Introduction
Introduction
A Preposition is a word that is placed before a noun or a pronoun to show the relation between the nearby words in a sentence.
In the following examples, the highlighted word shows the relation between the mouse and the box.
Based on the construction of Preposition them selves:
Sometimes prepositions are also divided on the basis of their own construction. They are:
Some more prepositional phrases are given below.
Participle Preposition:
Preposition acting like a participle are participle preposition. Example: concerning, withstanding, pending, during, assuming, considering.
- The mouse is in the box.
- The mouse is behind the box.
- The mouse in under the box.
- The mouse is in front of the box.
- The mouse is over the box.
- The mouse is on the box.
- The mouse is next to the box.
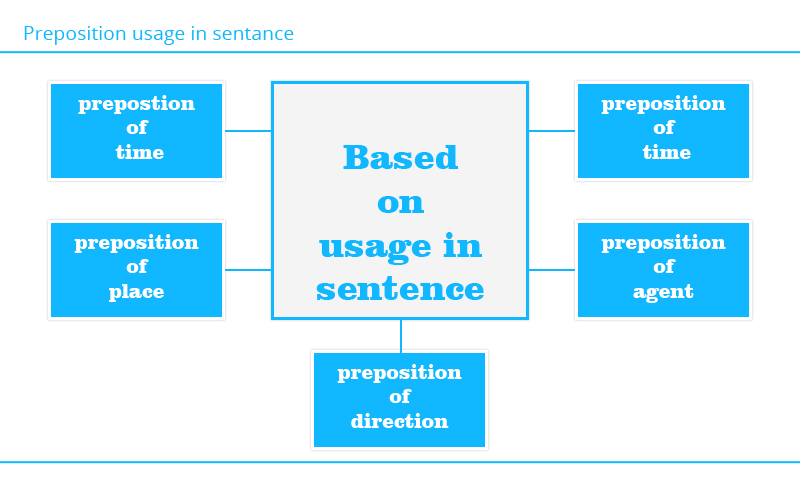
- Prepositions of time
- Prepositions of place
- Prepositions of direction
- Prepositions of agent
- Prepositions of instruments
The prepositions used to refer time in many features are prepositions of time. Example: at, on, in.
| Prepositions | Time reference |
|---|---|
| IN | In April, in 2017, in evening, in the 5th week of April, in spring, in the 21st century |
| ON | On Sunday, on 21st November, on Gandhi Jayanti, |
| AT | At 3 O’ clock, at sunrise, at the moment. |
The prepositions used to refer some place are prepositions of place. Example: on, at, in.
| Prepositions | Place |
|---|---|
| IN | In hall, in dining room, in the box, in the library, in Africa. |
| ON | On the table, on the box, on the wall, on the map, on the roof. |
| AT | At the bus stop, at the entrance, at the bottom of the glass. |
Words which express the direction of something are prepositions of direction. Example: towards, downstairs, through, into.
- The baby crawled through the hallway straight into the kitchen.
- The boy saw the tiger coming towards him.
- The flower vase is kept downstairs.
- The children jumped into the river.
Prepositions used to define a casual relationship between the doer and the action is prepositions of agent. Example: by, with
- A nice song was sung by the school choir.
- The jug is filled with juice.
Prepositions used for joining other words to nouns in the sentence are prepositions of device. Example: on, by, with the help of.
- He went to the office bybus.
- She broke the bricks with a punch.
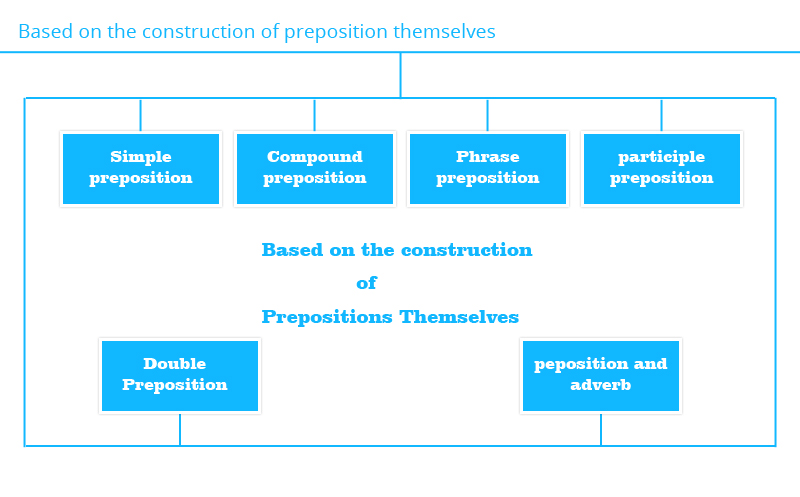
- Simple prepositions
- Compound prepositions
- Phrase prepositions
- Participle prepositions
- Double prepositions
- Prepositions and adverb
Simple prepositions are used in simple sentences. For example:
- Radha sat on the bed.
- He fell off the ladder.
- The dog was hiding under the table.
Prepositions which are used to join two nouns, pronouns or phrases are called compound prepositions. For example: about, among, before, beside, inside, between, behind, around, beneath.
- The river was flowing between the mountains.
- The book was kept beside the telephone on the table.
- The enquired about the admission criteria in the college.
Prepositions indicating the relationships among various elements in the sentence are phrase prepositions. Example: because of, in reference to, instead of.
- She is crying because of her brother.
- I am giving this information on behalf of the teachers.
- Rohit works hard in order to get good marks.
- I get sick during the winter season.
- His holiday homework is still pending.
- Assuming the professor to be absent, the students left the class.
- Suddenly he emerged from beneath the bed.
- The shadow appeared from behind the curtain.
- Solve two out of the four questions.
- He sat in the armchair. (In is the preposition and armchair is the subject) Please come in. (In is used as an adverb and there is no subject)
- He stood before his parent. (Before is the preposition and parents are the object) I have never seen him before. (Before is the adverb and there is no subject)
- He will return after a month. (after is the preposition and month is the object) He came soon after. (After is the adverb and there is no subject)
| Letter | Prepositions |
|---|---|
| A | about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at |
| B | before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, but, by |
| C | concerning |
| D | despite, down, during |
| E | except |
| F | for, from |
| I | in, inside, into |
| L | like |
| O | of, off, on, onto, out, outside, over |
| P | past |
| S | since |
| T | through, throughout, toward, to |
| U | under, until, up, upon, underneath |
| W | with, within, without |
 Rules
Rules
Grammar Rules While Using Prepositions:
Rule 1. A preposition does not have to come before its noun or pronoun. One of the never dying rules of English grammar is that a sentence can never end with a preposition. This is wrong. A sentence can end with a preposition if the meaning of the sentence is clear.
- That is something I will never agree with.
- How many of you can he depend on?
 Tips
Tips
Tips for Using Prepositions
- It is alright to end a sentence with a preposition.
- A noun always comes after preposition.
- A verb never comes after a preposition.
- It is alright to begin a sentence with a prepositional phrase, or a preposition, but be careful when you do so.
- A prepositional phrase will always begin with a preposition but will always end with an object of the preposition, i.e. a noun or a pronoun.
- The subject will never be considered a part of the prepositional phrase.
- A verb too cannot be a part of prepositional phrase.