Introduction
Introduction
A computer network is a group of two or more computers connected together to share information and resources. A computer network permits sharing of resources among devices communicated in the network.
ARPANET is the first network developed by Robert Kahn and Vinton Cart in 1969.
 Concepts
Concepts
Benefits of Network
Nowadays, a computer network is very useful for communication all over the world.
Connection method
A computer network can be classified based on the software and hardware technologies used for communicating computer systems.
Local Area Network
LAN is a network, in which computers are interconnected within a small geographical area such as home, office buildings, and schools.
- Facilitating communication: By using the network, people can communicate easily at anywhere throughout the world. Example: E-mail, Facebook, Video telephone calls and chat rooms.
- Sharing hardware: In the network, users can access and use hardware components like printers, hard drives, and CD-ROM drives. If a printer is connected to the network, then every user can access the printer.
- Sharing software: By using the network, each user can access applications.
- Sharing files: In the network, any user can access the data or information and can be shared with other users. It can share the storage files and information.
- Connection method
- Wired technologies
- Wireless technologies
- Ethernet is a physical and data link layer of LAN network. It can explain how the data is transmitted to other network devices on the same network.
- Ethernet is using wiring technology to communicate with computers. It includes hubs, switches, bridges and routers.
- Twisted wires are mainly used to reduce cross-talk and electromagnetic induction.
- Transmission speed range is 2-100 million bits per second.
- Transmission speed range is 200-500 million bits per second.
- Fiber-optic cables cannot be affected by electromagnetic radiation.
- Transmission speed is trillions of bits per second. Transmission speed is hundred times faster than coaxial and thousand times faster than twisted pair wire.
- Terrestrial Microwaves are utilizing earth-based transmitter and receiver with low gigahertz range. Microwave antennas are placed on the top of buildings, towers, and hills. These are stationed in space at 30 miles.
- Communications Satellites have the capability of receiving and relaying voice, data and TV signals. These are stationed in space at 22,000 miles above the equator.
- Cellular and PCS Systems are used in radio communication technologies. It relays the calls from one area to the next area with a low power transmitter.
- Wireless LANs are used to allow communication between multiple devices in a limited area by using spread spectrum technology. Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol used for data transfer over a short distance.
- Local Area Network
- Wide Area Network
- Metropolitan Area Network.
- LAN is a single-site network and works based on the Ethernet technology. In this network, each computer is called as a node. LAN can use client & server architecture and peer-to-peer architecture.
- All the terminals are communicated with the main computer, which is known as the server. Data transfer range is 10-100 megabits per second. LAN is owned by single organization or person.
- Wireless LAN works on radio waves and gives the network connection to all users in the surrounding area.
- Wi-Fi stands for Wireless - Fidelity and is used for providing wireless internet access and implements WLANs by using radio waves.
- A WAN is connected to LAN through a network device called as the router. It is connected by using telephone wires, satellite links, and other long-range communication technologies.
- A WAN is not owned by a single organization but exists under collective or distributed ownership. It works on physical, data link layer and network layer.
- MAN is mainly used for sharing hardware and software resources among various users.
- This network uses coaxial cables or optical fiber cables and also uses the hub, routers, and switches.
- The other types of networks are
- PAN: PAN stands for Personal Area Network. It is a small communication network and establishes communication between various technological devices. PAN is connected within 10 meters and is created by using USB and Bluetooth.
- VPN: VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It is a global internet used for Intra and inter-organization. VPN is a private, but virtual network is used to divide traffic of various user communities under network with strong security features.
- Intranet and Extranet: These are the extensions of a computer network. An intranet is a group of networks connected by using Internet protocol and IP tools. A large intranet should have one or more web servers to provide information to the user. An extranet has limited connections to the network and does not include single LAN network.
- Network interface card: It is a part of computer hardware component used to access computers and to connect with a network. It can provide low-level addressing system through the use of MAC address. Sometimes these acts like Ethernet cards.
- Repeaters: A repeater is an electronic device that consists of two ports and two segments to connect to LAN. Repeaters are required for cable in twisted wire Ethernet configuration. Repeaters can operate on the physical layer.
- Hub: It is similar to Repeater, but consists of multiple ports to connect to the network. It works on the physical layer. Hub receives a packet data from one network channel and transmits to the other network channels. It acts as the main connection for various computers and server in a network.
- Switch: It is small hardware component used to forward and filter data link layer data grams based on MAC address. These are mainly used for forwarding decisions of frames. Switches that have the capability of routing additional layers are called as multi-layer switches.
- Bridges: A Bridge is used to establish communication between multiple networks at the data link layer of OSI model. If a bridge is connected to a port and address, it will send traffic for that particular address only.
- Local bridge is directly communicated with local area networks.
- Remote bridges can be used to implement a wide area network.
- Wireless bridges can be used to connect remote stations to Local Area Networks.
- Routers: A router is a hardware device, which can move the packets from one network to other networks using information in protocol headers.
- Narrow band uses the narrow set of frequency in the communication channel. It is more narrow than broadband and is easy to focus on particular technological solutions. The frequency range of narrow band is 300-340 Hz.
- The range of ultra frequency band of the electromagnetic spectrum is 300-3000 Hz. A single voice- frequency transmission channel can allocate 4kHz bandwidth. 8 kHz frequency is used for the digital PSTN on the basis of the pulse code modulation.
- Telephone wires transmit the data in analog form. A sound is directly converted into electrical signal but results in analog signals. A telephone wire is connected to the modem to convert analog signals into digital signals.
- These frequencies can be divided into channels. A television antenna has the capability of receiving a wide range of frequencies. In data communication, a digital modem will transmit 56 kilobits per second.
- Broadband is used to increase the effective rate of data transmission. Broadband in analog video distribution is used to refer to individual channels that are modulated at fixed frequencies.
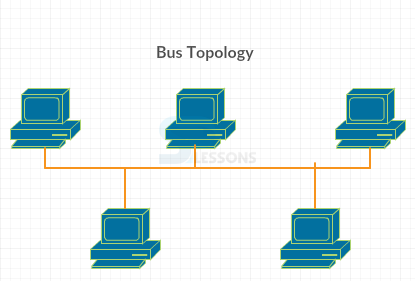
- All the nodes are directly connected to each other, so it requires very short length cable.
- The architecture is very simple and can be easily extended to other sides.
- The bus topology requires less number of cables and the cables are less expensive.
- It is difficult to find the problem in communication.
- Flat isolation is difficult in data transmission and it becomes slow while increasing nodes in the network.
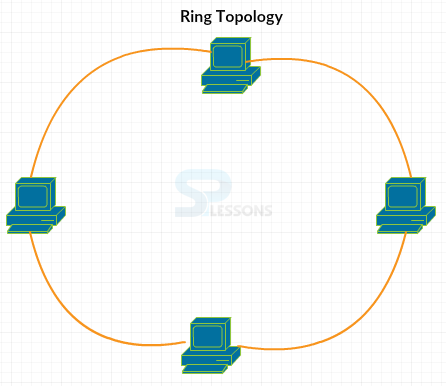
- Ring topology is implemented as Token ring and Fiber distributed data interface by using protocols.
- This data is transmitted in the form of token ring. The nodes are connected in a circular way.
- In ring topology, nodes are connected in a circular way, if any transmission problem occurs, then the entire network will stop functioning.
- In this, fault diagnosis is difficult and every node must connect with two other nodes. If the ring is broken, then that particular node cannot work.
- If any computer fails, then that affects the entire network. The network gets disturbed while adding and removing nodes in the network.
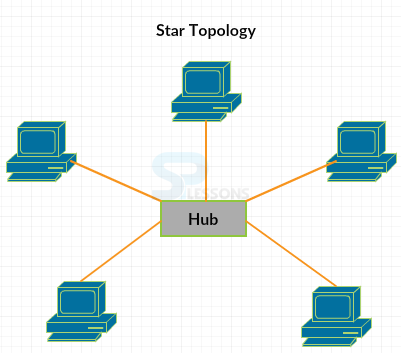
- All the nodes are directly connected to the central node.
- Installation of this topology is very easy and the faults can be found easily.
- If a node fails, then it will not affect the other systems.
- It requires cable length and if the hub fails, the entire network will be disabled.
- It is difficult to expand.
 Questions
Questions
1. The structure or format of data is called_________.
- Syntax
- Semantics
- Structure
- None of the above
- Automatic
- Half-duplex
- DFull-duplex
- Simplex
- The first network
- CNNET
- ASAPNET
- ARPANET
- Path
- Medium
- Protocol
- Route
- Unipoint
- Multipoint
- Point to point
- None of the above
- Server
- Client
- Mainframe
- All of the above
- Bus
- Star
- Memory
- All of the above
- Server
- star
- Ring
- CPU
- International Standard Organization
- International Student Organization
- Integrated Services Organization
- Internet Standard Oriented
- Application
- Network
- Physical
- All of the above
- Circuited switched
- Packet switched
- Network switched
- None of the above
- Communication server
- Print server
- File server
- Network
- Queue
- Spool
- Node
- Diode
- LAN intrinsic software
- Lan aware software
- Groupware
- All of the above
- Configuration management
- security management
- performance Management
- None of the above
- 100 ft
- 200 ft
- 100 mt
- 200 mt
- 100 mbps
- 10 mbps
- 1000 mbps
- 1000 mbps
- BNC
- RJ-11
- RJ-45
- RJ-69
- STP Server
- SHUB/ switch
- PDC
- Router
- bus
- star
- ring
- mesh
- WAN
- MAN
- LAN
- PAN
- bridge
- router
- repeater
- gateway
- PAN
- MAN
- LAN
- RAM
- bus
- star
- ring
- mesh