Description
Description
A
Database is a huge gathering of logical related information which can be created, accessed, managed, and updated. The data can be in any form like text and numbers.
There are many type of data stores, such as files on the file system, where data reading and writing will be very slow. So in the present generation, Relational Database Administration framework is being utilized to store and oversee colossal measure of information.
MySQL is a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) which is an accessible source database. MySQL is authorized under GNU(General Public Licence). It is a multi-client, multi-threaded database administrator framework.
MySQL is extremely well known on the Web. It is one of the parts of LAMP platform. Currently, MySQL is possessed by Oracle. MySQL database is accessible on most vital OS stages.  Description
Description
The following are the steps needs to be performed in this example.
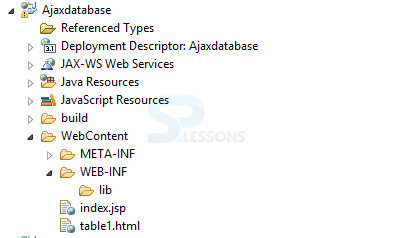
The following is the structure of an application.
table1.html
[html]
<html>
<head>
<script>
var request;
function sendInfo(){
var v = document.vinform.t1.value;
var url = "index.jsp?val=" + v;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
request = new XMLHttpRequest();
} else if (window.ActiveXObject)
{
request = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
try {
request.onreadystatechange = getInfo;
request.open("GET", url, true);
request.send();
} catch (e) {
alert("Unable to connect to server");
}
}
function getInfo() {
if (request.readyState == 4) {
var val = request.responseText;
document.getElementById('amit').innerHTML = val;
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="skyblue">
<h1>Welcome To Splessons</h1>
<form name="vinform">
Enter id:
<input type="text" name="t1" onkeyup="sendInfo()">
</form>
<span id="amit"> </span>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
The following are the properties of XMLHttpRequest object.
index.jsp
[html]
<%@ page import="java.sql.*"%>
<%
String s=request.getParameter("val");
if(s==null || s.trim().equals(""))
{
out.print("Please enter id");
}
else
{
int id=Integer.parseInt(s);
out.print(id);
try
{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/splessons","root","root");
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement("select * from players where id=?");
ps.setInt(1,id);
ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next())
{
out.print(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2));
}
con.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
%>
[/html]
JSP stands for
- Load the org.json.jar file.
- Create input page to get data.
- create server side page.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| onreadystatechange | The onreadystatechange function will be put away and will be called naturally every time readyState property changes |
| responseText | Give back the response data in the form of a string. |
| responseXML | Give back the response data in the form of a XML. |
| readyState | To catch the status of the XMLHttpRequest. 0: request not initialized 1: server connection established 2: request received 3: processing request 4: request finished and response is ready |
| status | To give back the status-number of a request 200: OK 403: Forbidden 404: Not Found |
| statusText | To give back the status-text. |
Java Servlet Pages and is utilized for server-side technology which is an augmentation of Servlet technology that was created by Sun Microsystem. The servlet will get executed on client browser where as JSP will get executed on the server. JSP is utilized to create dynamic web applications like as a Servlet technology, but gives extra functionalities like custom tags, JSTL, expression dialect.
JSP concentrates for the most part of presentation logic of the application. Servlet run quicker than JSP, the fundamental favorable position of JSP is less coding contrasted with servlets.The DriverManager.getConnection() method is used to establish a connection.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.