Introduction
Introduction
What is Quantitative Aptitude test?
Quantitative Aptitude is one of the prominent competitive aptitude subjects which evaluates numerical ability and problem solving skills of candidates. This test forms the major part of a number of important entrance and recruitment exams for different fields. The Quantitative Aptitude section primarily has questions related to the Simplification, Numbering Series, and Compound Interest, etc.
A candidate with quantitative aptitude knowledge will be in a better position to analyse and make sense of the given data. Quantitative Aptitude knowledge is an important measure for a prospective business executive's abilities.
The article IBPS SO Quantitative Aptitude Quiz 2 provides Quantitative Aptitude questions with answers useful to the candidates preparing for Competitive exams, Entrance exams, Interviews etc. The article IBPS SO Quantitative Aptitude Quiz 2 will assist the students to know the expected questions from Quantitative Aptitude.
 Quiz
Quiz
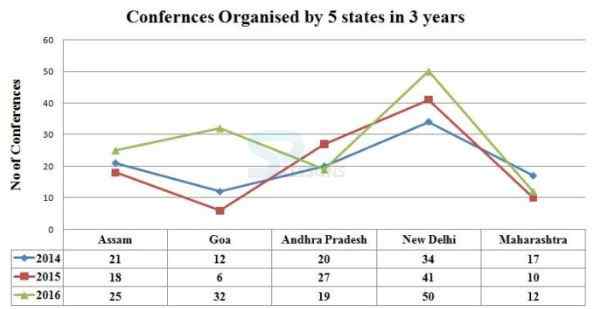
Directions(1 – 5): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
1. How many conferences totally organised by five states in the year 2014 and 2015?
- A. 197
B. 243
C. 312
D. 206
- A. 2014, 2015, 2016
B. 2016, 2014, 2015
C. 2016, 2015, 2014
D. 2014, 2016, 2015
- A. 126%
B. 156%
C. 176%
D. 167%
- A. 22
B. 18
C. 20
D. 32
- A. 35
B. 29
C. 33
D. 27
1. The ratio of Ekta’s and Reema’s income last year was 10: 3. The ratio of Ekta’s this year income and last year income is 6: 5 and the ratio of Reema’s this year income and last year income is 2: 3. If the sum of Ekta’s and Reema’s present incomes is Rs. 5124, what was Reema’s income last year?
- A. 1830
B. 1370
C. 1372
D. 1098
- A. 4 months
B. 3 months
C. 6 months
D. 8 months
- A. 80
B. 20
C. 70
D. 50
- A. 396
B. 456
C. 486
D. 482
- A. 56236
B. 96336
C. 85236
D. 76236
Direction(1-3): What approximate value should come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question (Note: You are not expected to calculate the exact value)?
1. [latex]{(14.999)}^{2} - \sqrt[4] {1300} + \sqrt {99} = [/latex]?
- A. 250
B. 229
C. 270
D. 255
- A. 120
B. 90
C. 80
D. 140
- A. 45
B. 200
C. 4050
D. 10500
- A. 58
B. 33
C. 107
D. 186
- A. 26
B. 56
C. 276
D. 1008