
A. Prismatic compass
B. Surveyor’s compass
C. Theodolite
D. Sextant
-
A. Agate cap
B. Prism cap
C. Brake pin
D. Jewel bearing
-
A. Prismatic compass
B. Surveyor’s compass
C. Theodolite
D. Sextant
-
A. Prismatic compass
B. Surveyor’s compass
C. Theodolite
D. Sextant
Other Articles
 Study Guide
Study Guide
| Competitive Exams - Study Guide | ||
|---|---|---|
| Category | ||
| Quantitative Aptitude | Reasoning Ability | General Awareness |
| Computer Awareness | English Knowledge | Banking Awareness |
| General Science | World of Words | Descriptive Test |
 Exams
Exams
| Competitive Exams - Entrance Exams | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Notification | ||
| UG | NSTSE 2020 | RIMC Admission 2020 | WBJEE EVETS 2019 |
| Diploma | HPBOSE D.El.Ed CET 2019 | Goa Diploma Admissions 2019 | |
| PG | GATE 2020 | ATMA 2019 | XAT 2020 |
| Click Here For – All India Entrance Exam Notifications | |||
 Daily CA
Daily CA
 Job-Alerts
Job-Alerts
 SP Quiz
SP Quiz
| Competitive Exams - Practice Sets | |
|---|---|
| Category | Quiz |
| Quant Aptitude | Current Affairs |
| Spotting Errors | |
| Reasoning Ability | Puzzles |
| Insurance Awareness | Insurance Awareness |
 GK
GK
| General Knowledge for Competitive Examinations | |
|---|---|
| Topic | Name of the Article |
| GK - World | First in World |
| Seas and Oceans of the World | |
| GK - India | Anglo Mysore – War |
| River and Glacier system | |
| GK - Abbreviations | Computer Abbreviations |
| Finance Abbreviations | |
| GK - Banking & Insurance | RBI Surplus Transfers |
| Financial Awareness Practice Set 1 | |
| GK - Science & Technology | Energy Transformation Devices |
| IBM IIT Bombay AI Research | |